Микробиология, 2023, T. 92, № 3, стр. 310-317
Биодеструкция эфиров фталевой кислоты грибом белой гнили Peniophora lycii
О. С. Савинова a, А. В. Шабаев a, Т. В. Федорова a, *
a Институт биохимии им. А.Н. Баха, ФИЦ “Фундаментальные основы биотехнологии”
Российской академии наук
119071 Москва, Россия
* E-mail: fedorova_tv@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 15.12.2022
После доработки 17.01.2023
Принята к публикации 19.01.2023
- EDN: FWTPAT
- DOI: 10.31857/S0026365622600857
Аннотация
Впервые изучена способность гриба белой гнили Peniophora lycii LE-BIN 2142 к деструкции эфиров фталевой кислоты (ЭФК), таких как диэтилфталат (ДЭФ), дибутилфталат (ДБФ), ди(2-этилгексил)фталат (ДЭГФ), диизобутилфталат (ДиБФ) и бутилбензилфталат (ББФ). Показано, что ДЭГФ наиболее эффективно подвергался биодеструкции грибом (более 98% на 6 сут культивирования). Остаточное содержание ДБФ и ДиБФ в культуральной жидкости на 10 сут составляло 17‒18%. ББФ оказался наиболее трудно деградируемым соединением – его остаточное содержание на 10 сут культивирования P. lycii составляло около 40%. ДЭФ был устойчив к биодеструкции и в концентрации 1.5 г/л оказывал токсическое действие: скорость радиального роста гриба на агаризованной среде снижалась в 3 раза по сравнению с контролем, а количество грибной биомассы при жидкофазном глубинном культивировании – примерно в 1.5 раза. В процессе культивирования P. lycii на средах с ЭФК было показано увеличение примерно в 2 раза эстеразной и значительное снижение (в 2‒4 раза) оксидазной активностей по сравнению с контрольной средой без фталатов.
Эфиры фталевой кислоты (ЭФК, фталаты) – токсичные соединения, широко используемые для производства различных полимеров, резин, пластмасс, красок, изделий медицинского назначения, а также продукции для личной гигиены (Weaver et al., 2020; Tran et al., 2022). Попадая в окружающую среду, они оказывают негативное влияние на микробные сообщества почвы, круговорот питательных веществ, а также наносят вред здоровью животных и человека, в частности, приводят к нарушению работы эндокринной системы (т.н. “эндокринные разрушители”) (de Souza Machado et al., 2019; Iqbal et al., 2020). Неблагоприятными последствиями этого может являться изменения фертильности сперматозоидов, нарушения работы половых органов, эндометриоз, раннее половое созревание, дисфункции нервной системы, ослабление иммунитета, аллергии, респираторные и сердечно-сосудистые заболевания и многое другое (Tran et al., 2022). Широкое распространение токсичных эндокринных разрушителей в окружающей среде повышает актуальность исследований, направленных на разработку эффективных способов их удаления из загрязненных объектов. Для удаления фталатов из окружающей среды предложены различные физико-химические (абиотические) способы, например, фотохимическое разрушение, фотокаталитическое озонирование, сонолитическое разрушение (под воздействием ультразвука), химическая минерализация и ряд других методов (Das et al., 2021). Однако разрушение фталатов микроорганизмами считается наиболее эффективным, экологически безопасным и экономичным процессом, чем вышеупомянутые абиотические подходы (Boll et al., 2020). При этом биоремедиация ЭФК с использованием грибов (микоремедиация), в т.ч. базидиомицетов, имеет ряд преимуществ перед бактериальной деструкцией фталатов, в первую очередь, из-за бóльшего разнообразия протекающих ферментативных процессов и, как следствие, более выраженной способности грибов к разрушению фталатов (Akerman-Sanchez et al., 2021). Помимо ферментативных процессов значительный вклад в эффективность микоремедиации вносит биосорбция фталатов на поверхности грибного мицелия. Так, ранее сообщалось о высоких скоростях биотрансформации ЭФК, проявляющих сильную сорбцию на поверхности грибных клеток (Hofmann, Schlosser, 2016; Carstens et al., 2020).
В последнее время активно изучаются процессы биодеструкции ЭФК с использованием грибов белой гнили, принадлежащих к различным видам, таких как Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Polyporus brumalis, Pleurotus eryngii, P. djamor, P. ostreatus, Au-ricularia polytricha, Trametes versicolor и др. (Naveen et al., 2022). Показано, что способность грибов к биодеструкции ЭФК зависит от штамма, при этом за деградацию фталатов ответственны как внеклеточные, так и внутриклеточные ферменты. Комплекс секретируемых ферментов грибов белой гнили включает гидролитические и неспецифические окислительные ферменты, которые образуют так называемую лигнинолитическую ферментативную систему грибов. Данная система преимущественно представлена марганец пероксидазами, лигнин пероксидазами и лакказами, обладающими широкой субстратной специфичностью и способностью разрушать соединения со сложной химической структурой (Chang et al., 2021). Одними из таких грибов-деструкторов являются представители рода Trametes sp., способные разрушать различные токсичные соединения (Moiseenko et al., 2019). Однако известны и другие виды грибов белой гнили, в составе лигнинолитической ферментативной системы которых пероксидазы не обнаружены, например, представители рода Peniophora sp. (Brenelli et al., 2019; Ma et al., 2021; Shabaev et al., 2022). В связи с этим оценка эффективности биодеградации ЭФК грибами рода Peniophora представляется интересной.
Следует отметить, что внутриклеточная ферментативная система грибов включает белки семейства цитохромов Р450 (гемсодержащие монооксигеназы), которые также могут играть важную роль в механизме детоксикации ЭФК (Naveen et al., 2022).
Ранее нами были исследованы несколько видов грибов белой гнили из разных экофизиологических групп и показано, что базидиомицет Trametes hirsuta LE-BIN 072 (первичный дереворазрушающий сапротроф) является одним из перспективных штаммом для биоремедиации ЭФК (Савинова и соавт., 2022). Основными секретируемыми белками данного гриба являются различные пероксидазы и лакказа (Shabaev et al., 2022). Также нами было обнаружено, что лигнинолитическая ферментативная система другого гриба белой гнили, Peniophora lycii LE-BIN 2142, характеризуется полным отсутствием пероксидаз, но при этом включает не описанный ранее белок (FAD-binding domain-containing protein) и лакказу.
Целью исследования было оценить способность гриба белой гнили P. lycii LE-BIN 2142 осуществлять процесс биодеградации ЭФК и провести сравнение эффективности данного процесса для P. lycii LE-BIN 2142 и T. hirsuta LE-BIN 072. В исследовании применялись наиболее опасные соединения из класса фталатов, такие как диэтилфталат (ДЭФ), дибутилфталат (ДБФ), ди(2-этилгексил)фталат (ДЭГФ), диизобутилфталат (ДиБФ) и бензилбутилфталат (ББФ) (рис. 1), широко используемые в различных отраслях промышленности (Dutta et al., 2020).
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Реактивы. В работе использовали ДЭФ, ДБФ, ДЭГФ, ДиБФ и ББФ фирмы “Sigma-Aldrich” (США). Другие материалы и растворители квалификации “х. ч.” и “ч. д. а.” были приобретены у российских производителей.
Условия культивирования. Штамм базидиомицета P. lycii LE-BIN 2142 получен из Коллекции культур Ботанического института им. В.Л. Комарова (Санкт-Петербург, Россия).
Для оценки роста в присутствии ЭФК и определения общей оксидазной активности грибную культуру выращивали на твердой среде следующего состава (г/л): неохмеленный солодовый экстракт Maltax 10 (“OY Maltax AB”, Финляндия) – 50; агар-агар – 20; рН 6.0. В стерильную охлажденную до 40‒50°С среду вносили ЭФК в концентрациях: 0.5, 1.0 и 1.5 г/л. Среды с внесенными ЭФК обрабатывали в ультразвуковой бане при 50°С в течение 5 мин. На подготовленные чашки Петри засевали мицелиальные блоки (d = 8 мм) гриба и инкубировали в термостате при температуре 25°С, измеряя в процессе роста диаметр мицелиального мата.
Инокулят гриба выращивали стационарно в конических колбах объемом 750 мл с фарфоровыми бусами в глюкозо-пептонной среде следующего состава (г/л): пептон – 3.0, глюкоза – 10, KH2PO4 – 0.6, K2HPO4 · 3H2O – 0.4, MgSO4 · 7H2O – 0.5, CaCl2 – 0.5, MnSO4 · 5H2O – 0.05, ZnSO4 – 0.001, FeSO4 – 0.0005, при температуре 25°С в течение 10‒14 сут в зависимости от скорости роста гриба. Посевной материал измельчали с помощью бус (20 мин, 180 об./мин) до получения однородной суспензии, которую затем в объеме 10% стерильно вносили в колбы для культивирования.
Грибную культуру выращивали глубинным способом в глюкозо-пептонной среде на роторной качалке при 180 об./мин и температуре 27°C. Выросшие грибные пеллеты отделяли фильтрованием и промывали 0.02%-м стерильным водным раствором Твин 80, после чего 10 г грибной биомассы стерильно переносили в конические колбы объемом 250 мл со 100 мл жидкой минеральной среды следующего состава (г/л): KH2PO4 – 0.6, K2HPO4 – 0.4, MgSO4 · 7H2O – 0.5, CaCl2 – 0.05, MnSO4 – 0.05, ZnSO4 – 0.001, FeSO4 – 0.0005, NaNO3 – 3.0, глюкоза – 10.0, Твин 80 – 0.2. Перед внесением грибной биомассы в колбы стерильно добавляли растворы ЭФК в концентрации 1.0 г/л, инкубировали на роторной качалке при 100 об./мин и температуре 25°C. Образцы культуральной жидкости отбирали на 1, 2, 3, 6 и 10 сут инкубации и хранили при –73°C до проведения эксперимента. Грибную биомассу отделяли фильтрованием и высушивали при температуре 100 ± 5°С до постоянной массы.
Скорость радиального роста (ur) рассчитывали по графику зависимости диаметра колонии от времени роста с анализом линейной регрессии. Диаметр колоний измеряли с помощью линейки с первых суток инкубации до полного покрытия поверхности чашки Петри мицелиальным матом (Suárez-Segundo et al., 2013).
Общая эстеразная активность. Оценку эстеразной активности проводили при культивировании грибов в жидкой минеральной среде, содержащей 1.0 г/л фталатов. Активность определяли с использованием спектрофотометра PerkinElmer Lambda 35 (“PerkinElmer”, США), используя п‑нитрофенил бутират (“Sigma-Aldrich”, США) в качестве субстрата, согласно руководству (Синицын и соавт., 1995). Реакцию проводили в натрий-ацетатном буфере рН 4.5 при температуре 40°С в течение 10 мин. Для остановки реакции использовали натрий-фосфатный буфер (рН 7.3), значение оптической плотности определяли при длине волны 400 нм. Расчет эстеразной активности проводили по формуле:
где RЕ – предварительное разбавление образца перед внесением в раствор субстрата;
А400(S) – контроль, в котором вместо образца использовали воду (~0.05‒0.3 опт. ед.);
А400(Е) – контроль без внесения в реакционную смесь субстрата.
Определение общей оксидазной активности. Грибную культуру выращивали в жидкой минеральной среде, содержащей 1.0 г/л фталатов. Оксидазную автивность определяли с помощью спектрофотометра Lambda 35 (“Perkin Elmer”, США) при длине волны 436 нм в 0.1 М натрий-ацетатном буфере (рН 4.5), как описано в работе (Савинова и соавт., 2022) с использованием раствора 2,2'-азино-бис-(3-этилбензтиозолин-6-сульфокислоты) диаммониевой соли (АБТС) в качестве хромогенного субстрата. За 1 условную единицу активности принимали увеличение оптической плотности в 1 мл реакционной смеси за 1 мин.
Газовая хроматография с масс-спектрометрической детекцией (ГХ-МС). Оценку скорости биодеструкции ЭФК в процессе культивирования грибной культуры проводили с использованием метода ГХ-МС, как описано ранее (Савинова и соавт., 2022). Для этого получали гексановые экстракты образцов культуральной жидкости (1 : 1; об./об.), которые анализировали методом газо-жидкостной хроматографии в двух режимах: регистрация ионных масс в полном спектре (TIC, диапазон масс m/z 45–400) и регистрация по характерному для ЭФК основному иону (MIC, m/z = 149 – протонированный фталевый ангидрид).
Анализ проводили с использованием газового хроматографа GC-MS QP 2010 Ultra EI (“Shimadzu”, Япония), снабженного автоматическим устройством ввода пробы и квадрупольным масс-спектрометрическим детектором. Сбор данных и обработку хроматограмм проводили с помощью программного обеспечения LabSolutions GCMSsolution (“Shimadzu”, Япония). Использовали колонку MDN-5 30 м × 250 мкм × 0.25 мкм (“Supelco”, США), подвижная фаза – гелий, скорость потока элюента 1 см3/мин, деление потока 1 : 5. Объем вводимой пробы 1 мкл, температура термостата 120°С, температура инжектора 200°С. Температурный градиент: 120°С, выдержка 1 мин; с 120 до 280°С со скоростью 10°С/мин, изотерма 3 мин.
Все измерения проводили в 3-х независимых повторностях. Результаты представлены в виде среднего значения ± стандартное отклонение. При статистической обработке данных использовали метод дисперсионного анализа. При обнаружении достоверного значения (р < 0.05) F-статистики, различия между индивидуальными средними оценивали с использованием теста множественного сравнения Тьюки (р ≤ 0.05).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Влияние различных концентраций ЭФК в агаризованной среде на рост P. lycii. Известно, что исходная концентрация ЭФК в окружающей среде влияет на способность микроорганизмов к биодеградации фталатов (Suárez-Segundo et al., 2013; González-Márquez et al., 2015). Экстремальные концентрации загрязняющих веществ трудно поддаются деструкции большинством организмов, поэтому было проведено исследование влияния разных концентраций фталатов на ростовые характеристики штамма P. lycii LE-BIN 2142. В табл. 1 представлены скорости радиального роста грибной культуры на средах с ДЭФ, ДБФ, ДЭГФ, ДиБФ и ББФ в диапазоне концентраций от 0.5 до 1.5 г/л.
Таблица 1.
Скорость радиального роста (ur, мм/сут) гриба белой гнили P. lycii на агаризованной среде с разным содержанием ЭФК
| Концентрация ЭФК, г/л | ДЭФ | ДБФ | ДЭГФ | ДиБФ | ББФ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (контроль) | 5.85 ± 0.25 | 5.85 ± 0.25 | 5.85 ± 0.25 | 5.85 ± 0.25 | 5.85 ± 0.25 |
| 0.5 | 5.92 ± 0.23 | 4.68 ± 0.19 | 4.46 ± 0.29 | 3.97 ± 0.32 | 4.16 ± 0.27 |
| 1.0 | 2.88 ± 0.12 | 4.50 ± 0.18 | 6.01 ± 0.33 | 3.82 ± 0.36 | 4.42 ± 0.24 |
| 1.5 | 1.46 ± 0.06 | 4.33 ± 0.19 | 6.29 ± 0.31 | 3.80 ± 0.28 | 3.95 ± 0.21 |
Показано, что с увеличением концентраций большинства ЭФК в среде культивирования наблюдалось замедление скорости роста P. lycii. Наибольшее ингибирование роста гриба отмечено на среде с ДЭФ: при концентрации 1.5 г/л скорость роста P. lycii снижалась в 4 раза по сравнению с контролем (табл. 1), тогда как увеличение содержания в ростовой среде ДБФ, ДиБФ и ББФ до 1.5 г/л приводило к незначительному снижению скорости роста. Иная картина наблюдалась при росте P. lycii на среде с ДЭГФ: скорость роста гриба в присутствии 0.5 г/л ЭФК несколько снижалась по сравнению с ростом на среде без ЭФК. При дальнейшем увеличении концентрации ДЭГФ до 1.0 и 1.5 г/л, напротив, показано увеличение радиальной скорости роста гриба по отношению к контрольной среде. Увеличение скорости роста при повышении содержания ДЭГФ в средах было также отмечено для других видов грибов белой гнили, таких как Agrocybe praecox, Trametes hirsuta, Pleurotus pulmonarius, P. ostreatus и Lentinula edodes (Suárez-Segundo et al., 2013; González-Márquez et al., 2015; Савинова и соавт., 2022). Выдвинуто предположение, что грибы могут использовать фталаты в качестве источника углерода и энергии для своего роста и развития.
Влияние ЭФК на рост P. lycii при жидкофазном глубинном культивировании в минеральной среде с глюкозой. На следующем этапе исследовали способность гриба P. lycii к биодеструкции фталатов в жидких средах с глюкозой в присутствии фталатов в концентрации 1 г/л. Как было показано выше, данная концентрация не приводила к значительному ингибированию роста гриба. Увеличение биомассы P. lycii наблюдалось в течение 10 сут культивирования как на контрольной среде, так и на средах с ЭФК, однако динамика накопления биомассы различалась (рис. 2). Наименьший прирост биомассы был отмечен на среде с ДЭФ: количество биомассы в конце культивирования было в 1.4 раза ниже максимального количества на контрольной среде. На средах с ДБФ, ДЭГФ, ДиБФ и ББФ количество биомассы на 10 сут культивирования составляло около 0.6 г, что соответствовало максимальному значению на контрольной среде на 6 сут роста гриба. Таким образом, в присутствии всех ЭФК наблюдалось замедление прироста биомассы P. lycii, по сравнению с контрольной средой. Причем на среде с ДЭФ биомасса увеличивалась к 3 сут, далее практически не менялась, что согласуется с результатами по ингибированию роста гриба на агаризованной среде с ДЭФ. В присутствии других ЭФК рост биомассы P. lycii продолжался в течение всего периода культивирования, и на 10 сут количество биомассы достигало максимальных контрольных значений на 6 сут. Причем в конце культивирования (на 10 сут) на контрольной среде наблюдался лизис грибной культуры.
Рис. 2.
Диаграмма накопления биомассы по весу абсолютно сухой биомассы (г АСВ/л) при росте гриба Peniophora lycii в средах с ЭФК (1 г/л): К – контрольная среда без добавления ЭФК; 0 – количество внесенной грибной биомассы в расчете на АСВ мицелия в начале культивирования; 3, 6 и 10 – грибная биомасса на 3, 6 и 10 сут культивирования соответственно.
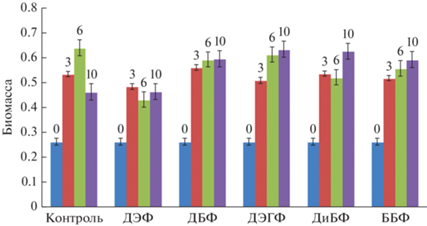
Ранее мы показали, что у гриба T. hirsuta в присутствии 1 г/л ДЭФ в аналогичной ростовой среде прирост биомассы не наблюдался в течение всего периода культивирования (10 сут) (Савинова и соавт., 2022), в отличие от гриба P. lycii, у которого на 3 сут биомасса увеличивалась в 2 раза и далее до конца культивирования не менялась. В присутствии ДБФ в такой же концентрации биомасса T. hirsuta увеличивалась примерно в 1.5 раза к концу периода культивирования, а биомасса P. lycii – в 2.3 раза. Аналогичная тенденция наблюдалась и для ДиБФ – прирост биомассы выше у P. lycii (увеличивался в 2.5 раза) по сравнению с T. hirsuta (в 1.8 раз). Что касается ДЭГФ и ББФ, то здесь у обоих грибов биомасса увеличивалась одинаково (примерно вдвое) к концу культивирования на 10 сут.
Влияние ЭФК на рН и активность секретируемых ферментов при глубинном жидкофазном культивировании P. lycii в минеральной среде с глюкозой. Известно, что на начальной стадии ключевыми ферментами, участвующими в деградации ЭФК, являются эстеразы (Changet et al., 2021). Они осуществляют гидролитическое расщепление сложноэфирной связи между боковыми алкильными цепями и ароматическим кольцом ЭФК с образованием спиртов и моноэфиров. Затем происходит гидролиз последних до фталевой кислоты, после чего бензольное кольцо фталевой кислоты может расщепляться с образованием различных метаболитов. На данной стадии в биодеструкцию могут быть вовлечены такие ферменты, как декарбоксилазы, оксигеназы, оксидазы/дегидрогеназы и др. (Gao, Wen, 2016; Ahmadi et al., 2017; Tang et al., 2017; Ahuactzin-Perez et al., 2018).
В ходе жидкофазного культивирования гриба P. lycii в средах с ЭФК, за исключением ДЭФ, наблюдалось постепенное снижение рН (рис. 3а). Наибольшее закисление среды отмечено в среде с ДЭГФ (рН в конце культивирования около 3.5), в средах с ДБФ, ДиБФ и ББФ – рН около 4.0 (рис. 3а). При этом в среде с ДЭФ значение рН культуральной жидкости в первые 3 сут культивирования несколько повышалось (с 5.0 до 5.5); на 6 сут снова снижалось (до 5.0) и далее до конца культивирования не менялось. При этом оксидазная активность в образцах с ДЭФ практически не детектировалась, в то время как эстеразная активность в первые сутки культивирования вырастала до значения 0.1 ед./мл и до конца культивирования оставалась на данном уровне, что превышало контрольные значения эстеразной активности в 2.5 раза (рис. 3б). Самая высокая эстеразная активность детектировалась в средах с ДиБФ и ДЭГФ, пик активности которых приходился на 2 и 3 сут культивирования соответственно, достигая значения около 0.12 ед./мл, после чего активность снижалась. Аналогичная динамика изменения эстеразной активности была в средах с ББФ и ДБФ, с пиками активности на 1 и 3 сут (рис. 3б). Следует отметить, что в целом эстеразная активность штамма возрастала в средах с ЭФК (особенно в начале культивирования), а оксидазная активность, наоборот, снижалась (рис. 3в).
Рис. 3.
Динамика рН (а), оксидазной (б) и эстеразной (в) активностей в процессе жидкофазного культивирования гриба белой гнили Peniophora lycii в контрольной среде и средах с добавлением ЭФК (1 г/л). 1 ‒ контрольная среда; 2 ‒ среда с ДЭФ; 3 ‒ с ДБФ; 4 ‒ с ДЭГФ; 5 ‒ с ДиБФ; 6 ‒ с ББФ.
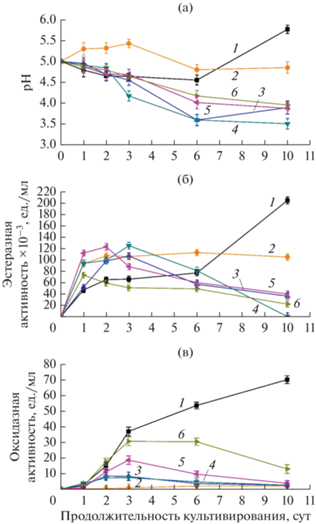
Таким образом, для гриба P. lycii во всех средах (за исключением ДЭФ) сохранялась общая тенденция к снижению значений рН в процессе культивирования до 3.5‒4.0. Этот результат коррелирует с существенным падением эстеразной активности к 10 сут культивирования. Известно, что гидролиз ЭФК в щелочной среде проходит более интенсивно, чем в кислой. Ранее мы показали (Савинова и соавт., 2022), что гриб белой гнили T. hirsuta в динамике роста в средах с ЭФК закисляет среду до значений рН 4.3−4.5; при этом отмечается сильная (в 7‒8 раз) индукция оксидазной активности по сравнению с контролем (за исключением среды с ДЭГФ), в отличие от P. lycii, чья окислительная активность в присутствии фталатов падает. Такое различие в профилях ферментативных активностей говорит о реализации разных механизмов деструкции ЭФК у двух грибов белой гнили P. lycii и T. hirsuta.
Эффективность биодеструкции ЭФК грибом P. lycii при жидкофазном глубинном культивировании в минеральной среде с глюкозой. Анализ экстрактов культуральной жидкости P. lycii методом ГХ-МС показал, что ДЭФ в концентрации 1 г/л практически не подвергался биодеструкции грибом – остаточное количество данного фталата на 10 сут культивирования составляло ~92‒95%. Полученные данные коррелируют со значительным снижением скорости роста P. lycii на агаризованной среде и накоплением биомассы в жидкой среде с ДЭФ в концентрации 1 г/л. Существенного убывания ДЭФ во времени не было зафиксировано и при культивировании гриба T. hirsuta (Савинова и соавт., 2022). Похожие результаты были получены в работе (Hwang et al., 2008), в которой грибы белой гнили P. ostreatus и T. versicolor менее эффективно деградировали ДЭФ, по сравнению с диметилфталатом и ББФ. Наиболее трудно деградируемым и токсичным для грибов белой гнили, очевидно, является ДЭФ, что подтверждается известными значениями токсичности использованных ЭФК: токсичность убывает в ряду ДЭФ > ДБФ > ДЭГФ (Шкаева и соавт., 2019).
Динамика деструкции ДБФ, ДЭГФ, ДиБФ и ББФ грибом P. lycii представлена в табл. 2. Показано, что наиболее эффективно гриб P. lycii разрушает ДЭФГ (более 99% на 10 сут), а наименее эффективно − ББФ (около 60% на 10 сут). Эффективность биодеструкции ДБФ и ДиБФ была сопоставима и составляла около 80% на 10 сут культивирования. Как показали наши предыдущие исследования, эффективность деструкции данных ЭФК грибом T. hirsuta была выше, чем при использовании P. lycii, особенно в отношении ББФ (табл. 2). При этом скорости деструкции ДБФ и ДЭГФ этими двумя грибами сопоставимы. Показано, что в процессе деструкции ЭФК грибом P. lycii участвуют преимущественно гидролитические ферменты (эстеразы, липазы), а грибом T. hirsuta ‒ окислительные ферменты (марганец пероксидазы, лигнин пероксидаза и лакказа) (Savinova et al., 2022). Очевидно, что профиль метаболитов у разных грибов должен различаться. Примечательно, что при примерно равной скорости деструкции ДБФ прирост биомассы на 10 сут культивирования у гриба P. lycii был выше, чем у T. hirsuta (биомасса увеличивается в 2.3 и 1.5 раза соответственно). Схожая картина наблюдалась в присутствии ДиБФ и ББФ. Прирост биомассы у P. lycii был выше в присутствии ДиБФ и ББФ по сравнению с T. hirsuta, а скорость деструкции фталатов грибами P. lycii и T. hirsuta ниже – 80 и 95% на 10 сут в среде с ДиБФ, около 60 и почти 100% в среде с ББФ соответственно (табл. 2).
Таблица 2.
Динамика биодеградации ЭФК (1 г/л) грибами белой гнили Peniophora lycii (Pl) и Trametes hirsuta (Th) в процессе жидкофазного глубинного культивирования
| Время, сут | Остаточное количество ЭФК*, % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ДБФ | ДЭГФ | ББФ | ДиБФ | |||||
| Pl | Th** | Pl | Th** | Pl | Th** | Pl | Th** | |
| 3 | 53.3 ± 1.8 | 34.0 ± 2.0 | 22.3 ± 1.5 | 60.8 ± 1.9 | 89.2 ± 2.3 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 60.0 ± 1.8 | 19.0 ± 1.2 |
| 6 | 19.8 ± 1.3 | 21.7 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 7.4 ± 0.2 | 65.5 ± 1.7 | 0.2 ± 0.05 | 38.8 ± 1.5 | 8.0 ± 0.6 |
| 10 | 17.8 ± 0.9 | 11.8 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 40.5 ± 1.2 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 19.3 ± 0.8 | 4.8 ± 0.3 |
По нашим данным, деструкция ЭФК при участии окислительных лигнолитических ферментов протекает более эффективно, чем при наличии ферментов преимущественно гидролитического действия. Однако образующиеся в результате окислительных реакций метаболиты могут оказаться более токсичными как для окружающей среды, так и для самих грибов. Например, в культуральной жидкости гриба T. hirsuta, выращенного в присутствии ДБФ и ДЭГФ, обнаружен 2,6-дитретбутил-4-метилфенол (ионол), отсутствующий в контрольных образцах (Савинова и соавт., 2022). Ионол часто встречается в качестве вторичного метаболита, продуцируемого различными группами организмов, в частности, грибами, однако является аутотоксичным (Zhao et al., 2020). Предположительно, индукция биосинтеза ионола грибами является своеобразной защитной реакцией от свободных радикалов, образующихся в результате ферментативного окисления ЭФК. Однако, ввиду своей аутотоксичности, накопление ионола в ходе биотрансформации фталатов T. hirsuta может приводить к торможению роста гриба.
Таким образом, эффективность биодеструкции ЭФК с помощью грибов разных экофизиологических групп может сильно варьировать, что обусловлено существенными различиями в составе и композиции их секретируемых и внутриклеточных мультиферментных комплексов. Полученные результаты могут быть использованы для установления механизмов биоразложения ЭФК различными грибами белой гнили. Также результаты могут быть приняты во внимание при отборе конкретных штаммов базидиальных грибов для использования с целью биоремедиации.
Список литературы
Савинова О.С., Шабаев А.В., Глазунова О.А., Еремин С.А., Федорова Т.В. Биодеструкция эфиров фталевой кислоты грибами белой гнили // Прикл. биохимия и микробиология. 2022. Т. 58. С. 484‒499.
Savinova O.S., Shabaev A.V., Glazunova O.A., Eremin S.A., Fedorova T.V. Biodestruction of phthalic acid esters by white rot fungi // Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2022. V. 58. P. 598–612. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0555109922050142
Синицын А.П., Гусаков А.В., Черноглазов В.М. Биоконверсия лигноцеллюлозных материалов. М.: Изд-во МГУ, 1995. 224 с.
Шкаева И.Е., Солнцева С.А., Никулина О.С., Николаев А.И., Дулов С.А., Земляной А.В. Токсичность и опасность фталатов // Токсикологический вестник. 2019. Т. 159. № 6. С. 3–9.
Ahmadi E., Yousefzadeh S., Ansari M., Ghaffari H.R., Azari A., Miri M., Nabizadeh A.M.R., Kakavandi B., Ahmadi P., Badi M.Y., Gholami M., Sharafi K., Karimaei M., Ghoochani M., Brahmand M.B., Mohseni S.M., Sarkhosh M., Rezaei S., Asgharnia H., Dehghanifard E., Jafari B., Mortezapour A., Moghaddam V.K., Mahmoudi M.M., Taghipour N. Performance, kinetic, and biodegradation pathway evaluation of anaerobic fixed film fixed bed reactor in removing phthalic acid esters from wastewater // Sci. Rep. 2017. V. 7. 41020. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41020
Ahuactzin-Perez M., Tlecuitl-Beristain S., García-Davila J., Santacruz-Juárez E., González-Pérez M., Gutiérrez-Ruíz M.C., Sánchez C. Mineralization of high concentrations of the endocrine disruptor dibutyl phthalate by Fusarium culmorum // 3 Biotech. 2018. V. 8. № 42. P. 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1065-2
Akerman-Sanchez G., Rojas-Jimenez K. Fungi for the bioremediation of pharmaceutical-derived pollutants: A bioengineering approach to water treatment // Environ. Adv. 2021. V. 4. 100071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100071
Boll M., Geiger R., Junghare M., Schink B. Microbial degradation of phthalates: biochemistry and environmental implications // Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2020. V. 12. P. 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12787
Brenelli L.B., Persinoti G.F., Franco Cairo J.P.L. Liberato M.V., Gonçalves T.A., Otero I.V.R., Mainardi P.H., Felby C., Sette L.D., Squina F.M. Novel redox-active enzymes for ligninolytic applications revealed from multiomics analyses of Peniophora sp. CBMAI 1063, a laccase hyper-producer strain // Sci. Rep. 2019. V. 9. 17564. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53608-1
Carstens L., Cowan A.R., Seiwert B., Schlosser D. Biotransformation of phthalate plasticizers and bisphenol A by marine-derived, freshwater, and terrestrial fungi // Front. Microbiol. 2020. V. 11. 317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00317
Chang B.V., Yang C.P., Yang C.W. Application of fungus enzymes in spent mushroom composts from edible mushroom cultivation for phthalate removal // Microorganisms. 2021. V. 9. 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091989
Das M.T., Kumar S.S., Ghosh P., Shah G., Malyan S.K., Bajar S., Thakur I.S., Singh L. Remediation strategies for mitigation of phthalate pollution: challenges and future perspectives // J. Hazard. Mater. 2021 V. 409. 124496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124496
de Souza Machado A.A., Lau C.W., Kloas W., Bergmann J., Bachelier B.J., Faltin E., Becker R., Görlich A.S., Rillig M.C. Microplastics can change soil properties and affect plant performance // Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019. V. 53. P. 6044−6052. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01339
Dutta S., Haggerty D.K., Rappolee D.A., Ruden D.M. Phthalate exposure and long-term epigenomic consequences: a review // Front. Genet. 2020. V. 11. 405. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00405
Gao D., Wen Z. Phthalate esters in the environment: a critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes // Sci. Total Environ. 2016. V. 541. P. 986–1001.
González-Márquez A., Ahuactzin-Pérez M., Sánchez C. Lentinula edodes grown on di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate-containing media: mycelial growth and enzyme activities // BioResources. 2015. V. 10. P. 7898–7906. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.10.4.7898-7906
Hofmann U., Schlosser D. Biochemical and physicochemical processes contributing to the removal of endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pharmaceuticals by the aquatic ascomycete Phoma sp. UHH 5-1-03 // Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016. V. 100. P. 2381–2399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7113-0
Hwang S., Choi H.T., Song H. Biodegradation of endocrine-disrupting phthalates by Pleurotus ostreatus // J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008. V. 18. P. 767–772.
Li H., Dai Q., Yang M., Li F., Liu X., Zhou M., Qian X. Unraveling consequences of soil micro- and nano-plastic pollution on soil-plant system: implications for nitrogen (N) cycling and soil microbial activity // Chemosphere. 2020. V. 260. 127578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127578
Ma J., Yue H., Li H., Zhang J., Zhang Y., Wang X., Gong S., Liu G. Selective delignification of poplar wood with a newly isolated white‑rot basidiomycete Peniophora incarnata T‑7 by submerged fermentation to enhance saccharification // Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2021. V. 14. P. 135. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-01986-y
Moiseenko K.V., Glazunova O.A., Shakhova N.V., Savinova O.S., Vasina D.V., Tyazhelova T.V., Psurtseva N.V., Fedorova T.V. Fungal adaptation to the advanced stages of wood decomposition: insights from the Steccherinum ochraceum // Microorganisms. 2019. V. 7. 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110527
Naveen K.V., Saravanakumar K., Zhang X. Anbazhagan K., Wang M. Impact of environmental phthalate on human health and their bioremediation strategies using fungal cell factory – a review // Environ. Res. 2022. V. 214. 113781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113781
Savinova O.S., Shabaev A.V., Glazunova O.A. et al. Benzyl butyl phthalate and diisobutyl phthalate biodegradation by white-rot fungus Trametes hirsuta // Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2022. V. 58. Suppl. 1. P. S113‒S125. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683822100118
Shabaev A.V., Moiseenko K.V., Glazunova O.A. Savinova O.S., Fedorova T.V. Comparative analysis of Peniophora lycii and Trametes hirsuta exoproteomes demonstrates “Shades of Gray” in the concept of white-rotting fungi // Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022. V. 23. 10322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810322
Suárez-Segundo J.L., Vazquez-Lopez D., Torres-Garcia J.L., Ahuactzin-Perez M., Montiel-Martínez N., Tlecuitl-Beristain S., Sánchez C. Growth of colonies and hyphal ultrastructure of filamentous fungi grown on dibutyl phthalate and di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate // Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química. 2013. V. 12. P. 499–504.
Tang Y., Zhang Y., Jiang L., Yang C., Rittmann B.E. Enhanced dimethyl phthalate biodegradation by accelerating phthalic acid di-oxygenation // Biodegradation. 2017. V. 28. P. 413–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9805-x
Tran H.T., Lin C., Bui H.-T., Nguyen M.K., Cao N.D.T., Mukhtar H., Hoang H.G., Varjani S., Ngo H.H., Nghiem L.D. Phthalates in the environment: characteristics, fate and transport, and advanced wastewater treatment technologies // Bioresour. Technol. 2022. V. 344. 126249. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02479
Weaver J.A., Beverly B.E.J., Keshava N. Mudipalli A., Arzuaga X., Cai C., Hotchkiss A.K., Makris S.L., Yost E.E. Hazards of diethyl phthalate (DEP) exposure: a systematic review of animal toxicology studies // Environ. Int. 2020. V. 145. 105848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105848
Zhao F., Wang P., Lucardi R.D., Su Z., Li S. Natural sources and bioactivities of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and its analogs // Toxins. 2020. V. 12. 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010035
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.