Известия РАН. Серия биологическая, 2023, № 5, стр. 451-462
Разнообразие генов главного комплекса гистосовместимости класса I у дальневосточного леопарда (Panthera pardus orientalis)
К. К. Тарасян 1, *, П. А. Сорокин 1, М. В. Холодова 1, С. В. Найденко 1, В. В. Рожнов 1
1 Институт проблем экологии и эволюции им. А.Н. Северцова Российской академии наук
119071 Москва, Ленинский проспект, 33, Россия
* E-mail: tarasyan_k@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 22.04.2023
После доработки 02.05.2023
Принята к публикации 02.05.2023
- EDN: WMGZLT
- DOI: 10.31857/S1026347023600413
Аннотация
Исследовано состояние генов главного комплекса гистосовместимости (ГКГ) класса I у дальневосточного леопарда (Panthera pardus orientalis). Из 11 образцов тканей дальневосточного леопарда получены 20 аллелей генов ГКГ, 19 из них описаны для леопарда впервые. Показано высокое разнообразие аллелей как на уровне отдельных особей, так и на уровне популяции. Сравнительный анализ полиморфизма исследуемых генов у разных подвидов леопарда показал, что генетическое разнообразие дальневосточного подвида не уступает, а возможно и превышает таковое у африканского и индийского подвидов. Высокое аллельное разнообразие исследуемых генов дальневосточного леопарда поддержано действием балансирующего отбора, действующего на антиген-связывающий регион кодируемого ими белкового продукта. Сделан вывод о том, что низкая численность дальневосточного леопарда к настоящему времени не привела к непоправимым потерям генетического потенциала популяции.
Дальневосточный леопард (Panthera pardus orientalis) населяет крайнюю северо-восточную часть видового ареала – юго-западное Приморье на российском Дальнем Востоке и северо-восточную часть Китая вдоль границы с Россией в провинциях Цзилинь и Хейлунцзян. Его популяция крайне малочисленна, всего около 110 особей (Виткалова и др., 2022). Дальневосточный леопард занесен Красную книгу Российской Федерации (Найденко и др., 2021), а также в Красный список МСОП как подвид, находящийся под угрозой исчезновения.
Малый размер популяции леопарда может привести к уменьшению генетического разнообразия, а, следовательно – к снижению эффективности размножения, уменьшению адаптационных возможностей особей и повышению их чувствительности к патогенам, в том числе привносимым со стороны домашних животных (Parmar et al., 2017). По имеющимся данным литературы на основании анализа мтДНК и микросаттеллитов дальневосточный леопард обладает крайне низким генетическим разнообразием по сравнению с другими подвидами леопарда (Uphyrkina et al., 2001; Uphyrkina, O’Brien, 2003; Рожнов и др., 2013).
В данной работе мы оценили генетическое разнообразие дальневосточного леопарда на основании функционально значимых ядерных генов главного комплекса гистосовместимости (ГКГ) I класса. Богатство аллельных вариантов генов ГКГ, присутствующих в популяции, принято ассоциировать с адаптированностью к широкому спектру патогенов, а также с увеличением эффективности размножения (Brouwer et al., 2010; Burger et al., 2017; Manlik et al., 2019). Обеднение аллельного разнообразия генов ГКГ в популяции, напротив, может привести к повышению чувствительности животных к патогенам (Siddle et al., 2007), пониженной жизнеспособности рождающегося потомства и, как следствие, к продолжению падения численности популяции даже в условиях восстановления среды обитания и обилия кормовых объектов, как это было отмечено для командорских песцов, тасманийского дьявола и других млекопитающих (Siddle et al., 2007; Bahr, Wilson, 2012; Ploshnitsa et al., 2012).
В геноме кошачьих гены ГКГ расположены на хромосоме В2, их организация и роль в формировании иммунного ответа подробно рассмотрены в литературе (Yuhki et al., 2007, 2008; Тарасян и др., 2014). Для генов данного комплекса характерна высокая полигенность и высокий полиморфизм. Чаще всего для анализа аллельного разнообразия в ГКГ I класса используют последовательность экзона 2. Он кодирует последовательность антиген-связывающего региона. Этот участок высоко изменчив и играет определяющую роль в функционировании белка в целом.
Целью настоящей работы был анализ генетического разнообразия и полиморфизма генов ГКГ класса I у дальневосточного подвида леопарда в сравнении с более широко распространенными и многочисленными подвидами леопарда (Kitchener et al., 2017): африканским (P. p. pardus) и индийским (P. p. fusca).
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ
Мы исследовали образцы 11 дальневосточных леопардов, индивидуально идентифицированных ранее на основании анализа микросателлитных последовательностей (Рожнов и др., 2013). Все исследованные животные жили в естественной среде обитания, степень родства между ними известна только для двух особей (fem и emb являются образцами погибшей самки и ее эмбриона, см. табл. 1). Образцы крови и тканей получали в ходе ветеринарного обследования живых леопардов, а также от животных, погибших в результате несчастных случаев. В табл. 1 приведены сведения об исследуемых животных, месте сбора образца и его типе (кровь, мышцы или экскременты).
Таблица 1.
Описание образцов леопарда, используемых в работе
| Образец | Пол животного | Тип пробы | Дата сбора | Место сбора |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1m | Самец | Кровь | 13.08.2011 | Бассейн рек Барабашевка и Амба, Национальный парк “Земля леопарда”, Хасанский р-н, Приморский край |
| 2m | Самец | Кровь | 14.08.2011 | Там же |
| 3m | Самец | Кровь | 04.09.2011 | Там же |
| 4f | Самка | Кровь | 08.09.2011 | Там же |
| 5f | Самка | Кровь | 23.09.2011 | Там же |
| 6f | Самка | Кровь | 06.10.2011 | Там же |
| fem | Самка | Мышцы | 15.02.2009 | Приморская сельскохозяйственная академия, Уссурийск |
| emb | Самка | Мышцы | 15.02.2009 | Там же |
| 8m | Самец | Кровь | 04.06.2015 | Хасанский р-н, Приморский край |
| 1a | Самец | Экскременты | 17.02.2010 | Бассейн рек Нежинка и Ананьевка, Национальный парк “Земля леопарда”, Хасанский р-н, Приморский край |
| 8a | Самец | Экскременты | 02.09.2010 | Там же |
ДНК из образцов тканей и крови выделяли набором DNAeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Германия), а из экскрементов – набором QIAamp stool mini kit (Qiagen, США) согласно инструкциям производителя. Для каждого леопарда мы проводили от 2 до 4 независимых амплификаций. Для проведения ПЦР использовали праймеры Acju_Ex2MhcI_cF и Papa_Ex2MhcI_kR (Liu et al., 2005), позволяющие амплифицировать последовательность второго экзона генов ГКГ класса I (ожидаемая длина 229 пар нуклеотидов), соответствующую антиген-связывающему региону (Yuhki, O’Brien, 1990; Castro-Prieto et al., 2011).
Амплификация проходила в конечном объеме 20 мкл, содержащем 10 мкмоль dNTPs, 10 пмоль каждого праймера, 1 е.а. Taq-полимеразы (ООО “СибЭнзайм”, Россия) и 1 е.а. Pfu-полимеразы (ООО “СибЭнзайм”, Россия). Программа амплификации: первичная денатурация при 95°С – 3 мин, 30 циклов (95°С – 30 с, 60°С – 30 с, 72°С – 45 с) и элонгация при 72°С – 5 мин.
Для каждого леопарда мы проводили от 2 до 4 независимых амплификаций. Каждый полученный продукт лигировали в плазмидный вектор, которым далее трансформировали клетки E. coli JM109. Для проведения всей процедуры клонирования использовали готовый набор p-Gem T Easy Vector System II (Promega, США). После выращивания отдельных колоний плазмиды со вставками подходящих размеров выделяли набором реактивов Plasmid Miniprep (Евроген, Россия). Вставку в плазмиде секвенировали на автоматическом генетическом анализаторе ABI 3130 (Applied Biosystems, США) с набором BigDye Terminator kit v. 3.1 (Applied Biosystems, США) с использованием праймеров m13F(-20): 5'-GTAAAACGACGGCCAGTG-3' и m13R(-48): 5'-AGCGGATAACAATTTCACAC-3'. Количество плазмид, секвенированных для каждого леопарда, варьировало от 14 до 32 (в среднем 24) для каждой реакции амплификации. В связи с неизбежным получением артефактных последовательностей, связанным с особенностями используемых методов (Sommer et al., 2013), мы применили процедуру верификации аллелей, предложенную в большинстве публикаций (Kennedy et al., 2003). Истинным аллелем мы считали последовательность, полученную минимум в двух ПЦР от одного животного. Работа проводилась в ЦКП “Инструментальные методы в экологии” при ИПЭЭ РАН.
Выравнивание последовательностей произвели в программе Bioedit v.7.0.5.3 (Hall, 1999).
Определение вариабельных позиций в нуклеотидных и аминокислотных последовательностях производили в среде R, для работы с последовательностями использовали пакет “Ape” v.5.6-2 (Paradis E., et al., 2004). Для оценки нуклеотидного и аминокислотного разнообразия внутри и между подвидами были использованы генетические дистанции между нуклеотидными и аминокислотными последовательностями, соответственно. Расчеты генетических дистанций осуществили путем подсчета количества различий между аллелями в ходе попарных сравнений (pairwise distances). Стандартное отклонение (SE) при расчете дистанций внутри и между группами рассчитывали на основе проведения бутстреп-анализа (1000 реплик).
Оценку нормальности распределений, необходимую для выбора адекватных статистических критериев, проводили методом Шапиро–Уилка (Shapiro–Wilk normality test), входящего в базовый пакет R.
Оценку статистической достоверности разницы между подвидовыми выборками генетических дистанций проводили с помощью теста Краскела–Уоллиса (Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance), предназначенного для проверки гипотезы о равенстве медиан нескольких выборок. Данный метод является ранговым и предназначен для анализа выборок, не отвечающих критериям нормального распределения. Попарные сравнения выборок проводили методом Манна–Уитни (Mann–Whitney U test) – непараметрического критерия, предназначенного для оценки различий между двумя независимыми выборками. Оценку статистической достоверности разницы средних генетических дистанций между подвидами оценивали методом χ2.
Расчет филогенетической сети аллелей был произведен методом median-joining в программе Network4 (Bandelt H.-J. et al., 1999).
Для поиска признаков действия естественного отбора мы использовали комбинированный подход. В качестве первого подхода для анализа всех последовательностей был применен Z-тест на наличие отбора (Codon-based Z-test of selection), реализованный в MegaX (Kumar et al., 2018). Он сравнивает относительное количество синонимичных (dS) и несинонимичных (dN) замен в последовательностях в попарном сравнении последовательностей в выборке, усредняет эти значения и дает оценку вероятности отклонения от H0-гипотезы об отсутствии действия естественного отбора, а также вероятности балансирующего или очищающего отбора (в зависимости от выбранной альтернативной гипотезы H1). Для расчетов использовали модифицированный метод Нея–Гойобори (Nei–Gojobori) с поправкой по Джуксу–Кантору (Jukes–Cantor), поскольку в этом случае рассматривается возможность разной частоты для транзиций и трансверсий и вносится поправка на возможные множественные замены в одном локусе.
Для выделения кодонов, предположительно участвующих в связывании антигена, мы опирались на данные литературы. В работе Кастро–Приэто с соавторами (Castro–Prieto et al., 2011) указаны 17 кодонов, предположительно участвующих в связывании антигена. Наши последовательности были получены с тех же праймеров, совпадали по размеру и выравнивались на последовательности африканского леопарда без разрывов (gaps). Поэтому для поиска признаков действия естественного отбора мы использовали те же 17 кодонов (№№ 2, 15, 17, 19, 38, 51, 52, 55, 56, 59, 60, 63, 66, 67, 70, 73, 74).
В качестве второго подхода по поиску признаков действия естественного отбора (positive selection) были использованы программы codeml из пакета PAML4.9 (Yang, 2007; Xu, Yang, 2013), а также методами FEL и MEME, являющимися частью пакета программ HyPhy и реализованными на платформе www.datamonkey.org.
Для трактовки результатов расчетов codeml сравнивали модели максимального правдоподобия, предполагающие отсутствие действия отбора (М1, М7), и модели, предполагающие его наличие (М2, М8). Для оценки, какая из моделей лучше описывает наши данные, был использован тест отношения правдоподобия (LRT), в котором иерархически вложенные модели тестируются на значимость улучшения соответствия модели конкретному набору данных. С помощью этого теста были проверены пары моделей M1vsM2 и M7vsM8. Если сравнение моделей показывало, что модели М2 и М8 лучше соответствовали нашим данным, мы рассматривали кодоны, находящиеся под действием естественного отбора. Согласно рекомендациям авторов программного обеспечения, мы ограничивались кодонами, предлагаемыми результатом BEB (Bayes Empirical Bayes method).
Для построения необходимой для расчетов в codeml филогении подбор модели нуклеотидных замен и получение соответствующего филогенетического дерева проводили в программе jModelTest2 (Darriba et al., 2012), опираясь на критерии BIC и AICc.
Поскольку результаты codeml сильно зависят от филогенетических деревьев, положенных в основу его расчетов, дополнительно мы применили методы FEL и MEME, реализующие поиск кодонов, находящихся под действием постоянного или эпизодического балансирующего отбора. Для исключения ложноположительных результатов в качестве дополнительного шага мы выполнили поиск точек возможной рекомбинации в исследуемых последовательностях методом GARD (Kosakovsky Pond et al., 2006), также представленным на платформе www.datamonkey.org.
Для сравнения дальневосточного леопарда с другими подвидами мы использовали последовательности аллелей ГКГ класса I африканского (GenBank HQ318105, HQ318106, HQ318107, HQ318108, HQ318109, HQ318110), опубликованные в статье Кастро-Приэто с соавторами (Castro-Prieto et al., 2011) и индийского подвидов (GenBank KT781695, KT781696, KT781701, KT781702, KT781708, KT781729, KT781740, KT781750, KT781756), опубликованные в статье Пармар с соавторами (Parmar et al., 2017).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Из образцов 11 животных мы идентифицировали 21 аллель генов ГКГ класса I, из которых 19 были впервые нами описаны. Номера последовательностей аллелей, депонированных нами в Генбанке, приведены в табл. 2. В генотипе каждого животного было обнаружено от 3 до 7 аллелей генов класса I (в среднем 4.9 ± 1.4 аллеля/особь). Последовательность одного обнаруженного нами аллеля ГКГ I дальневосточного леопарда (GenBank: KT906236) совпадает с последовательностью аллеля индокитайского тигра, P. tigris corbetti (GenBank: OQ473885), а также последовательностью того же гена бенгальского тигра, P. t. tigris – GenBank: HQ157994 и MT258444.
Таблица 2.
Распределение аллелей ГКГ I в выборке
| № Генбанка | Животные | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1m | 2m | 3m | 4f | 5f | 6f | fem | emb | 8m | 1a | 8a | |
| KT906232 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| KT906233 | + | + | + | ||||||||
| KT906234 | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| KT906235 | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| KT906236 | + | ||||||||||
| KT906237 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| KT906238 | + | + | |||||||||
| KT906239 | + | ||||||||||
| KT906240 | + | + | |||||||||
| KT906241 | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| KT906243 | + | + | |||||||||
| KT906244 | + | + | |||||||||
| KY679822 | + | ||||||||||
| KY679823 | + | + | + | ||||||||
| KY679824 | + | ||||||||||
| KY679825 | + | + | |||||||||
| KY679826 | + | + | |||||||||
| MN879769 | + | ||||||||||
| MN879770 | + | ||||||||||
| MN879771 | + | ||||||||||
| OQ871582 | + | + | |||||||||
У двух из изученных нами леопардов (особи 2m и 5f) мы обнаружили семь аллелей генов ГКГ I класса. Все аллели были подтверждены путем повторного получения в независимой ПЦР, а также не несли стоп-кодонов, делеций или вставок в функциональной рамке считывания.
Изменчивость генов ГКГ класса I. Выделенные нами последовательности ГКГ класса I высокоизменчивы: 93 (40.6%) нуклеотидных последовательностей являются вариабельными, из них 70 – парсимониально информативны. В последовательностях аминокислот вариабельной является 41 позиция (табл. 3).
Таблица 3.
Изменчивость генов ГКГ класса I у дальневосточного, африканского и индийского леопардов
| Подвиды | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| P. p. orientalis | P. p. pardus | P. p. fusca | |
| Кол-во исследованных особей | 11* | 25** | 13*** |
| Кол-во найденных аллелей | 21 | 6 | 9 |
| Среднее число аллелей на особь | 4.9 | 4.0 | – |
| Число аллелей на особь | 3–7 | 2–6 | 1–3 |
| Кол-во вариабельных позиций в нуклеотидной последовательности (процент от общего числа позиций) | 93 (40.6%) |
46 (20.1%) |
38 (16.6%) |
| Кол-во вариабельных позиций в аминокислотной последовательности (процент от общего числа позиций) | 41 (53.9%) |
26 (34.2%) |
23 (10.0%) |
Мы сравнили нуклеотидное и аминокислотное разнообразие ГКГ класса I, характеризующее каждый подвид леопарда (см. табл. 4). Поскольку распределения значений генетических дистанций внутри каждого подвида не соответствуют нормальному распределению, в таблице приведены не только средние значения, но и медианы выборок, соответствующих каждому подвиду.
Таблица 4.
Нуклеотидное и аминокислотное разнообразие гена ГКГ класса I у трех подвидов леопарда, оцениваемое по количеству различий между последовательностями в попарных сравнениях
| Подвид | Нуклеотидное разнообразие | Аминокислотное разнообразие | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Среднее | SE | Медиана | Среднее | SE | Медиана | |
| P. p. orientalis | 29.03 | 2.74 | 28 | 16.89 | 2.19 | 18 |
| P. p. pardus | 19.73 | 2.62 | 19 | 12.67 | 2.20 | 12 |
| P. p. fusca | 14.00 | 2.19 | 16 | 8.83 | 1.75 | 10 |
Различия между подвидовыми выборками статистически достоверны как для нуклеотидных, так и для аминокислотных последовательностей: для нуклеотидных тест Краскела–Уоллиса показал χ2 = 50.62, df = 2, p < 0.001; для аминокислотных последовательностей тест Краскела–Уоллиса – χ2 = 51.27, df = 2, p < 0.001. Такие результаты свидетельствуют о том, что, по крайней мере одна выборка сильно отличается от другой, поэтому мы провели серию попарных сравнений подвидовых выборок с помощью критерия Манна–Уитни. Различия между всеми подвидами леопарда как на нуклеотидном, так и на аминокислотном уровне были статистически достоверны (табл. 5).
Значения генетических дистанций между подвидами леопарда, оцененных на основании количества различий между известными нуклеотидными и аминокислотными последовательностями ГКГ класса I, приведены в табл. 6. Согласно полученным данным, как по нуклеотидным, так и по аминокислотным дистанциям подвиды практически равноудалены друг от друга, причем индийский и дальневосточный леопарды отличаются друг от друга сильнее, чем по отдельности каждый из этих подвидов от африканского. Различия генетических дистанций между парами подвидов статистически не значимы (для нуклеотидных дистанций χ2 = 1.006, df = 2, p = 0.60; для аминокислотных – χ2 = 0.433, df = 2, p = 0.81).
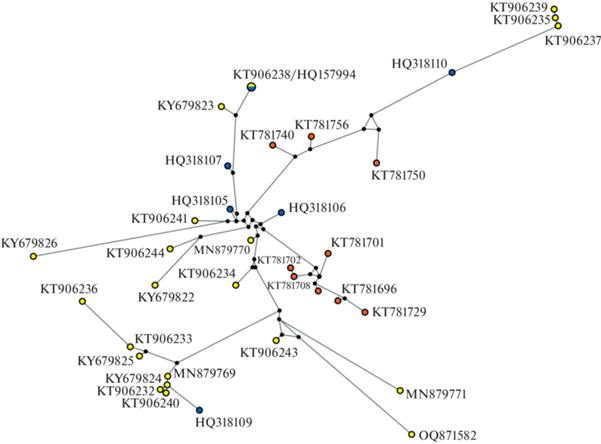
Для оценки филогенетических отношений между последовательностями аллелей генов ГКГ I леопардов разных подвидов мы построили сеть методом median-joining (рис. 1). Интересно отметить, что большинство аллелей, известных для индийского леопарда, сгруппированы на отдельной ветви сети. Кроме того, аллели африканского леопарда занимают более центральное расположение на сети по отношению к аллелям дальневосточного леопарда.
Рис. 1.
Медианная сеть нуклеотидных последовательностей аллелей гена ГКГ класса I, известных для дальневосточного (желтый), африканского (синий) и индийского (красный) подвидов леопарда. Черными кругами обозначены узловые гипотетические аллели. Длина ветвей отражает количество мутаций, необходимых для перехода между аллелями.
Естественный отбор. Z тест на нейтральность отбора (MegaX) целых последовательностей как для дальневосточного, так и для остальных подвидов леопарда не показал статистически значимого отклонения от гипотезы об отсутствии влияния отбора. Поэтому мы решили проанализировать отдельно кодоны, предположительно участвующие в связывании антигена. В этом случае при анализе антиген-связывающих кодонов в выборке, включающей все последовательности всех подвидов, мы увидели статистически значимое отклонение в пользу гипотезы о действии балансирующего отбора (dN-dS = 2.05, p = 0.02). Если анализировать антиген-связывающие кодоны у каждого подвида отдельно, то становится заметно сильное отличие между подвидами: у дальневосточного леопарда гипотеза о действии балансирующего отбора получает статистическую значимость (dN-dS = 2.58, p = 0.01). У африканского подвида количество несинонимичных замен превышает количество синонимичных, но эти отличия не имеют статистической достоверности, поэтому можно говорить только о тенденции к балансирующему отбору среди антиген-связывающих кодонов (dN-dS = 1.36, p = 0.09). У индийского подвида вообще нет оснований говорить о действии отбора на эти кодоны (dN-dS = 0.32, p = 0.37).
Для остальных кодонов Z тест не показал признаков действия какого-либо типа отбора (dN-dS = = –1.02, p = 0.31), вне зависимости от того, рассматривали мы все подвиды вместе или по отдельности.
Анализ действия отбора на отдельные кодоны был проведен с помощью двух разных подходов: сodeml из пакета программ PAML 4.9 (Yang, 2007; Xu, Yang, 2013) и методами FEL и MEME. Для методов FEL и MEME был дополнительно выполнен поиск точек возможной рекомбинации. В табл. 7 представлены результаты работы разных алгоритмов для каждого подвида отдельно и для всех леопардов в целом.
Таблица 7.
Кодоны, находящиеся под действием балансирующего отбора, по версии разных алгоритмов поиска
| Подвид леопарда | Codeml | До разбиения по сайту возможной рекомбинации | После разбиения по сайту возможной рекомбинации | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| р > 0.5 | р > 0.95 | FEL | MEME | FEL | MEME | |
| P. p. orientalis | 2, 4, 5, 10, 17, 38, 45, 48, 55, 56, 59, 60, 63, 66, 67, 70, 72, 74 | 2, 10, 17, 38, 55, 56, 59, 60 | 55 | 17, 55, 68 | 68 | 55, 56, 68 |
| P. p. pardus | 2, 45, 55, 56, 59, 60, 63, 66, 67, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76 | 59, 63, 67 | 68 | 68 | Анализ не выполняли (см. текст) | |
| P. p. fusca | Нет признаков действия отбора | Нет сайтов | Нет сайтов | Не обнаружено признаков рекомбинации | ||
| Все леопарды вместе | 2, 4, 5, 10, 17, 38, 42, 45, 48, 55, 56, 59, 60, 63, 67, 72, 74, 76 | 2, 38, 48, 56, 59, 60, 63, 74 | 55 | 4, 10, 55, 68 | Не обнаружено признаков рекомбинации | |
Последовательности ГКГ класса I дальневосточного леопарда содержали больше всего кодонов с отношением dN/dS > 1, в том числе и кодонов с высокой вероятностью находящихся под воздействием балансирующего отбора. Большая часть этих кодонов, предположительно, участвует в связывании антигена. Методом FEL мы обнаружили один, а методом МЕМЕ – три кодона, находящихся под действием балансирующего или диверсифицирующего отбора. Поскольку в группе аллелей дальневосточного леопарда была обнаружена точка вероятной рекомбинации (в 41 кодоне между 122-м и 123 сайтами), то в соответствии с рекомендациями авторов данных методов мы повторили анализ для каждого участка по обе стороны от точки рекомбинации. Это привело к частичному изменению результатов расчетов: 17-й кодон перестал рассматриваться как находящийся под действием положительного отбора, а вероятность нахождения под действием отбора для 56-го кодона стала статистически достоверной (р < 0.1). Следует отметить, что роль 55 и 56 кодонов в ГКГ класса I, возможно, нуждается в более подробном исследовании, поскольку практически все алгоритмы, как codeml, так и HyPhy, выделяют либо один из этих кодонов, либо оба вместе как находящиеся под действием балансирующего отбора.
Анализ последовательностей африканского леопарда показал, что большая часть кодонов, для которых соотношение dN/dS > 1, предположительно участвует в связывании антигена, в том числе три кодона, которые находятся под действием балансирующего отбора с высокой статистической достоверностью (p > 0.95, табл. 7). Методы FEL и MEME выявили только один кодон – 68-й, статистически достоверно находящийся под действием балансирующего или диверсифицирующего отбора. Этот сайт также предположительно участвует в связывании антигена. В последовательностях африканского леопарда методом GARD были найдены две точки возможной рекомбинации: в 52 кодоне между 155-м и 156-м сайтами, а также в 66 кодоне между 196-м и 197-м сайтами. Обычно рекомендуют разделить последовательности в соответствии с местом нахождения точек рекомбинации и повторить поиск признаков положительного отбора. Мы не стали повторять алгоритмы HyPhy для африканского леопарда в связи с малым размером выборки и крайне малыми размерами получающихся фрагментов.
В ГКГ класса I индийского леопарда были выявлены кодоны, в которых соотношение dN/dS > 1, но действие отбора на них статистически недостоверно (Parmar et al., 2017). Мы повторили эти расчеты и подтвердили, что модели, не предусматривающие действие балансирующего отбора на последовательности ГКГ I класса индийского леопарда, достоверно лучше соответствуют исходным данным. Методы FEL и MEME также не показали признаков действия балансирующего отбора на какие-либо кодоны индийского леопарда. Признаков рекомбинационных событий на рассматриваемом участке гена обнаружено не было.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТОВ
Мы описали и проанализировали 21 аллель ГКГ класса I дальневосточного леопарда. Большинство животных несло в своем генотипе от 3 до 6 различных аллелей гена ГКГ I, но у двух леопардов (2m и 5f) было обнаружено 7 аллелей данного гена. В литературе обычно упоминается до 6 различных аллелей ГКГ I, определенных в генотипе отдельных особей среди представителей крупных кошачьих (Sachdev et al., 2005; Castro-Prieto et al., 2011). Это соответствует присутствию в геноме Pantherinae как минимум трех копий данного гена. Только у бенгальского тигра были найдены животные, несущие от 3 до 7 аллелей ГКГ I (Pokorny et al., 2010), что говорит о возможно большем количестве копий данного гена. Наши данные подтверждают наличие в геноме крупных кошачьих не менее 4 копий гена ГКГ I класса. Покорный с соавторами (Pokorny et al., 2010) определяют одну из семи полученных ими последовательностей как псевдоген, поскольку в ней обнаружена делеция двух нуклеотидов, ведущая к сдвигу рамки считывания. Из этого они делают вывод о возможном существовании трех копий функциональных генов ГКГ класса I и псевдогена того же класса. Последовательности, полученные от дальневосточного леопарда, не несут делеций, вставок или стоп-кодонов, в связи с чем, мы не можем сделать аналогичный вывод о наличии или отсутствии среди них нефункциональных псевдогенов.
Сравнение полученных нами последовательностей подтвердило наличие общих аллелей как у особей разных подвидов одного вида (Panthera pardus), так и факт межвидового полиморфизма, описанного ранее для генов ГКГ класса II крупных кошачьих (Wang et al., 2008; Wei et al., 2010). Наличие общих аллелей у дальневосточного леопарда и двух подвидов тигров можно объяснить как сохранением предковых форм аллелей, не утративших своего значения в ходе исторического распространения общего предка крупных кошек, так и конвергенцией нуклеотидных последовательностей, вызванной наличием общего патогена, оказывающего сильное влияние на естественный отбор и ведущего к вторичному возникновению и закреплению данного аллеля. При построении филогенетической сети аллели ГКГ класса I дальневосточного леопарда занимают преимущественно периферическое положение по отношению к другим подвидам, что соответствует эволюционной истории вида (Uphyrkina et al., 2001).
Сравнение разнообразия аллелей, выявленных у отдельных животных, показало, что у дальневосточного леопарда оно наибольшее по среднему числу аллелей на особь по сравнению с африканским подвидом, а по разбросу значений количества аллелей – по сравнению с индийским подвидом (см. табл. 3). Обнаруженная нами высокая степень генетической изменчивости сохраняется и на аминокислотном уровне.
Высокая степень изменчивости на уровне аминокислот позволяет заключить, что причиной изменчивости является не отсутствие отбора на фоне мутационного процесса, а балансирующий отбор, поддерживающий наличие в популяции функционально разнообразных аллельных вариантов и дающий преимущество гетерозиготным особям, способным противостоять большему числу патогенов вследствие кодоминантного характера генов ГКГ.
Поиск признаков действия естественного отбора в исследуемых популяциях показал, что на кодоны, предположительно не участвующие в связывании антигена, действие отбора не выявляется, а нуклеотидные замены в них преимущественно синонимичны. Кодоны, находящиеся под действием балансирующего отбора, обладают схожим паттерном распределения в последовательностях африканского и дальневосточного леопардов. Количество сайтов, для которых вероятен или статистически доказан балансирующий отбор, у дальневосточного леопарда выше, чем у африканского. Кастро-Прието с соавторами (Castro-Prieto et al., 2011) упоминают, что низкое разнообразие в исследуемых ими образцах может быть связано с особенностями выборки, но, вероятно, не характерно для всего подвида в целом. Численность популяции африканского леопарда оценивают в 5–10.5 тыс. особей (Hanssen, Stander, 2004), а в статье Кастро-Прието с соавторами (Castro-Prieto et al., 2011) приведены результаты исследования 25 особей из отдельной части ареала – Намибии. Требуется больше данных, чтобы прояснить вопрос о реальной вариабельности генов ГКГ у африканского подвида леопарда.
Остается неясной причина относительной низкой вариабельности ГКГ класса I индийского леопарда. Численность индийского леопарда довольно высока: размер популяции – 12–14 тыс. особей (Jacobson et al., 2016), при этом 13 особей, вошедших в выборку индийских леопардов, не являются родственниками. Половина из них содержится в неволе и участвует в природоохранной программе разведения (Сonservation breeding programme of the Central Zoo Authority of India). Пармар с соавторами (Parmar et al., 2017) лаконично упоминают о возможном влиянии ограничений в системе спаривания или сниженном давлении отбора на генетическое разнообразие генов ГКГ. Возможно, именно эти причины объясняют меньшее количество аллелей ГКГ класса I у особей индийского леопарда. Интересно, что в сети аллелей две трети последовательностей индийского леопарда формируют отдельную ветвь, для перехода к которой требуется значительное количество мутационных изменений (см. рис. 1). Вполне вероятно, что эта ветвь отражает изолированную эволюционную историю ряда последовательностей.
Наши результаты позволяют сделать вывод, что генетическое разнообразие генов ГКГ класса I у дальневосточного подвида леопарда как минимум не уступает, а возможно и превышает таковое у других подвидов леопарда, находящихся в более благополучных условиях обитания и поддерживающих более высокую численность. Схожая ситуация была описана и для рода рысей (Lynx): пиренейская рысь (L. pardinus), пережившая в конце XX в. резкое снижение численности и обладающая низким разнообразием нейтральных генетических маркеров, тем не менее сохранила аллельное разнообразие генов ГКГ, сравнимое с таковым у родственной ей широко распространенной евразийской рыси (L. lynx), численность которой не вызывает опасений (Marmesat et al., 2017).
Гены ГКГ класса I во многом определяют устойчивость к патогенам вирусной природы. К сожалению, сложно оценить таковую для дальневосточного леопарда по сравнению с другими подвидами. Известно, что дальневосточный леопард, как и некоторые другие подвиды, чувствителен к вирусу чумы плотоядных, заболевание которым может приводить к гибели животного (Sulikhan et al., 2018; Kadam et al., 2022; Rahman et al., 2022; Bodgener et al., 2023). Доля серопозитивных животных среди дальневосточных леопардов была ниже, чем среди индийских (Naidenko et al., 2018; Bodgener et al., 2023). Сопоставить зараженность или серопозитивность к широкому спектру патогенов у дальневосточного леопарда с другими подвидами невозможно из-за отсутствия данных. Вместе с тем, серопозитивность дальневосточного леопарда к вирусным патогенам существенно ниже, чем амурского тигра и дальневосточного лесного кота, однако, существенно выше, чем у евразийской рыси (Naidenko et al., 2018). Очевидно, что требуется дальнейшее исследование активности иммунной системы дальневосточных леопардов в сравнении с другими видами кошачьих.
Таким образом, у дальневосточного леопарда наблюдается высокое генетическое разнообразие генов ГКГ класса I. Наблюдаемое разнообразие и полиморфизм последовательностей иммунных генов класса I дальневосточного леопарда не уступают таковым других подвидов леопарда, обитающих в более благоприятных условиях. С точки зрения состояния функционально значимых генов иммунитета снижение численности дальневосточного леопарда к настоящему времени не привело к непоправимым потерям генетического потенциала популяции. Это имеет принципиальное значение для сохранения дальневосточного леопарда: несмотря на неоднократно описанное низкое генетическое разнообразие подвида по митохондриальной ДНК и микросаттелитным локусам, именно высокая изменчивость генов ГКГ позволяет предположить, что популяция обладает внутренним потенциалом к восстановлению и достаточной устойчивостью к патогенной нагрузке.
Работа выполнена в рамках Постоянно действующей экспедиции РАН по изучению животных Красной книги Российской Федерации и других особо важных животных фауны России при финансовой поддержке Русского географического общества (проект “Изучение редких видов животных (амурский тигр, дальневосточный леопард, ирбис (снежный барс), белуха, белый медведь)”).
Список литературы
Виткалова А.В., Дарман Ю.А., Марченкова Т.В., Матюхина Д.С., Рыбин А.Н., Сторожук В.Б., Титов А.С., Седаш Г.А., Сонин П.Л., Петров Т.А., Мазур М.А., Николаева Е.И., Блидченко Е.Ю., Костыря А.В., Шевцова Е.И., Арамилев В.В., Микелл Д.Г. Фотомониторинг дальневосточного леопарда на территории юго-западного Приморья (2014–2020 гг.). Владивосток: Апельсин, 2022. 116 с.
Найденко С.В., Матюхина Д.С., Магомедов М.-Р.Д., Рожнов В.В. Леопард Panthera pardus (Linnaeus, 1758) // Красная книга Российской Федерации, том “Животные”. 2-ое издание. М: ФГБУ “ВНИИ Экология”, 2021. С. 994‒996.
Рожнов В.В., Сорокин П.А., Лукаревский В.С., Найденко С.В., Эрнандес-Бланко Х.А., Лукаревский С.В. Индивидуальная идентификация дальневосточных леопардов (Panthera pardus orientalis) молекулярно-генетическими методами и ее использования для оценки численности популяции // Известия РАН. Серия биологическая. 2013. № 2. С. 138‒143. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0002332913020124
Тарасян К.К., Сорокин П.А., Холодова М.В., Рожнов В.В. Главный комплекс гистосовместимости (major histocompatibility complex, MHC) у млекопитающих и его значение в изучении редких видов (на примере семейства Felidae) // Журн. общей биологии. 2014. Т. 75. № 4. С. 302‒314.
Bahr A., Wilson A.B. The evolution of MHC diversity: evidence of intralocus gene conversion and recombination in a single-locus system // Gene. 2012. V. 497. № 1. P. 52‒57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.017
Bandelt H.-J., Forster P., Röhl A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies // Mol Biol Evol. 1999. V. 16. P. 37‒48. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036
Bodgener J., Sadaula A., Thapa P.J., Shrestha B.K., Gairhe K.P., Subedi S., Rijal K.R., Pandey P., Joshi J.D., Kandel P., Himal L., Navapon T., Martin G. Canine distemper virus in tigers (Panthera tigris) and leopards (P. pardus) in Nepal // Pathogens. 2023. V. 12. № 2. P. 1‒13. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020203
Brouwer L., Barr I., van de Pol M., Burke T., Komdeur J., Richardson D.S. MHC-dependent survival in a wild population: evidence for hidden genetic benefits gained through extra-pair fertilizations // Mol. Ecol. 2010. V. 19. № 16. P. 3444‒3455. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04750.x
Burger D., Thomas S., Aepli H., Dreyer M., Fabre G., Marti E., Sieme H., Robinson M.R., Wedekind C. Major histocompatibility complex-linked social signalling affects female fertility // Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2017. V. 284. № 1868. P. 20171824. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2017.1824
Castro-Prieto A., Wachter B., Melzheimer J., Thalwitzer S., Sommer S. Diversity and evolutionary patterns of immune genes in free-ranging namibian leopards (Panthera pardus pardus) // J. Heredity. 2011. V. 102. № 6. P. 653‒665. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esr097
Darriba D., Taboada G.L., Doallo R., Posada D. jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 2012. V. 9. №8. P. 772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
Hall T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT // Nucleic Acids Symposium Series. 1999. V. 41. P. 95‒98. https://doi.org/10.14601/phytopathol_mediterr-14998u1. 29
Hanssen L., Stander P. Namibia large carnivore Atlas Report. Vol. 1 Windhoek (Namibia): Predator Conservation Trust, Ministry of Environment and Tourism, Division of Specialty Support Services., 2004. 12 p.
Jacobson A.P., Gerngross P., Lemeris J.R., Jr., Schoonover R.F., Anco C., Breitenmoser-Wursten C., Durant S.M., Farhadinia M.S., Henschel P., Kamler J.F., Laguardia A., Rostro-Garcia S., Stein A.B., Dollar L. Leopard (Panthera pardus) status, distribution, and the research efforts across its range // PeerJ. 2016. V. 4. P. e1974. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1974
Kadam R.G., Karikalan M., Siddappa C.M., Mahendran K., Srivastava G., Rajak K.K., Bhardwaj Y., Varshney R., War Z.A., Singh R., Ghosh M., Beena V., Pawde A.M., Singh K.P., Sharma A.K. Molecular and pathological screening of canine distemper virus in Asiatic lions, tigers, leopards, snow leopards, clouded leopards, leopard cats, jungle cats, civet cats, fishing cat, and jaguar of different states, India // Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022. V. 98. P. 105211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105211
Kennedy L.J., Ryvar R., Brown J.J., Ollier W.E., Radford A.D. Resolution of complex feline leukocyte antigen DRB loci by reference strand-mediated conformational analysis (RSCA) // Tissue Antigens. 2003. V. 62. № 4. P. 313‒323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-002-0465-5
Kitchener A.C., Breitenmoser-Wursten C., Eizirik E., Gentry A., Werdelin L., Wilting A., Yamaguchi N., Abramov A.V., Christiansen P., Driscoll C., Duckworth J.W., Johnson W., Luo S.-J., Meijaard E., O’Donoghue P., Sanderson J., Seymour K., Bruford M., Groves, C., Hoffmann M., Nowell K., Timmons Z., Tobe S. A revised taxonomy of the Felidae. The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN. 2017. 80 p.
Kosakovsky Pond S.L., Posada D., Gravenor M.B., Woelk C.H., Frost S.D.W. Automated phylogenetic detection of recombination using a genetic algorithm // Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2006. V. 23. № 10. P. 1891‒1901. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl051
Kumar S., Stecher G., Li M., Knyaz C., Tamura K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms // Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2018. V. 35. P. 1547‒1549. .https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Liu X.H., Zhao Y.H., Zhang Y.H., Liu W., Li N. Cloning and mapping MC1R to chromosome 16 in giant panda // Anim. Genet. 2005. V. 36. № 3. P. 280‒281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2005.01296.x
Manlik O., Krützen M., Kopps A.M., Mann J., Bejder L., Allen S.J., Frère C., Connor R.C., Sherwin W.B. Is MHC diversity a better marker for conservation than neutral genetic diversity? A case study of two contrasting dolphin populations // Ecol. Evol. 2019. V. 9. № 12. P. 6986‒6998. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5265
Marmesat E., Schmidt K., Saveljev A.P., Seryodkin I.V., Godoy J.A. Retention of functional variation despite extreme genomic erosion: MHC allelic repertoires in the Lynx genus // BMC Evolutionary Biology. 2017. V. 17. № 1. P. 158. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-017-1006-z
Naidenko S.V., Hernandez-Blanco J.A., Pavlova E.V., Erofeeva M.N., Sorokin P.A., Litvinov M.N., Kotlyar A.K., Sulikhan N.S., Rozhnov V.V. Primary study of seroprevalence to virus pathogens in wild felids of South Primorie, Russia // Canadian J. Zoology. 2018. V. 96. № 8. P. 839‒846. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjz-2017-0192
Paradis E, Claude J, Strimmer K. A{PE}: analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in {R} language. Bioinformatics. 2004. V. 20. P. 289–290. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty633
Parmar D.R., Mitra S., Bhadouriya S., Rao T., Kunteepuram V., Gaur A. Characterization of major histocompatibility complex class I, and class II DRB loci of captive and wild Indian leopards (Panthera pardus fusca) // Genetica. 2017. V. 145. № 6. P. 541‒558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-017-9979-5
Ploshnitsa A.I., Goltsman M.E., Macdonald D.W., Kennedy L.J., Sommer S. Impact of historical founder effects and a recent bottleneck on MHC variability in Commander Arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus) // Ecol. Evol. 2012. V. 2. № 1. P. 165‒180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.42
Pokorny I., Sharma R., Goyal S.P., Mishra S., Tiedemann R. MHC class I and MHC class II DRB gene variability in wild and captive Bengal tigers (Panthera tigris tigris) // Immunogenetics. 2010. V. 62. № 10. P. 667‒679.
Rahman D.A., Saepuloh U., Santosa Y., Darusman H.S., Romaria Pinondang I.M., Kindangen A.S., Pertiwi A.P., Sari L., Irawan A., Sultan K., Rianti P. Molecular diagnosis with the corresponding clinical symptoms of canine distemper virus infection in javan leopard (Panthera pardus ssp. melas) // Heliyon. 2022. V. 8. № 11. P. e11341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11341
Sachdev M., Sankaranarayanan R., Reddanna P., Thangaraj K., Singh L. Major histocompatibility complex class I polymorphism in Asiatic lions // Tissue Antigens. 2005. V. 66. № 1. P. 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399?0039.2005.00432.x
Siddle H.V., Kreiss A., Eldridge M.D., Noonan E., Clarke C.J., Pyecroft S., Woods G.M., Belov K. Transmission of a fatal clonal tumor by biting occurs due to depleted MHC diversity in a threatened carnivorous marsupial // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007. V. 104. № 41. P. 16 221‒16 226. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704580104
Sommer S., Courtiol A., Mazzoni C.J. MHC genotyping of non-model organisms using next-generation sequencing: a new methodology to deal with artefacts and allelic dropout // BMC Genomics. 2013. V. 14. P. 542. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-542
Sulikhan N.S., Gilbert M., Blidchenko E.Y., Naidenko S.V., Ivanchuk G.V., Gorpenchenko T.Y., Alshinetskiy M.V., Shevtsova E.I., Goodrich J.M., Lewis J.C.M., Goncharuk M.S., Uphyrkina O.V., Rozhnov V.V., Shedko S.V., McAloose D., Miquelle D.G., Seimon T.A. Canine distemper virus in a wild far eastern leopard (Panthera pardus orientalis) // J. Wildl. Dis. 2018. V. 54. № 1. P. 170‒174. https://doi.org/10.7589/2017-03-065
Uphyrkina O., Johnson W.E., Quigley H., Miquelle D., Marker L., Bush M., O’Brien S.J. Phylogenetics, genome diversity and origin of modern leopard, Panthera pardus // Mol. Ecol. 2001. V. 10. № 11. P. 2617‒2633. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0962-1083.2001.01350.x
Uphyrkina O., O’Brien S.J. Applying molecular genetic tools to the conservation and action plan for the critically endangered Far Eastern leopard (Panthera pardus orientalis) // C. R. Biol. 2003. V. 326 Suppl 1. P. S93‒97. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1631-0691(03)00044-1
Wang Q., Wu X., Yan P., Zheng S. Sequence variability analysis on major histocompatibility complex class II DRB alleles in three felines // Frontiers of Biology in China. 2008. V. 3. № 1. P. 55‒62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-008-0004-3
Wei K., Zhang Z., Wang X., Zhang W., Xu X., Shen F., Yue B. Lineage pattern, trans-species polymorphism, and selection pressure among the major lineages of feline Mhc-DRB peptide-binding region // Immunogenetics. 2010. V. 62. № 5. P. 307‒317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-010-0440-5
Xu B., Yang Z. PAMLX: a graphical user interface for PAML // Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013. V. 30. P. 2723‒2724. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst179
Yang Z. PAML4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood // Mol Biol Evol. 2007. V. 24. P. 1586‒1591. https://doi.org/0.1093/molbev/msm088
Yuhki N., Beck T., Stephens R., Neelam B., O’Brien S.J. Comparative genomic structure of human, dog, and cat MHC: HLA, DLA, and FLA // J. Hered. 2007. V. 98. № 5. P. 390‒399. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esm056
Yuhki N., Mullikin J.C., Beck T., Stephens R., O’Brien S.J. Sequences, annotation and single nucleotide polymorphism of the major histocompatibility complex in the domestic cat // PLoS One. 2008. V. 3. № 7. P. e2674. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002674
Yuhki N., O’Brien S.J. DNA variation of the mammalian major histocompatibility complex reflects genomic diversity and population history // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1990. V. 87. № 2. P. 836‒840.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Известия РАН. Серия биологическая




