Коллоидный журнал, 2023, T. 85, № 5, стр. 556-565
Динамические свойства монослоев легочных липидов на поверхности растворов полистиролсульфоната натрия и полидиаллилдиметиламмония хлорида
А. Г. Быков 1, *, М. А. Панаева 1
1 Санкт-Петербургский государственный университет, Институт химии
198504 Санкт-Петербург,
Университетский просп., 26, Россия
* E-mail: ag-bikov@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 28.06.2023
После доработки 18.07.2023
Принята к публикации 26.07.2023
- EDN: DGYIFV
- DOI: 10.31857/S0023291223600505
Аннотация
Легочный сурфактант, состоящий из сложной смеси липидов и белков, играет ключевую роль в обеспечении функциональных свойств органов дыхания. Для поддержания низких значений поверхностного натяжения при постоянных деформациях растяжения/сжатия липиды образуют комплексы с белками. Однако, до сих пор неизвестно за счет каких взаимодействий происходит образование комплексов, что значительно затрудняет разработку синтетических аналогов природного легочного сурфактанта. В данной работе с помощью методов поверхностной реологии и эллипсометрии были исследованы динамические свойства нанесенных модельных монослоев фосфолипидов на поверхности растворов синтетических полиэлектролитов. Было показано, что для эффективного образования комплексов и поддержания низких значений поверхностного натяжения одних электростатических или гидрофобных взаимодействий между липидами и макромолекулами оказывается недостаточно.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Легочный сурфактант состоит из липидов и белков [1, 2]. Раствор легочного сурфактанта покрывает поверхность альвеол легких, обеспечивая их функциональность за счет поддержания низких значений поверхностного натяжения при растяжении и практически нулевых значений после сжатия [2, 3]. Недостаточное количество легочного сурфактанта приводит к различным заболеваниям легких, в частности, к появлению респираторного дистресс-синдрома новорожденных [4, 5]. В процессе лечения данного заболевания, вызванного недостатком собственного сурфактанта, применяются природные препараты легочного сурфактанта, полученные из легких домашних животных (быка, теленка, свиньи) [6]. Кроме того, эти препараты применялись для лечения пациентов при тяжелом течении коронавирусной инфекции COVID-19 [7, 8]. Так как природные препараты имеют ряд недостатков (высокая стоимость, производственные ограничения, риск наличия в составе иммуногенов и про-воспалительных медиаторов), на разработку синтетического аналога направлено большое количество исследований [9, 10]. Основная сложность на пути создания синтетического аналога заключается в отсутствии понимания механизма действия легочного сурфактанта [11]. Дополнительная информация о механизме может быть получена при исследовании динамических поверхностных свойств модельных систем.
Известно, что главным компонентом сурфактанта является насыщенный цвиттер-ионный фосфолипид дипальмитоил фосфатидилхолин (ДПФХ), который формирует на поверхности раздела фаз жидкость/газ высоко упорядоченный монослой и позволяет достигать крайне низких значений поверхностного натяжения при сжатии [12]. Поэтому ДПФХ используется в качестве главного компонента модельной системы легочного сурфактанта [1, 3]. При периодических деформациях растяжения-сжатия монослой ДПФХ может терять способность к снижению поверхностного натяжения из-за необратимого коллапса и медленной адсорбции дополнительных молекул из объема [13, 14]. В составе сурфактанта также присутствуют другие фосфолипиды, которые способствуют перестройке структуры монослоя при деформациях за счет образования многофазной структуры: нано- и микродоменов жидко-конденсированной фазы (ЖК), распределенных по жидко-растянутой фазе (ЖР) [15]. Важной функциональной особенностью отрицательно заряженных фосфолипидов (например, дипальмитоил глицерофосфоглицерина (ДПФГ)) является способность к формированию комплексов с поверхностно-активными белками (“surfactant proteins” SP-B и SP-C), входящими в состав легочного сурфактанта [1–3, 14–16]. Данные комплексы фосфолипидов и белков препятствуют необратимому коллапсу монослоя при деформациях, однако механизм их образования и действия слабо изучен [17].
Белки являются природными полиэлектролитами, несущими на себе положительный и отрицательный заряды, поэтому изучение взаимодействий между монослоем липидов и синтетическими полиэлектролитами с различными знаками зарядов и поверхностной активностью помогает понять какие взаимодействия между компонентами играют ключевую роль при образовании комплексов [18–21]. Ранее было обнаружено значительное влияние электростатических и гидрофобных взаимодействий на поверхностные свойства нанесенных монослоев липидов со знаком заряда противоположным, чем у находящихся в объеме раствора синтетических полиэлектролитов (полистиролсульфоната натрия (ПСС) и полидиаллилдиметиламмоний хлорида (ПДАДМАХ)) [22–24]. Однако большая часть исследований была направлена на изучение равновесных поверхностных свойств в области высоких поверхностных натяжений, в то время как внутренняя поверхность легких характеризуется низкими значениями поверхностного натяжения, а поверхностный слой находится вдали от равновесного состояния. Рассматривать полиэлектролиты ПСС и ПДАДМАХ в качестве синтетических аналогов не представляется возможным из-за простой структуры макромолекул по сравнению с белками SP-B и SP-C. В то же время целью данной работы было определение влияния макромолекул, характеризующихся разным знаком зарядов функциональных групп и степенью гидрофобности, на свойства модельного монослоя легочных липидов в условиях, близких к физиологическим. В настоящей работе проведены исследования динамических поверхностных свойств в области высоких и низких значений поверхностного натяжения нанесенных модельных монослоев фосфолипидов на поверхности растворов полиэлектролитов. В процессе исследования рассмотрено влияние гидрофобных и электростатических взаимодействий между макромолекулами полиэлектролита и молекулами фосфолипидов на поведение модельной системы при периодических деформациях растяжения и сжатия поверхностного слоя, имитирующих процесс дыхания.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
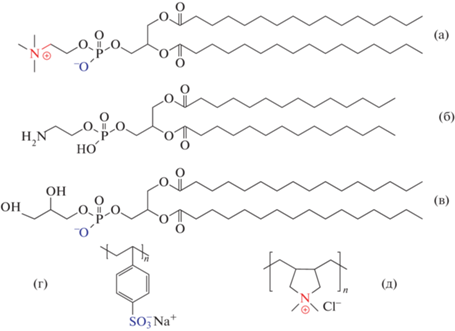
В работе использовали: ДПФХ, димиристоилфосфатидилэтаноламин (ДМЭА), ДПФГ, ПСС и ПДАДМАХ (Sigma-Aldrich, Германия) без дополнительной очистки (рис. 1). Для создания растворов липидов с концентрацией 1 мг/мл был взят хлороформ (Sigma-Aldrich, Германия), очищенный методом перегонки. Из растворов липидов в хлороформе готовили смеси ДПФХ/ДПФГ, ДПФХ/ДМЭА в объемном соотношении 3/1 путем смешения ранее приготовленных растворов. В качестве водной фазы выступал фосфатный буфер с pH 7 и добавлением NaCl, прокаленного при температуре 750°C в муфельной печи. Добавление NaCl необходимо для достижения условий изотонического раствора (0.9 мас. %). Монослой липидов формировали на поверхности водной фазы методом прикапывания фиксированных объемов растворов липидов в органическом растворителе. Под нанесенный монослой липида впрыскива-ли концентрированный раствор полиэлектролита для достижения необходимого содержания в подложке (для ПДАДМАХ 0.2 мас. %, а для ПСС от 0.02 до 0.2 мас. %). Затем, после часа ожидания значения поверхностного натяжения достигали равновесных значений, и проводили измерения динамических поверхностных свойств монослоя липидов на поверхности раствора полиэлектролита. Для изучения поверхностных свойств в области высоких поверхностных натяжений впрыскивание полиэлектролита осуществляли под монослой фосфолипидов с нулевым поверхностным давлением. Для исследования области низких поверхностных натяжений полиэлектролит впрыскивали под монослой с поверхностным натяжением монослоя липидов около 30 мН/м. Все измерения проводили при 25°C.
Рис. 1.
Структурные формулы фосфолипидов ДПФХ (а), ДМЭА (б), ДПФГ (в); полиэлектролитов ПСС (г), ПДАД-МАХ (д).
Поверхностное натяжение измеряли методом пластинки Вильгельми с использованием пластинки из фильтровальной бумаги шириной 10 мм. Величина поверхностного давления связана с поверхностным натяжением и определяется выражением (1):
где γw – поверхностное натяжение на межфазной границе водный раствор буфера−воздух, γ – поверхностное натяжение раствора полиэлектролита или нанесенного монослоя.Динамическую поверхностную упругость измеряли с помощью метода осциллирующего барьера на реометре межфазного сдвига (KSV NIMA, Финляндия). Метод основан на регистрации периодических изменений поверхностного натяжения в результате изменения площади межфазного слоя, вызываемого периодическими колебаниями двух барьеров. Ванна Ленгмюра была оснащена барьерами с дополнительной гибкой тефлоновой лентой, чтобы исключить нежелательное перетекание монослоя под барьерами при высоких поверхностных давлениях (низких поверхностных натяжениях) [25]. Частота колебаний площади поверхности составляла 30 мГц. Амплитуда гармонических колебаний площади поверхности варьировалась от 4 до 32%. Измерения поверхностного натяжения производили с использованием пластинки Вильгельми, которая была подвешена в центре над ванной Ленгмюра, параллельно барьерам с целью уменьшения влияния поверхностных сдвиговых деформаций. При малой амплитуде гармонических колебаний площади модуль динамической поверхностной упругости определяется соотношением (2):
(2)
$\varepsilon = {{\varepsilon }_{{{\text{Re}}}}} + i{{\varepsilon }_{{{\text{Im}}}}} = \varepsilon {\kern 1pt} \cos {\kern 1pt} \delta + i\varepsilon {\kern 1pt} \sin {\kern 1pt} \delta = \frac{{\Delta {{\gamma }}}}{{\Delta {\text{А/}}{{{\text{A}}}_{0}}}},$В случае больших деформаций $\left( {\Delta {\text{А/}}{{{\text{A}}}_{0}} > {\text{ }}5\% } \right)$ поведение системы оказывается нелинейным, и использование соотношения (2) в таких условиях для определения динамической упругости становится невозможным. Однако существует подход, который позволяет в этих условиях определять эффективную динамическую упругость в области крайне высоких поверхностных давлений [26–28]. Для получения поверхностной упругости в широкой области поверхностных давлений применяется подход разложения напряжений [26]: строятся графики Лиссажу (зависимости поверхностного натяжения от относительной деформации площади) для различных периодических деформаций с разными амплитудами колебаний, из них определяются максимумы и минимумы для каждой фигуры Лиссажу. По формуле (3) рассчитываются значения эффективной динамической поверхностной упругости:
(3)
${{{{\varepsilon }}}_{{{\text{ef}}}}} = ({{\gamma }_{{n + 1}}} - {{\gamma }_{n}})\frac{{{\text{(}}{{{\text{A}}}_{0}} \pm {{{\text{A}}}_{1}})}}{{{\text{(}}{{{\text{A}}}_{{n + 1}}} - {{{\text{A}}}_{n}})}},$В работе был использован нуль-эллипсометр Multiskop (Optrel GBR, Германия) для эллипсометрических измерений поверхности исследуемых систем. Длина волны составляла 632.8 нм при постоянном значении угла падения 49°, близком к углу Брюстера. Известно, что разность (∆surf) между эллипсометрическим углом ∆ для исследуемого раствора и чистой воды зависит от показателя преломления поверхностного слоя и пропорциональна количеству вещества на поверхности [29].
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
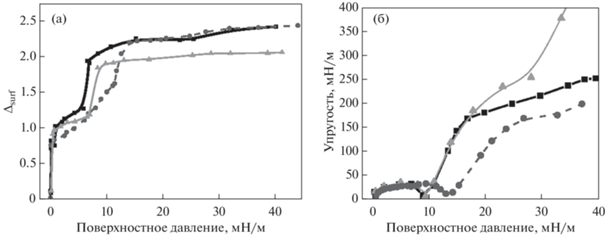
Исследования однокомпонентных монослоев ДПФХ, ДПФГ и ДМЭА на растворе фосфатного буфера с помощью эллипсометрии показали, что даже небольшое увеличение поверхностного давления после нанесения липида приводит к значительному росту значений ∆surf для всех трех липидов (рис. 2а). Это связано с изменением показателя преломления при переходе нанесенного монослоя от газообразного к ЖР состоянию, который происходит при поверхностных давлениях меньше 1 мН/м. Дальнейшее увеличение поверхностной концентрации и давления приводит к постепенному увеличению значений ∆surf. Затем в области перехода от ЖР к ЖК состоянию монослоя вновь наблюдаются резкие изменения значений. Эти результаты хорошо согласуются с данными поверхностной упругости. При малых амплитудах колебания поверхностной площади были получены величины динамической поверхностной упругости монослоя ДПФХ в области низких значений поверхностного давления (рис. 2б, черные закрашенные квадраты). На рис. 2 показано, что с возрастанием поверхностной концентрации молекул липида поверхностное давление и упругость увеличиваются. Затем в диапазоне поверхностных давлений около 10 мН/м для монослоя ДПФХ наблюдается минимум поверхностной упругости. Это связано с двумерным фазовым переходом от ЖР к ЖК состоянию поверхностного слоя. Образование доменов ЖК фазы приводит к появлению релаксационного процесса, причиной которого является обмен молекулами между ЖР и ЖК фазами. Так как обмен молекулами между разными фазами происходит с меньшим характеристическим временем, чем период колебаний площади поверхности, то поверхностная упругость снижается при появлении неоднородностей. При последующем увеличении поверхностного давления до 50 мН/м монослой находится в ЖК состоянии с плотной упаковкой, что приводит к увеличению упругости до 250–300 мН/м. Сравнение динамической поверхностной упругости в области низких значений поверхностного давления чистых монослоев ДМЭА с результатами для ДПФХ показало, что в диапазоне давлений от 0 до 17 мН/м поведение монослоев ДПФХ и ДМЭА не имеет различий: для обоих монослоев в области 10 мН/м наблюдается минимум, связанный с фазовым переходом ЖР−ЖК (рис. 2б). При более высоких значениях давления упругость ДМЭА становится значительно выше, чем упругость ДПФХ. Это может быть связано с фазовым переходом из ЖК в твердообразную фазу [30]. Молекулы ДПФХ не образуют твердой фазы в этой области поверхностных давлений. При сравнении поведения монослоев ДПФХ и ДПФГ (рис. 2б) наблюдается смещение минимума в области низких давлений для монослоя ДПФГ (15 мН/м) относительно ДПФХ (10 мН/м), это объясняется меньшей упорядоченностью и электростатическим отталкиванием между отрицательно заряженными молекулами ДПФГ в монослое. При повышенном давлении (30 мН/м) поверхностная упругость монослоя ДПФГ снижается относительно значений ДПФХ, что также подтверждает предположение о меньшей плотности упаковки молекул ДПФГ по сравнению с монослоем ДПФХ.
Рис. 2.
Зависимости ∆surf (а) и динамической поверхностной упругости (б) от поверхностного давления для нанесенных монослоев ДПФХ (черные квадраты), ДМЭА (светло-серые треугольники), ДПФГ (серые круги) на буфере при Т = 25°C.
Для исследования упругости монослоя ДПФХ в области высоких поверхностных давлений (от 50 до 72 мН/м) были проведены измерения эффективной поверхностной упругости с помощью подхода, основанного на больших деформациях площади поверхности (рис. 3). Для этого на поверхности буфера формировали монослой с поверхностным давлением около 32 мН/м и подвергали серии деформаций с большими амплитудами колебания барьеров. В области низких поверхностных давлений значения эффективной упругости хорошо согласуются с данными поверхностной упругости, полученными с помощью стандартного метода (рис. 2б). При поверхностных давлениях 40–50 мН/м эффективная поверхностная упругость достигает максимума 250–300 мН/м. Дальнейшее возрастание поверхностного давления до 60 мН/м ведет за собой снижение упругости, что является следствием изменения структуры поверхностного слоя. Это может быть вызвано образованием многослойной структуры за счет вытеснения молекул липида в подслой. В области крайне низких поверхностных натяжений или высоких поверхностных давлений (60–70 мН/м) поверхностная упругость остается выше 50–100 мН/м вплоть до коллапса монослоя, который происходит при нулевом поверхностном натяжении. Эти результаты хорошо согласуются с данными предыдущих исследований [31].
Рис. 3.
Зависимости динамической и эффективной поверхностных упругостей для нанесенных монослоев ДПФХ (черные закрашенные и пустые квадраты соответственно), ДПФХ/ДПФГ 3/1 (светло-серые закрашенные и пустые круги соответственно), ДП-ФХ/ДМЭА 3/1 (серые закрашенные и пустые треугольники соответственно) от поверхностного давления на буфере при Т = 25°C.
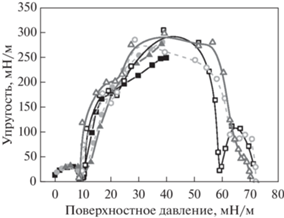
Результаты измерений поверхностной упругости для смешанных монослоев ДПФХ и ДПФГ, в котором около 25% молекул липида ДПФХ в составе монослоя заменены на липид ДПФГ, несущий на себе отрицательный заряд, оказывались близки к данным для чистого монослоя ДПФХ в области малых поверхностных давлений до 40 мН/м (рис. 3). Вероятно, из-за близкой молекулярной структуры и поверхностных свойств этих двух липидов, присутствие дополнительного липида не препятствует двумерным фазовым переходам в поверхностном слое. Однако в диапазоне низких поверхностных давлений заметно слабое смещение минимума в область более высоких давлений (от 10 к 12 мН/м), что можно связать с нарушением упорядоченности в упаковке смешанного монослоя (рис. 3). Кроме того, при добавлении ДПФГ снижение поверхностной упругости происходит при больших поверхностных давленияx и высоких поверхностных концентрациях. В результате при поверхностных давлениях около 60 мН/м эффективная поверхностная упругость монослоя ДПФХ/ДПФГ оказалась больше, чем для ДПФХ. Можно предположить, что молекулы ДПФГ затрудняют структурные превращения в поверхностном слое и замедляют релаксационные процессы. Таким образом, введение дополнительного липида может приводить к увеличению поверхностной упругости при высоких поверхностных давлениях. Аналогичные результаты были получены для двухкомпонентного монослоя ДПФХ и ДМЭА (рис. 3, серые треугольники). Различие заключалось только в более резком снижении поверхностной упругости при достижении высоких значений поверхностного давления. Следует отметить, что ДМЭА является цвиттер-ионным липидом, однако имеет меньшую плотность положительного заряда по сравнению с молекулой ДПФХ (рис. 1а, 1 б).
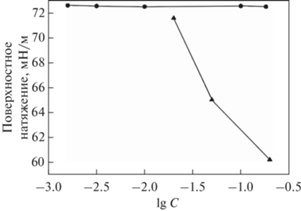
Дополнительно были проведены исследования поверхностных свойств полиэлектролитов ПСС и ПДАДМАХ. В результате были получены зависимости поверхностного натяжения от десятичного логарифма концентраций полиэлектролита (мас. %). При увеличении концентрации растворов ПСС (0.02–0.2 мас. %) поверхностное натяжение снижалось до 60 мН/м (рис. 4, треугольники). Полиэлектролит ПДАДМАХ, в отличие от ПСС, не обладает поверхностной активностью в исследуемой области концентраций: поверхностное натяжение было постоянным при варьировании концентрации ПДАДМАХ и близким к поверхностному натяжению воды (рис. 4, круги). Эллипсометрические измерения также согласуются со сделанными выводами о поверхностной активности полиэлектролитов ПДАДМАХ и ПСС. Для растворов ПДМДАХ значения ∆surf были близки к нулю. При этом для раствора ПСС (0.2 мас. %) ∆surf растет со временем и достигает 0.85º в состоянии равновесия, что свидетельствует об адсорбции макромолекул ПСС на поверхность.
Рис. 4.
Зависимости поверхностного натяжения от десятичного логарифма концентраций полиэлектролита (мас. %) ПСС (треугольники), ПДАДМАХ (круги) при Т = 25°C.
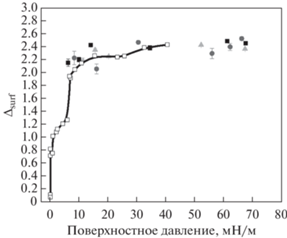
Далее были проведены исследования динамической и эффективной поверхностной упругости для монослоев ДПФХ на поверхности ПДАДМАХ с концентрацией (0.2 мас. %). Было показано, что результаты практически совпадают с данными для монослоя на чистом буфере во всей области поверхностных давлений (рис. 5, 6а). Это указывает на отсутствие влияния полиэлектролита на поверхностные свойства. Кроме того, отсутствие взаимодействия между полиэлектролитом и липидом также подтверждается при рассмотрении фигур Лиссажу (рис. 6б), которые практически совпадают для монослоя ДПФХ на чистом буфере и растворе полиэлектролита. Дополнительно была измерена разность эллипсометрических углов ∆surf для монослоя ДПФХ в присутствии ПДАДМАХ в условиях периодических деформаций растяжения-сжатия. Было показано, что величина ∆surf для монослоя на поверхности раствора полиэлектролита не отличается в пределах погрешности от значений, полученных для монослоя ДПФХ на буфере в аналогичных условиях (рис. 7). Следовательно, ПДАДМАХ, не обладающий собственной поверхностной активностью, не оказывает большого влияния на свойства монослоя ДПФХ.
Рис. 5.
Зависимости динамической упругости от поверхностного давления для монослоя ДПФХ на растворе ПДАДМАХ 0.2 мас. % (пустые круги), на буфере (закрашенные квадраты) при Т = 25°C.
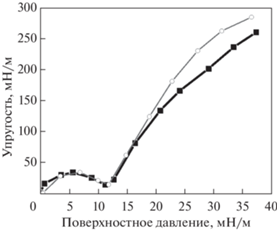
Рис. 6.
(а) Зависимости эффективной поверхностной упругости от поверхностного давления для нанесенных монослоев ДПФХ (черные закрашенные звезды), ДПФХ/ДПФГ 3/1 (черные пустые круги) на растворе ПДАДМАХ 0.2 мас. % и ДПФХ/ДПФГ 3/1 на растворе буфера (серые закрашенные круги). (б) Фигуры Лиссажу для монослоев ДПФХ (черные закрашенные звезды), ДПФХ/ДПФГ 3/1 (черные пустые круги) на растворе ПДАДМАХ 0.2 мас. % и ДП-ФХ/ДПФГ 3/1 на растворе буфера (серые закрашенные круги) при деформации площади 20%. Исследования проведены при Т = 25°C.
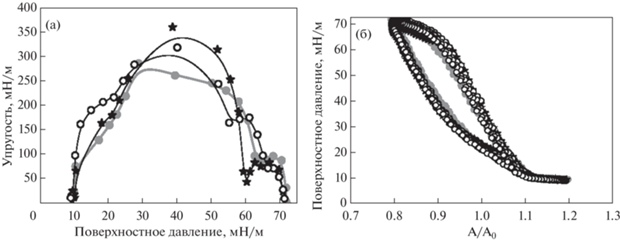
Рис. 7.
Зависимости ∆surf от поверхностного давления, измеренные в статических условиях для ДПФХ на буфере (пустые черные квадраты) и при колебаниях площади поверхности для ДПФХ на буфере (закрашенные черные квадраты), ПДАДМАХ 0.2 мас. % (серые круги), ПСС 0.2 мас. % (светло-серые треугольники).
Затем для усиления взаимодействия между макромолекулами полиэлектролита и поверхностным слоем к монослою ДПФХ был добавлен липид, который будет иметь знак заряда, противоположный полиэлектролиту ПДАДМАХ. Ранее было показано, что ПДАДМАХ адсорбируется на монослое отрицательно заряженного липида [22]. В данной работе были проведены исследования смешанных монослоев ДПФХ и ДПФГ на поверхности раствора ПДАДМАХ. Результаты измерений для монослоев ДПФХ/ДПФГ (3/1) на поверхности раствора ПДАДМАХ (0.2 мас. %) указывают на отсутствие влияния полиэлектролита, несмотря на присутствие противоположно-заряженного липида в поверхностном слое. Зависимости эффективной поверхностной упругости и отклика поверхностного слоя на деформации (рис. 6а, 6б) для смешанного монослоя на буфере и растворе полиэлектролита практически совпадают. Следовательно, одних электростатических взаимодействий между модельным монослоем липидов и макромолекулами оказывается недостаточно для образования комплексов, которые бы препятствовали снижению поверхностного давления (увеличению поверхностного натяжения) при растяжении.
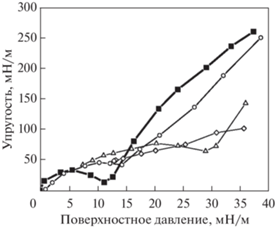
На следующем этапе было проведено исследование влияния поверхностно активного полиэлектролита ПСС на поведение монослоя ДПФХ. При малых деформациях были получены значения динамической поверхностной упругости в области малых поверхностных давлений для монослоя ДПФХ на растворах ПСС разной концентрации (рис. 8). Для самого разбавленного раствора ПСС с концентрацией 0.02 мас. %, при которой он практически не проявляет собственной поверхностной активности, зависимость поверхностной упругости монослоя ДПФХ близка к соответствующей зависимости на поверхности чистого буфера. Однако соответствующий двумерному фазовому переходу минимум на зависимости поверхностной упругости в присутствии полиэлектролита становился менее выраженным и был смещен в область более высоких поверхностных давлений. Это связано с встраиванием макромолекул в структуру липидного монослоя, когда концентрация молекул липида на поверхности мала. С увеличением концентрации полиэлектролита его влияние на свойства монослоя ДПФХ увеличиваются. При С = 0.05 мас. % минимум поверхностной упругости возникает в области давлений около 30 мН/м, а при концентрации 0.2 мас. % минимум поверхностной упругости отсутствует. Таким образом, в области малых поверхностных давлений происходит адсорбция полиэлектролита ПСС на поверхности раздела фаз. После адсорбции ПСС гидрофобные сегменты макромолекул оказываются близки к углеводородным хвостам липида, между которыми могут происходить гидрофобные взаимодействия, что может препятствовать формированию упорядоченных структур молекулами ДПФХ. Отсутствие высоко упорядоченных доменов в структуре монослоев подтверждает не только исчезновение минимума поверхностной упругости, но и более низкие значения упругости по отношению к значениям, полученным для монослоя ДПФХ в отсутствии ПСС, в области средних поверхностных давлений 30–35 мН/м.
Рис. 8.
Зависимости поверхностной динамической упругости от поверхностного давления для нанесенного монослоя ДПФХ на растворах ПСС с концентрацией 0 (закрашенные квадраты), 0.02 (круги), 0.05 (треугольники), 0.2 мас. % (ромбы) при Т = 25°C.
Присутствие ПСС в поверхностном слое при низких давлениях подтверждается изменением формы фигур Лиссажу при больших деформациях (рис. 9б). При рассмотрении фигур Лиссажу видно, что в растянутом состоянии с относительной деформацией 20% поверхностное давление монослоя ДПФХ на ПСС поднимается до 20 мН/м, в то время как давление монослоя на чистом буфере составляет 10 мН/м. Дело в том, что при концентрации ПСС 0.2 мас. % полиэлектролит имеет возможность снижать поверхностное натяжение (увеличивать давление) на 20 мН/м за счет собственной поверхностной активности. Таким образом, при растяжении и уменьшении поверхностного давления макромолекулы полиэлектролита адсорбируются на поверхности, а при сжатии, вероятно, вытесняются с нее. При высоких поверхностных давлениях результаты измерений эффективной поверхностной упругости на растворе полиэлектролита с высокой концентрацией ПСС (0.2 мас. %) и на растворе буфера оказываются близки друг к другу (рис. 9а). Это хорошо согласуется с результатами измерений отклика поверхностного слоя на периодические сжатия/растяжения, которые представлены в виде фигур Лиссажу (рис. 9б). В максимально сжатом состоянии значения поверхностного давления для монослоя достигают 72 мН/м как в присутствии полиэлектролита, так и без него. Значения ∆surf для ДПФХ на ПСС в области высоких поверхностных давлений в пределах погрешности совпадают с ∆surf для монослоя ДПФХ на буфере (рис. 7). Это подтверждает наши предположения о том, что макромолекулы ПСС вытесняются с поверхности при сжатии монослоя ДПФХ до высоких давлений, а затем адсорбируются при растяжении благодаря собственной гидрофобности, когда поверхностное давление приближается к 20 мН/м. Можно предположить, что одной поверхностной активности полиэлектролита недостаточно для образования комплексов между ДПФХ и макромолекулой полимера.
Рис. 9.
(а) Зависимости эффективной поверхностной упругости от поверхностного давления для нанесенных монослоев ДПФХ (черные закрашенные ромбы), ДПФХ/ДМЭА 3/1 (черные пустые ромбы) на растворе ПСС 0.2 мас. % и ДПФХ/ДМЭА 3/1 на растворе буфера (серые треугольники). (б) Фигуры Лиссажу для монослоев ДПФХ (черные закрашенные ромбы), ДПФХ/ДМЭА 3/1 (черные пустые ромбы) на растворе ПСС 0.2 мас. %, ДПФХ/ДМЭА 3/1 на растворе буфера (серые треугольники) при деформации площади 20%. Исследования проведены при Т = 25°C.
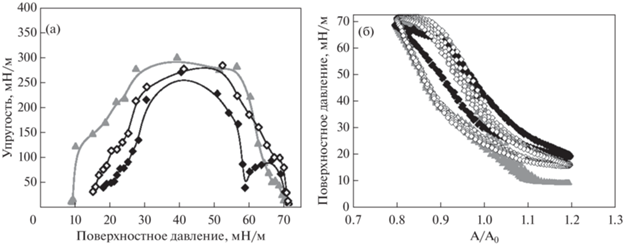
Следующим шагом стало исследование влияния дополнительного липида совместно с ДПФХ, которое может привести к усилению взаимодействия макромолекул полиэлектролита с поверхностным слоем из-за менее упорядоченной структуры липидного монослоя. Были проведены исследования поверхностных свойств смешанного монослоя ДПФХ/ДМЭА на поверхности раствора ПСС. Результаты измерений эффективной поверхностной упругости (рис. 9а) и форма отклика поверхностного слоя на деформации (рис. 9б) указывают на отсутствие образования комплексов между смешанным монослоем липидов и макромолекулами ПСС. Как и в случае однокомпонентного монослоя ДПФХ, присутствие ПСС в подложке (0.2 мас. %) препятствует снижению поверхностного давления ниже 15 мН/м при растяжении поверхностного слоя. В результате этого наблюдаются более низкие значения эффективной поверхностной упругости по сравнению с результатами, полученными для смешанного монослоя на буфере в этой области поверхностных давлений. В области высоких поверхностных давлений кривые (рис. 9а) для смешанного монослоя на буфере и на растворе ПСС оказываются близки друг к другу. Можно предположить, что при сжатии с поверхности вытесняются только макромолекулы полиэлектролита, а молекулы дополнительного липида ДМЭА остаются на поверхности.
ВЫВОДЫ
В данной работе были изучены динамические поверхностные свойства липидов, входящих в состав легочного сурфактанта, на поверхности растворов полиэлектролитов ПСС и ПДАДМАХ. Было показано, что цвиттер-ионный ДПФХ, составляющий основу легочного сурфактанта, не образует комплексы как с положительно, так и с отрицательно заряженными макромолекулами полиэлектролитов. Кроме того, присутствие в поверхностном слое липида с зарядом противоположным знаку заряда полиэлектролита, не обладающего собственной поверхностной активностью, не приводило к изменению поверхностных свойств. Можно предположить, что для образования комплексов полиэлектролит/липид, способствующих поддержанию низких значений поверхностного натяжения при деформациях, одних электростатических взаимодействий между молекулами липида и макромолекулами полиэлектролита оказывается недостаточно. Дополнительно было показано, что одной только поверхностной активности полиэлектролита и гидрофобных взаимодействий между сегментами макромолекул и молекулами липида также недостаточно для образования комплексов.
Список литературы
Echaide M., Autilio C., Arroyo R., Perez-Gil J. Restoring pulmonary surfactant membranes and films at the respiratory surface // Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes. 2017. V. 1859. № 9. P. 1725–1739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.03.015
Zuo Y.Y., Veldhuizen R.A.W., Neumann A.W. et al. Current perspectives in pulmonary surfactant — Inhibition, enhancement and evaluation // Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes. 2008. V. 1778. № 10. P. 1947–1977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.03.021
Autilio C., Perez-Gil J. Understanding the principle biophysics concepts of pulmonary surfactant in health and disease // Arch. Dis. Child Fetal. Neonatal Ed. 2018. V. 104. № 4. P. 343. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2018-315413
Raghavendran K., Willson D., Notter R.H. Surfactant therapy for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome // Crit. Care Clin. 2011. V. 27. № 3. P. 525–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2011.04.005
Martin J.A., Hamilton B.E., Sutton P.D. et al. Births: Final data for 2002 // Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2003. V. 52. № 10. P. 1–113.
Engle W.A., the Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Surfactant-replacement therapy for respiratory distress in the preterm and term neonate // Pediatrics. 2008. V. 121. № 2. P. 419–432. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2007-3283
Veldhuizen R.A.W., Zuo Y.Y., Petersen N.O. et al. The COVID-19 pandemic: A target for surfactant therapy? // Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021. V. 15. № 5. P. 597–608. https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2021.1865809
Herman L., De Smedt S.C., Raemdonck K. Pulmonary surfactant as a versatile biomaterial to fight COVID-19 // Journal of Controlled Release. 2022. V. 342. P. 170–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2021.11.023
Jeon G.W. Surfactant preparations for preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: Past, present, and future // Korean Journal of Pediatrics. 2019. V. 62. № 5. P. 155–161. https://doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2018.07185
Bae C., Chung S., Choi Y. Development of a synthetic surfactant using a surfactant protein-C peptide analog: In vitro studies of surface physical properties // Yonsei Med. J. 2016. V.57. № 1. P. 203–208. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.203
Castillo-Sánchez J.C., Cruz A., Pérez-Gil J. Structural hallmarks of lung surfactant: Lipid−protein interactions, membrane structure and future challenges // Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021. V. 703. P. 108850. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ABB.2021.108850
Goerke J. Pulmonary surfactant: Functions and molecular composition // Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease. 1998. V. 1408. № 2–3. P. 79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(98)00060-X
Lee K.Y.C. Collapse mechanisms of Langmuir monolayers // Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008. V. 59. P. 771–791. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physchem.58. 032806.104619
Schurch D., Ospina O.L., Cruz A.C., Perez-Gil J. Combined and independent action of proteins SP-B and SP-C in the surface behavior and mechanical stability of pulmonary surfactant films // Biophys. J. 2010. V. 99. № 10. P. 3290–3299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2010.09.039
Casals C., Cañadas O. Role of lipid ordered/disordered phase coexistence in pulmonary surfactant function // Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes. 2012. V. 1818. № 11. P. 2550–2562. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBAMEM.2012.05.024
Hobi N., Giolai M., Olmeda B. et al. A Small key unlocks a heavy door: The essential function of the small hydrophobic proteins SP-B and SP-C to trigger adsorption of pulmonary surfactant lamellar bodies // Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) – Molecular Cell Research. 2016. V. 1863. № 8. P. 2124–2134. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBAMCR.2016.04.028
Liekkinen J., Enkavi G., Javanainen M. et al. Surfactant lipid reorganization induced by the adsorption of the oligomeric surfactant protein B complex // J. Mol. Bi-ol. 2020. V. 432. № 10. P. 3251–3268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMB.2020.02.028
Lu K.W., Goerke J., Clements J.A., Taeusch H.W. Hyaluronan decreases surfactant inactivation in vitro // Pediatr. Res. 2005. V. 57. № 2. P. 237–241. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000150726.75308.22
Kundu S. Lipid–polyelectrolyte complexes at the air–water interface for different lipid packing // Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010. V. 368. № 1–3. P. 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2010.07.012
Chieng Y.Y., Chen S.B. Interaction between poly(acrylic acid) and phospholipid vesicles: Effect of pH, concentration, and molecular weight // J. Phys. Chem. B. 2010. V. 114. № 14. P. 4828–4835. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1002403
Bordi F., Cametti C., De Luca F. et al. Charged lipid monolayers at the air–solution interface: Coupling to polyelectrolytes // Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces. 2003. V. 29. № 2–3. P. 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7765(02)00185-6
de Meijere K., Brezesinski G., Möhwald H. Polyelectrolyte coupling to a charged lipid monolayer // Macromolecules. 1997. V. 30. № 8. P. 2337–2342. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma961490b
Brezesinski G., Kjaer K., Möhwald H. Structure studies in coupled lipid−polyelectrolyte monolayers with diluted charge densities // Langmuir. 1998. V. 14. № 15. P. 4204–4209. https://doi.org/10.1021/la9709397
Ortmann T., Ahrens H., Milewski S. et al. Lipid monolayers with adsorbed oppositely charged polyelectrolytes: Influence of reduced charge densities // Polymers. 2014. V. 6. № 7. P. 1999–2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6071999
Быков А.Г., Носков Б.А. Дилатационная поверхностная упругость растворов легочного сурфактанта в широкой области значений поверхностного натяжения // Коллоид. журн. 2021. Т. 80. № 5. С. 490–497. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1134/S0023291218050038
Bykov A.G., Loglio G., Miller R., Noskov B.A. Dilational surface elasticity of monolayers of charged polystyrene nano- and microparticles at liquid/fluid interfaces // Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015. V. 485. P. 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.09.004
Bykov A.G., Milyaeva O.Y., Isakov N.A. et al. Dynamic properties of adsorption layers of pulmonary surfactants. Influence of matter exchange with bulk phase // Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021. V. 611. P. 125851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125851
Ravera F., Miller R., Zuo Y.Y. et al. Methods and models to investigate the physicochemical functionality of pulmonary surfactant // Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021. V. 55. P. 101467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2021.101467
Motschmann H., Teppner R. Ellipsometry in interface science // Studies in Interface Science. 2001. V. 11. P. 1–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-7303(01)80014-4
Ghazvini S., Ricke B., Zasadzinski J.A., Dhar P. Monitoring phases and phase transitions in phosphatidylethanolamine monolayers using active interfacial microrheology // Soft. Matter. 2015. V. 11. № 17. P. 3313–3321. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SM02900C
Bykov A.G., Guzmán E., Rubio R.G. et al. Influence of temperature on dynamic surface properties of spread DPPC monolayers in a broad range of surface pressures // Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2019. V. 225. P. 104812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2019.104812
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Коллоидный журнал


