Известия РАН. Серия географическая, 2022, T. 86, № 6, стр. 845-847
От редакторов выпуска
- EDN: JSBTZU
- DOI: 10.31857/S2587556622060115
В сентябре 2021 г. на базе Беломорской биологической станции (ББС) МГУ имени М.В. Ломоносова прошла Всероссийская научная конференция “Белое море в плейстоцене, голоцене и антропоцене”, организованная совместными усилиями Института географии РАН, Центра морских исследований МГУ и ББС МГУ. Основной темой конференции была палеогеографическая модель развития Белого моря в позднем неоплейстоцене–голоцене, включающая в себя представления о геологических и геоморфологических процессах, формировавших беломорскую депрессию, ландшафты побережья и прибрежья; о хронологии важнейших геолого-геоморфологических событий; о гидрологических процессах, влияющих на седиментацию, соленость и другие параметры водных масс Белого моря. Во время конференции ее участники рассмотрели важнейшие результаты и новые данные, полученные разными научными группами по указанным проблемам. На конференции обсуждался и еще один аспект комплексного изучения палеогеографии и современного развития Белого моря, который связан с разработкой проекта разнопланового мониторинга на нескольких его участках в соответствии с исследовательскими целями разных научных групп.
Актуальность и активизация таких исследований в последнее время объясняются повышенным интересом научной (и не только) общественности к изучению разноплановых ресурсов окраинных морей Северного Ледовитого океана, а особый интерес именно к Белому морю связан с тем, что это полностью российское арктическое море. Сложная структурная позиция его котловины и побережья в пределах активно поднимающегося Балтийского (Фенноскандинавского) кристаллического щита, практически стабильной Русской плиты и частично Баренцевоморской плиты делают его уникальным объектом разноплановых исследований в области наук о Земле, которые, имея двухвековую историю, в последние десятилетия приобрели междисциплинарный характер.
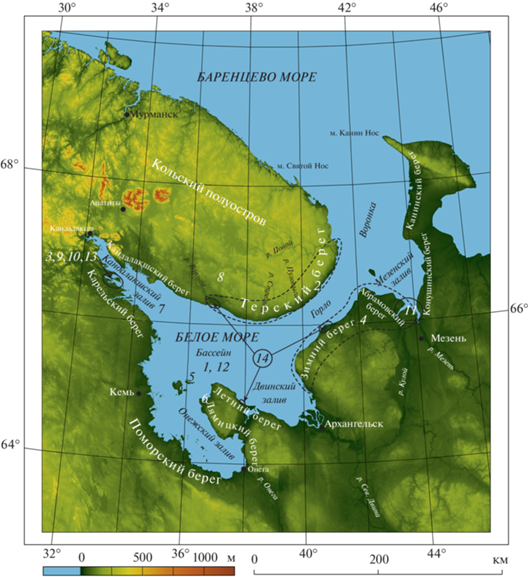
Предлагаемый выпуск журнала “Известия Российской академии наук. Серия географическая” сформирован на основе материалов, отобранных Оргкомитетом конференции. Тематика этого специального выпуска соответствует названию Всероссийской научной конференции 2021 г. В представленных статьях содержатся оригинальные результаты и научные обзоры, отражающие комплекс междисциплинарных исследований, проводимых как в самом Белом море, так и на его побережье (рис. 1). Сюда входят история его изучения, новые данные по четвертичной стратиграфии, палеогеографии и геохронологии. Часть статей посвящена новейшей тектонике региона, реконструкциям относительного перемещения береговой линии Белого моря после его дегляциации и истории изолированных бассейнов, в том числе меромиктических озер, а также развитию приморских болотных ландшафтов. Несколько статей освещают особенности современной седиментации в бассейне Белого моря и в устьях впадающих в него крупных рек. Особого внимания заслуживают публикации, посвященные взаимодействию природы и человека в беломорском регионе. Это и заселение региона первобытным человеком в условиях меняющейся береговой линии моря, и влияние современного человека на природные процессы и ландшафты берегов Белого моря.
Следует отметить, что многие результаты исследований, представленные в статьях данного выпуска журнала, были получены при поддержке научных фондов, таких как РФФИ (гранты 20-05-613, 19-05-00377) и РНФ (гранты 19-17-00234, 22-17-00081, 22-27-00499), которым авторы статей выражают свою благодарность.
Н.Е. Зарецкая, Институт географии РАН; Геологический институт РАН
Е.Д. Краснова, Беломорская биологическая станция МГУ; биологический факультет МГУ имени М.В. Ломоносова
О.П. Корсакова, Геологический институт Кольского научного центра РАН
А.Е. Рыбалко, ВНИИОкеангеология
Рис. 1.
Белое море и его побережье с районами, результаты изучения которых представлены в настоящем выпуске журнала. Цифровая модель рельефа по (Farr T.G., Rosen P.A., Caro E., et al. The shuttle radar topography mission // Reviews of geophysics. 2007. Vol. 45, Iss. 2. P. 1–33. https://doi.org/:10.1029/2005RG000183). Пунктирными линиями ограничены крупные районы исследований, сплошными – более мелкие. Цифрами обозначены ключевые участки Беломорского региона, отраженные в следующих публикациях настоящего cпецвыпуска: 1 – Рыбалко и др.; 2 – Корсакова; 3 – Бондарь, Гордеев; 4 – Зарецкая и др.; 5 – Кузнецов и др.; 6 – Леонтьев и др.; 7 – Кутенков и др.; 8 – Потапович и др.; 9 ‒ Краснова и др.; 10 – Плотников и др.; 11 – Демиденко; 12 – Новигатский и др.; 13 – Жульников; 14 – Репкина и др.
Fig. 1. The White Sea and its coasts with the studied areas, presented in the issue. Digital elevation model after (Farr T.G., Rosen P.A., Caro E., et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Reviews of geophysics, 2007, 45 (2), pp. 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005RG000183). Dashed lines delineate large study areas, solid lines delineate smaller ones. Numerals indicate the key areas of the White Sea region highlighted in this special issue: 1 – Rybalko et al.; 2 – Korsakova; 3 – Bondar and Gordeev; 4 –Zaretskaya et al.; 5 – Kuznetsov et al.; 6 – Leontiev et al.; 7 – Kutenkov et al.; 8 – Potapovich et al.; 9 – Krasnova et al.; 10 – Plotnikov et al.; 11 – Demidenko; 12 – Novigatsky et al.; 13 – Zhulnikov; 14 – Repkina et al.
EDITORS’ FOREWORD
In September 2021, the White Sea Biological Station (WSBS) of the Moscow State University hosted the All-Russian Scientific Conference “White Sea in the Pleistocene, Holocene and Anthropocene,” organized by the joint efforts of the Institute of Geography of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Center for Marine Research of the Moscow State University and the WSBS. The main topic of the conference was the paleogeographical model of the development of the White Sea in the Late Pleistocene–Holocene, which includes ideas about the geological and geomorphological processes that formed the White Sea depression, coastal and offshore landscapes, about the chronology of the most important geological and geomorphological events, as well as hydrological processes affecting sedimentation, salinity and other parameters of the White Sea water masses. During the conference, attendees discussed the most important results and new data on the mentioned challenges, which were obtained by various research teams. Another aspect of the complex study of paleogeography and the modern development of the White Sea, which is associated with the development of a project for diverse monitoring in several key areas in accordance with the research goals of different scientific groups, was also discussed at the conference.
The relevance and intensification of such kind of research have recently been explained by the increased interest of the scientific (and not only) community in the study of the diverse resources of the marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, and the special attention to the White Sea is due to the fact that it is a completely Russian Arctic sea. Complicated structure pattern of its basin and coasts within the actively uplifting Baltic (Fennoscandinavian) crystalline shield, the practically stable Russian Plate and partially the Barents Sea Plate makes the White Sea an unique object of diverse studies in the field of Earth sciences, which have acquired an interdisciplinary character only in recent decades, despite two-centuries research.
The presented issue of “Izvestiya Rossiiskoi Akademii Nauk. Seriya Geograficheskaya” includes the materials selected by the Conference Organizing Committee. The subjects of the issue correspond to the theme of the All-Russian Scientific Conference 2021. The presented articles contain original data and scientific reviews obtained as a result of a complex of interdisciplinary studies conducted both in the White Sea itself and on its coasts (Fig. 1). This includes the history of its study, new data on Quaternary stratigraphy, paleogeography and geochronology. Some of the articles are devoted to the neotectonics of the region, reconstructions of the relative White Sea level after deglaciation and the history of isolated basins, including meromictic lakes, as well as the evolution of maritime marsh landscapes. Several articles deal with the features of modern sedimentation in the White Sea basin and in the mouths of the inflowing great rivers. The articles devoted to the interaction between the nature and man in the White Sea region deserve special attention. This is the settlement of the region by prehistoric people in the conditions of the sea coastline changes, and the influence of modern man on natural processes and landscapes of the White Sea shores.
It should be noted that many of the research results, presented in the articles of the special issue were obtained with the financial support of scientific foundations, such as the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grants nos. 20-05-613 and 19-05-00377) and the Russian Science Foundation (grants nos. 19-17-00234, 22-17-00081, and 22-27-00499) acknowledged by the authors.
N.E. Zaretskaya, Institute of Geography of the Russian Academy of Sciences; Geological Institute of RAS
E.D. Krasnova, White Sea Biological Station; Department of Biology, Moscow State University
O.P. Korsakova, Geological Institute of the Kola Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences
A.E. Rybalko, VNIIOkeangeologia
Список литературы отсутствует.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Известия РАН. Серия географическая


