Коллоидный журнал, 2023, T. 85, № 5, стр. 705-714
Липидные наночастицы для инкапсулирования и доставки лютеина
А. Д. Широких 1, *, Ю. А. Гурулева 1, Е. А. Маринец 1, М. Ю. Королева 1, **
1 Российский химико-технологический университет им. Д.И. Менделеева
125047 Москва,
Миусская площадь, д. 9, Россия
* E-mail: adshirokikh@gmail.com
** E-mail: m.yu.kor@gmail.com
Поступила в редакцию 27.06.2023
После доработки 29.07.2023
Принята к публикации 31.07.2023
- EDN: DIKBRW
- DOI: 10.31857/S0023291223600530
Аннотация
В последнее время липидные наночастицы интенсивно исследуют в качестве носителей липофильных лекарственных соединений. В данной работе проведено изучение устойчивости наноэмульсий с углеводородным маслом, твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой и наноструктурированных липидных частиц, содержащих углеводородное масло и стеариновую кислоту в массовом соотношении 1 : 1. Результаты показали, что при стабилизации неионогенными поверхностно-активными веществами Tween 60 и Span 60 все исследованные липидные системы сохраняли устойчивость к агрегации и последующей седиментации более 30 сут. Включение в состав липидных дисперсий лютеина практически не оказывало влияния на их устойчивость, при этом размер твердых липидных наночастиц и наноструктурированных липидных частиц уменьшался от 28–30 до 15–17 нм. Биодоступность лютеина при его инкапсулировании в липидные наночастицы определялась по их влиянию на восстановление скорости кровотока при моделировании гемической гипоксии. Практически сразу же после нанесения липидных наночастиц снижение скорости кровотока прекращалось и через 5–10 мин наблюдалась тенденция к его восстановлению. Это показывает перспективность использования липидных наночастиц с углеводородным маслом и стеариновой кислотой для доставки липофильных лекарственных соединений.
1. ВВЕДЕНИЕ
В последнее время возрос интерес к исследованию липидных наночастиц для доставки различных биологически активных соединений, в том числе лекарственных. Благодаря наличию липидного ядра в такие наночастицы возможно инкапсулирование липофильных веществ и, соответственно, повышение их биодоступности. К подобным липидным носителям активных соединений относятся наноэмульсии, капли дисперсной фазы которых состоят из жидких липофильных соединений [1], твердые липидные наночастицы, образованные твердыми при комнатной или физиологической температурах липидами, и наноструктурированные липидные частицы, включающие смесь твердых и жидких липидов [2]. В данной работе исследованы липидные наночастицы, состоящие из жидкого углеводородного масла и твердой стеариновой кислоты, поэтому в дальнейшем мы будем придерживаться указанной выше терминологии.
Наноструктурированные липидные частицы, занимая промежуточное состояние между наноэмульсиями и твердыми липидными наночастицами, сочетают в себе ряд достоинств последних. Благодаря наличию жидких липидных компонентов для наноструктурированных липидных частиц характерна высокая емкость по отношению к липофильным лекарственным веществам, что свойственно наноэмульсиям. Присутствие твердых липофильных веществ в их составе обеспечивает высокую физическую и биологическую устойчивость по отношению к средам организма, которая является достоинством твердых липидных наночастиц [3, 4]. Помимо прочего, комбинирование твердого и жидкого липидов позволяет избежать перекристаллизации в более стабильные кристаллические модификации, приводящей к неконтролируемому высвобождению инкапсулированного активного вещества [5, 6].
Дисперсии липидных наночастиц являются кинетически стабильными системами, хотя следует отметить, что такие системы могут быть устойчивыми в течение длительного времени. Так как липидные наночастицы, предназначенные для биомедицинского применения, наиболее часто стабилизируют неионогенными поверхностно-активными веществами (ПАВ), то в их дисперсиях чаще протекают агрегация и оствальдово созревание [7, 8]. Агрегация липидных наночастиц может быть значительно замедлена при образовании твердообразной оболочки на поверхности липидных капель в наноэмульсиях или твердых липидных наночастицах [9]. Скорость оствальдова созревания можно снизить практически до нулевых величин при включении в состав жидких капель дисперсной фазы вещества, растворимость которого в дисперсионной среде значительно меньше, чем растворимость основного компонента [10]. Комбинирование липидов, имеющих разную растворимость в водной фазе, в том числе жидких и твердых, способствует повышению устойчивости дисперсий липидных наночастиц к оствальдову созреванию [11].
Липидные частицы получали из смеси стеариновой и олеиновой кислот [12], пальмитиновой и олеиновой кислот [13], пчелиного воска и олеиновой кислоты [14], комбинации каприновой (C10), миристиновой (C14) и стеариновой (C18) кислот с подсолнечным маслом [15]. Однако следует отметить, что в большинстве работ размеры полученных липидных частиц превышали 150–200 нм. Для стабилизации липидных частиц обычно используют Tween 80 [16–18], смесь хлорида цетилпиридиния и Span 20 [19], Span 60 [20], Span 80 [21], смесь Tween 60 и Span 60 [22], различные полоксамеры [23, 24].
Лютеин известен как биологически активное соединение, способствующее повышению остроты и защите органов зрения. Он может накапливаться в сетчатке глаза и выступать в качестве антиоксиданта, препятствующего образованию активных форм кислорода [25]. Помимо этого, отмечают его нейропротекторное [26] и противовоспалительное действия [27]. Поскольку основным источником лютеина является пища и лекарственные препараты для перорального введения, то для достижения сетчатки глаза необходимо преодоление разных физиологических барьеров. Увеличить биодоступность лютеина можно посредством его инкапсулирования в липидные наночастицы и последующим конъюнктивальным введением.
Для инкапсулирования лютеина исследовали наноэмульсии, состоящие из среднецепочечных триглицеридов и стабилизированные Tween 80, со средним диаметром капель ~100 нм [28]. Наноэмульсии на основе изопропилмиристата, триацетина, Tween 80 и этилового спирта, с размером капель 10–12 нм сохраняли стабильность более 7 сут [29]. Эмульсии, состоящие из лютеина, растворенного в подсолнечном масле с высоким содержанием олеиновой кислоты, имели капли дисперсной фазы ~220 нм при стабилизации крахмалом, модифицированным октенилсукцинатом, и ~170 нм при стабилизации моностеаратом сахарозы и сохраняли стабильность более 30 сут [30].
В эмульсиях, содержащих лютеин, растворенный в кукурузном масле, размер липидных капель составлял 220–250 нм. При этом эмульсии, стабилизированные Tween 80 и сапонином из квиллайи мыльной, сохраняли устойчивость более 10 сут. В эмульсии с изолятом сывороточного протеина размер капель увеличивался в течение данного интервала времени [31].
Наноэмульсии с лютеином с размером липидных капель 70–80 нм, стабилизированные изолятом сывороточного протеина, обладали низкой цитотоксичностью, при этом их захват клетками линии Caco-2 был высоким [32].
Биодоступность лютеина, инкапсулированного в наноэмульсиях из линолевой и олеиновой кислоты с размером капель ~110 нм, стабилизированных Tween 20, составляла 87.4% по сравнению с неинкапсулированным лютеином (15.0%) в экспериментах in vivo на крысах [33].
Твердые липидные частицы с лютеином, состоящие из глицеролмоностеарата, карнаубского воска и рыбьего жира, стабилизированные Tween 80 и Poloxamer 407, имели размер 167–207 нм [34]. Липидные частицы с лютеином диметром ~120 нм были получены из глицеролмоностеарата и стабилизированы лецитином и Poloxamer 188. Скорость проникновения таких частиц через роговицу была выше в 1.52 раза, чем у неинкасулированного лютеина [35].
Было проведено сравнение свойств эмульсий с кукурузным маслом, твердых липидных частиц из кокосового масла и наноструктурированных частиц из кукурузного и кокосового масел с инкапсулированным лютеином, стабилизированных Tween 80 или зейн пептидами. Размеры липидных частиц варьировались от 110 до 200 нм. Размеры твердых липидных частиц немного увеличивались в течение 10 сут из-за агрегации, а размеры наноэмульсий и наноструктурированных липидных частиц изменялись незначительно в течение этого же интервала времени [36].
Наноэмульсии из среднецепочечных триглицеридов Miglyol 812, твердые липидные частицы из цетилпальмитата, глицеролтрипальмитата или карнаубского воска, наноструктурированные липидные частицы из Miglyol 812 и глицеролтрипальмитата или карнаубского воска имели размеры от 150 до 350 нм. Наиболее высокая степень высвобождения лютеина через 24 ч наблюдалась из наноэмульсий и составляла 19.5%, средняя – из наноструктурированных липидных частиц (7.4–12.1%) и наиболее низкая – из твердых липидных частиц (0.4%). При этом проникновение твердых и наноструктурированных липидных частиц с лютеином через свежую свиную кожу в течение 24 ч практически отсутствовало и не превышало 0.37% в случае наноэмульсий, что свидетельствовало об их местном накоплении и отсутствии системной биодоступности [37].
Таким образом, липидные наночастицы являются перспективными носителями липофильных лекарственных соединений, в том числе и лютеина. Однако, как показал анализ литературных данных, большие размеры и недостаточная агрегативная устойчивость ограничивают эффективность их применения. Известно, что использование углеводородного масла и стеариновой кислоты в качестве основы для носителей активных соединений позволяет получать агрегативно устойчивые высокодисперсные системы [38, 39], однако отсутствуют публикации, посвященные их комбинации, инкапсулированию в них лютеина и влиянию его на агрегативную и седиментационную устойчивости. В данной работе изучена устойчивость наноэмульсий с углеводородным маслом, твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой и наноструктурированных липидных частиц, содержащих углеводородное масло и стеариновую кислоту. Биодоступность данных липидных дисперсий с инкапсулированным лютеином определяли по их влиянию на восстановление скорости кровотока при моделировании гемической гипоксии.
2. ЭКСПЕРИМЕНТАЛЬНАЯ ЧАСТЬ
2.1. Реактивы и материалы
В составе липидных наночастиц в качестве органической фазы использовали углеводородное масло (Britol 20 USP, puriss) и стеариновую кислоту (Sigma-Aldrich, ≥95%). В качестве ПАВ применяли полиэтиленгликоль сорбитанмоностеарат – Tween 60 (Sigma-Aldrich, ≥95%) и сорбитанмоностеарат – Span 60 (Sigma-Aldrich, ≥95%). В качестве водной фазы выступал физиологический раствор (0.15 М NaCl), для приготовления которого использовали NaCl (Merck, extra pure) и бидистиллированную воду. В качестве биологически активного соединения, инкапсулированного в липидных наночастицах, использовали масляный экстракт лютеина (≥20%; Shaanxi Jiahe Phytohem Co.). Реактивы, использованные в работе, дополнительной очистке не подвергали.
2.2. Получение дисперсий липидных наночастиц
Дисперсии липидных наночастиц получали методом температурной инверсии фаз [40]. В случае наноэмульсий органическая фаза состояла из углеводородного масла, твердые липидные наночастицы состояли из стеариновой кислоты, наноструктурированные липидные частицы – из смеси углеводородного масла и стеариновой кислоты в массовом соотношении 1 : 1. Доля органической фазы в дисперсиях составляла 25 об. %. Для стабилизации использовали 15 об. % смесь Tween 60 и Span 60 в мольном соотношении 0.76 [38]. Объем получаемых дисперсий составлял 10 мл.
Для получения дисперсий липидных наночастиц в стеклянный сосуд помещали углеводородное масло, либо стеариновую кислоту, либо смесь углеводородного масла и стеариновой кислоты, а также смесь Tween 60 и Span 60 и водный раствор NaCl. Полученную смесь нагревали до температуры, превышающей температуру инверсии фаз, при умеренном перемешивании. Затем смесь охлаждали в ледяной бане с температурой 0°С при интенсивном перемешивании.
В липидных наночастицах с инкапсулированным биологически активным соединением концентрация лютеина составляла 0.1 мас. %. Лютеин предварительно растворяли в углеводородном масле, стеариновой кислоте или их смеси при 80°С. Дальнейшее получение липидных наночастиц проводили по методике, описанной выше.
2.3. Исследование физико-химических свойств липидных наночастиц
Определение диаметра липидных наночастиц проводили методом динамического светорассеяния с помощью анализатора Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments), оснащенным гелий-неоновым лазером (λ = 633 нм) с регистрацией рассеянного света под углом 173°. Определение размеров наночастиц проводили без разбавления систем. Каждое измерение включало в среднем 14 пробегов. Распределения липидных наночастиц по размерам определяли с использованием модели Multiple Narrow Modes. В данной работе использовали гистограммы распределения размеров частиц по их объемной доле. Измерения проводили при 25°C. По результатам не менее пяти измерений каждого образца рассчитывали средние значения диаметров наночастиц.
Электрокинетический потенциал (ζ-потенциал) липидных наночастиц рассчитывали на основании измерений электрофоретической подвижности частиц с помощью анализатора Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments). Для определения ζ-потенциала липидных наночастиц дисперсии были разбавлены в 100 раз физиологическим раствором. Измерения проводили при 25°C. Каждый исследуемый образец анализировали не менее пяти раз и рассчитывали среднее значение.
Устойчивость дисперсий липидных наночастиц к агрегации и последующей седиментации исследовали путем анализа обратного светорассеяния монохромного излучения с использованием Multiscan MS 20 (DataPhysics Instruments GmbH). Измерения интенсивности обратного светорассеяния проводили при сканировании образца по высоте с шагом 20 мкм, скорость сканирования составляла 12.5 мм/c. Длина волны монохромного излучения была равна 880 нм. Измерения проводили при 25°C, между измерениями образцы хранили при той же температуре. С использованием полученных данных были построены зависимости обратного светорассеяния от высоты образца, на которых высота образца с дисперсией липидных наночастиц обозначена как расстояние от дна сосуда и выражена в относительных величинах – от 0 до 1.
2.4. Оценка биодоступности инкапсулированного лютеина
Оценку биологической активности дисперсий липидных наночастиц осуществляли методом ультразвуковой допплерографии на куриных эмбрионах с помощью ультразвукового допплеровского сканера Минимакс-Допплер-К (СП Минимакс) и программного обеспечения Minimax Doppler v.1.7. Для анализа использовали 9-дневные куриные эмбрионы. Поскольку скорость кровотока прямо пропорциональна давлению крови, ее изменение является свидетельством изменения кровяного давления и может использоваться для определения биологической активности веществ, обладающих потенциальным гипер- или гипотензивным действием. Для анализа скорости кровотока использовали датчик с частотой 25 МГц.
Анализ осуществляли в соответствии с методикой [41]. Куриные эмбрионы предварительно выдерживали при 37.8–38.0°C в течение 1 сут, а исследуемые образцы термостатировали при той же температуре не менее 2 ч. Воздушную камеру эмбриона освобождали от скорлупы и удаляли подскорлуповую оболочку, предварительно смочив ее физиологическим раствором и исключая повреждения хориоаллантоисной оболочки, затем наносили 400 мкл физиологического раствора для предотвращения высыхания. Для измерения скорости кровотока выбирали наиболее крупный сосуд на поверхности хориоаллантоисной оболочки и определяли скорость венозного кровотока в нем (нулевое измерение). Датчик располагали под углом 60° к сосуду и выбирали такое положение, при котором наблюдались слабые по амплитуде, без острых пиков пульсации на допплерограммах. Для анализа раздражающего действия дисперсий измерения проводили через 10, 30 и 60 мин. Между измерениями яйцо помещали в термостат с температурой 37.8–38.0°C.
Для анализа гипер- или гипотензивного действия дисперсий липидных наночастиц осуществляли моделирование гемической гипоксии посредством введения 400 мкл 0.15 М раствора нитрита натрия на хориоаллатоисную оболочку сразу после нулевого измерения. Исследуемые дисперсии липидных наночастиц, незагруженных и загруженных лютеином, предварительно разбавляли в 100 раз физиологическим раствором. Через 5 мин после введения раствора нитрита натрия на хориоаллантоисную оболочку наносили 400 мкл разбавленной дисперсии липидных наночастиц. Скорость венозного кровотока измеряли через 5, 25 и 55 мин после введения дисперсии липидных наночастиц, что соответствует 10, 30 и 60 мин после начала эксперимента.
Каждое измерение проводили не менее трех раз. Все системы были исследованы не менее, чем на пяти куриных эмбрионах. По полученным результатам находили среднее значение.
Исследования на хориоаллантоисной оболочке куриных эмбрионов не считаются экспериментами на животных в соответствии с Директивой Европейского парламента и Совета Европейского Союза 2010/63/ЕС от 22 сентября 2010 г. о защите животных, использующихся для научных целей, поскольку до 11 дня нервная система куриных эмбрионов не развивается.
3. РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
3.1. Влияние состава органической фазы на средний размер липидных наночастиц и устойчивость их дисперсий
В данной работе липидные наночастицы получали с использованием метода температурной инверсии фаз [38], в котором сначала получают обратную макроэмульсию при повышенной температуре. Затем эту макроэмульсию резко охлаждают ниже температуры инверсии фаз, что приводит к образованию прямой наноэмульсии или дисперсии липидных наночастиц. Для стабилизации липидных наночастиц использовали смесь ПАВ с высоким и низким значениями гидрофильно-липофильного баланса (ГЛБ) Tween 60 (ГЛБ 14.9) и Span 60 (ГЛБ 4.7), что позволяло эффективно стабилизировать как обратную макроэмульсию, так и прямую липидную нанодисперсию. Как было показано ранее, при адсорбции Tween 60 и Span 60 на поверхности липидных наночастиц образуется твердообразная оболочка, что способствует увеличению агрегативной устойчивости систем [9, 38, 42].
В наноэмульсиях с углеводородным маслом средний диаметр капель составлял 28 ± 5 нм (рис. 1а). Также в системе было небольшое количество флокул, но их содержание не превышало 1.7 об. %. Через 30 сут средний диаметр нанокапель практически не изменялся, количество флокул не увеличивалось. Это свидетельствует о высокой агрегативной устойчивости наноэмульсий.
Рис. 1.
Распределения по размерам капель дисперсной фазы в наноэмульсии с углеводородным маслом (а), наноструктурированных липидных частиц со стеариновой кислотой и углеводородным маслом в массовом соотношении 1 : 1 (б), твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой (в).
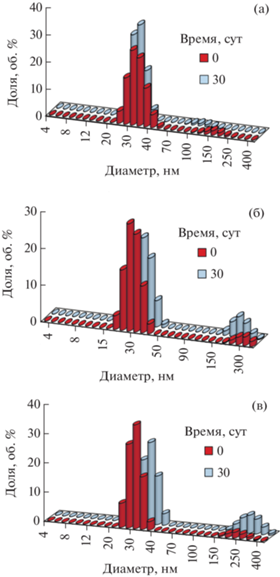
Включение в состав органической фазы стеариновой кислоты в массовом соотношении с углеводородным маслом 1 : 1 не приводило к заметному изменению размеров наноструктурированных липидных частиц. Их диаметр составлял 30 ± 5 нм (рис. 1б). В липидной дисперсии присутствовали агрегаты наночастиц со средним размером ~350 нм. Данные системы также были устойчивыми, средний диаметр частиц изменялся незначительно за 30 сут. При этом количество агрегатов наночастиц с течением времени немного возрастало, но не превышало 5.6 об. %.
Размер твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой составлял 28 ± 5 нм (рис. 1в). С течением времени наблюдалось некоторое увеличение содержания агрегатов от 2.0 до 6.2 об. %.
Сканирование по высоте столба наноэмульсий и дисперсий наноструктурированных липидных частиц показало, что обратное светорассеяние практически не изменялось более 30 сут (рис. 2а и 2б). Если не учитывать флуктуации светорассеяния, то его величина была относительно постоянной по высоте столба липидных дисперсий, что свидетельствует об однородности структуры этих систем в течение длительного времени.
Рис. 2.
Интенсивности обратного светорассеяния в наноэмульсии с углеводородным маслом (а), дисперсии наноструктурированных липидных частиц со стеариновой кислотой и углеводородным маслом в массовом соотношении 1 : 1 (б), дисперсии твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой (в).
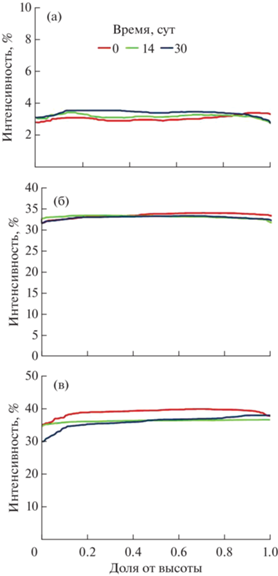
В дисперсиях твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой наблюдалось некоторое снижение обратного светорассеяния в нижней части сосуда (рис. 2в). Это может свидетельствовать о протекании обратной седиментации агрегатов наночастиц и некотором уменьшении концентрации частиц около дна сосуда. Это снижение концентрации органической фазы в нижних слоях было незаметно невооруженным глазом и не сопровождалось отслаиванием водной фазы.
ζ-потенциал капель дисперсной фазы в наноэмульсии составлял –(1.8 ± 0.4) мВ, наноструктурированных липидных частиц –(1.6 ± 0.5) мВ, твердых липидных наночастиц –(1.2 ± 0.7) мВ. Исследованные липидные наночастицы были стабилизированы неионогенными ПАВ, поэтому их поверхностный заряд был таким низким. При этом наноэмульсии были кинетически стабильны в течение более 30 сут. В дисперсиях твердых липидных наночастиц и наноструктурированных липидных частиц в некоторой степени протекала агрегация, но ее скорость была очень низкой, и это не приводило к расслаиванию систем. Наиболее вероятно, что устойчивость дисперсий была следствием образования твердообразной оболочки ПАВ на поверхности липидных наночастиц [38]. Наночастицы сталкивались в результате броуновского движения как “жесткие шары”, т. е. столкновения не были эффективными и не приводили к агрегации.
3.2. Влияние инкапсулированного лютеина на дисперсность и устойчивость дисперсий липидных наночастиц
Лютеин является природным пигментом и относится к группе гидроксилированных каротиноидов. Благодаря наличию полярных групп лютеин обладает амфифильными свойствами. Известно, что биодоступность лютеина, поступающего с пищей, повышается в присутствии липидов. Он встраивается в структуру мицелл, располагаясь на границе раздела фаз. При инкапсулировании в липидные наночастицы данное биологически активное соединение может оказывать влияние как на дисперсность, так и на стабильность липидных дисперсий. Концентрация лютеина в исследованных дисперсиях липидных наночастиц составляла 0.1 мас. %. Данная концентрация была получена расчетным путем, исходя из пересчета суточной дозы, необходимой человеку, на массу эмбриона с учетом объема аликвоты, вносимой при измерении скорости кровотока (см. раздел 3.3).
Исследования показали, что при инкорпорировании лютеина в наноэмульсии диаметр капель дисперсной фазы практически не изменялся (табл. 1). Включение лютеина в липидные наночастицы, в состав которых входила стеариновая кислота, заметно влияло на их размер.
Таблица 1.
Размер липидных наночастиц незагруженных и с инкапсулированным лютеином
| Состав дисперсной фазы | Средний диаметр наночастиц без лютеина, нм | Средний диаметр наночастиц с лютеином, нм | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 сут | 0 сут | 30 сут | |
| Углеводородное масло | 28 ± 5 | 28 ± 5 | 32 ± 5 |
| Углеводородное масло : стеариновая кислота (1 : 1) | 30 ± 5 | 17 ± 2 | 20 ± 5 |
| Стеариновая кислота | 28 ± 5 | 15 ± 2 | 18 ± 3 |
При этом средний размер наноструктурированных липидных частиц с лютеином был немного больше, чем твердых липидных наночастиц. По-видимому, лютеин, обладая амфифильными свойствами, наряду со стеариновой кислотой частично встраивался в адсорбционный слой на поверхности липидных наночастиц, что способствовало уменьшению их размера.
Следует отметить, что все исследованные липидные системы с лютеином были стабильны более 30 сут. В течение этого времени средний размер липидных наночастиц изменялся в пределах погрешности измерений.
3.3. Оценка биодоступности лютеина, инкапсулированного в липидныe наночастицы
9-дневный куриный эмбрион является распространенным объектом, на котором проводят исследования действия различных биологически активных соединений. К этому времени у него формируется развитая сосудистая сеть, но при этом белочная оболочка еще достаточно тонкая и возможно ее удаление без повреждения кровеносных сосудов. Хориоаллантоисная оболочка, прилегающая к белочной, является естественной окружающей средой для кровеносных сосудов и обеспечивает их взаимодействие с эмбрионом [34].
Влияние ненагруженных липидных наночастиц в отсутствии гемической гипоксии на скорость кровотока
Определение влияния дисперсий липидных наночастиц проводили в соответствии с методикой, описанной в разделе 2.4: разбавленную дисперсию липидных наночастиц наносили на хориоаллантоисную оболочку и измеряли скорость кровотока через определенные промежутки времени.
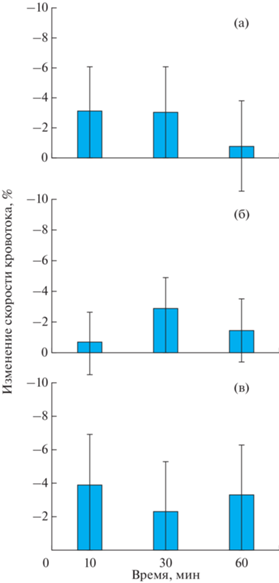
Как показали результаты измерений, при нанесении каждой из трех липидных дисперсий скорость кровотока уменьшалась не более чем на 4% (рис. 3). Такие колебания скорости кровотока являются допустимыми и связаны с жизнедеятельностью куриного эмбриона. Это показывает, что наноэмульсии, наноструктурированные липидные частицы и твердые липидные наночастицы данного состава и размера не оказывают существенного влияния на интенсивность кровотока куриных эмбрионов и могут быть использованы в качестве носителей для повышения биодоступности биологически активных соединений.
Рис. 3.
Изменение скорости венозного кровотока куриных эмбрионов после введения наноэмульсии с углеводородным маслом (а), дисперсии наноструктурированных липидных частиц со стеариновой кислотой и углеводородным маслом в массовом соотношении 1 : 1 (б), дисперсии твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой (в).
Влияние липидных наночастиц с инкапсулированным лютеином на скорость кровотока при моделировании гемической гипоксии
Для оценки биодоступности лютеина, инкапсулированного в липидные наночастицы, были проведены исследования по восстановлению скорости кровотока куриных эмбрионов после моделирования гемической гипоксии. На хориоаллантоисную оболочку наносили нитрит натрия, а затем – разбавленную дисперсию ненагруженных липидных наночастиц или липидных наночастиц с инкапсулированным лютеином, и для сравнения – водно-спиртовой раствор лютеина (0.1 мас. % раствор лютеина в этиловом спирте, разбавленный в 100 раз физиологическим раствором). Также наблюдали за контрольным образцом без воздействия липидных наночастиц и лютеина, в котором скорость кровотока восстанавливалась естественным образом.
Нанесение раствора нитрита натрия как наиболее известного метгемаглобинообразователя приводило к формированию гипоксического состояния. В результате этого наблюдалось резкое снижение скорости кровотока. Как видно на рис. 4, в течение первых 5 мин после введения нитрита натрия скорость кровотока уменьшилась более чем на 18%. Естественное восстановление скорости кровотока после моделирования гемической гипоксии происходило медленно и не достигало величин, близких к исходным, в течение 1 ч исследований.
Рис. 4.
Изменение скорости венозного кровотока куриных эмбрионов при моделировании гемической гипоксии после введения наноэмульсии с углеводородным маслом (а), дисперсии наноструктурированных липидных частиц со стеариновой кислотой и углеводородным маслом в массовом соотношении 1 : 1 (б), дисперсии твердых липидных наночастиц со стеариновой кислотой (в). ЛНЧ – липидные наночастицы.
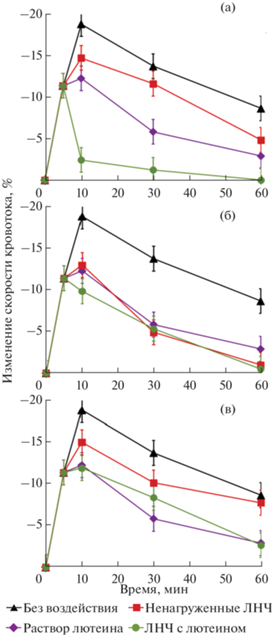
Лютеин относится к природным карротиноидам, обладающим антиоксидантным и противовоспалительным действиями. Известно его положительное воздействие при атеросклерозе, артериальной гипотензии и др. [36]. Он способствует связыванию активных форм кислорода и, как следствие, снижению воздействия свободных радикалов на клетки крови и кровеносных сосудов [37]. Таким образом, нанесение лютеина ожидаемо способствовало нормализации кровяного давления и восстановлению скорости кровотока после моделирования гемической гипоксии у куриных эмбрионов. При нанесении водно‑спиртового раствора лютеина на хориоаллантоисную оболочку наблюдалось заметное снижение интенсивности уменьшения скорости кровотока и более быстрое его восстановление. Однако использование таких лекарственных форм нецелесообразно из-за раздражающего действия этанола.
При инкапсулировании лютеина в липидных наночастицах заметно возрастала его биодоступность. Практически сразу же после нанесения липидных наночастиц на хориоаллантоисную оболочку снижение скорости кровотока прекращалось и через 5–10 мин наблюдалась тенденция к его восстановлению. Наиболее заметное влияние обнаружили при воздействии наноэмульсии с углеводородным маслом. В течение 5 мин после их нанесения на хориоаллантоисную мембрану куриных эмбрионов происходило практически полное восстановление скорости кровотока. При нанесении дисперсии наноструктурированных липидных частиц и твердых липидных наночастиц скорость кровотока восстанавливалась немного медленнее по сравнению с наноэмульсиями, но значительно быстрее, чем без воздействия лютеина. По-видимому, наличие жидкого при физиологической температуре углеводородного масла в липидных наночастицах способствовало более быстрому высвобождению лютеина, что увеличивало эффективность его воздействия на кровеносную систему куриных эмбрионов.
4. ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Возможность применения липидных наночастиц для повышения биодоступности биологически активных соединений связана с их дисперсностью, агрегативной и седиментационной устойчивостью. Кроме этого, компоненты, входящие в их состав, должны обладать высокой биосовместимостью и биоразлагаемостью. В данной работе были исследованы системы со стеариновой кислотой и углеводородным маслом, стабилизированные неионогенными ПАВ Tween 60 и Span 60.
Размер полученных наночастиц с углеводородным маслом, стеариновой кислотой и с их смесью в массовом соотношении 1 : 1 составлял 30 ± 5 нм, слабо зависел от состава дисперсной фазы и оставался неизменным более 30 сут. Инкапсулирование лютеина в наноэмульсии с углеводородным маслом практически не влияло на размер нанокапель. Инкорпорирование лютеина в липидные наночастицы, содержащие стеариновую кислоту, приводило к уменьшению их размеров до 15–17 нм. При этом все исследованные липидные системы с лютеином были стабильны более 30 сут.
Изучение биодоступности лютеина при инкапсулировании в липидные наночастицы проводили на 9-дневных куриных эмбрионах. Оценивали их влияние на восстановление скорости кровотока при моделировании гемической гипоксии. Практически сразу же после нанесения липидных наночастиц снижение скорости кровотока прекращалось, и через 5–10 мин наблюдалась тенденция к его восстановлению. Это показывает перспективность использования липидных наночастиц с углеводородным маслом и стеариновой кислотой для доставки липофильных лекарственных соединений.
Список литературы
Tadros T., Izquierdo P., Esquena J. Solans C. Formation and stability of nano-emulsions // Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004. V. 108. P. 303–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2003.10.023
McClements D.J., Decker E.A., Weiss J. Emulsion-based delivery systems for lipophilic bioactive components // J. Food Sci. 2007. V. 72. № 8. P. 109–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00507.x
Khosa A., Reddi S., Saha R.N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery // Biomed. & Pharmacother. 2018. V. 103. P. 598–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.055
Tang C.H., Chen H.L., Dong J.R. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) as food-grade nanovehicles for hydrophobic nutraceuticals or bioactives // Appl. Sci. 2023. V. 13. № 3. P. 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031726
Zhong Q., Zhang L. Nanoparticles fabricated from bulk solid lipids: Preparation, properties, and potential food applications // Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. V. 273. 102033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.102033
Gordillo-Galeano A., Mora-Huertas C.E. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review emphasizing on particle structure and drug release // Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018. V. 133. P. 285–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.10.017
McClements D.J., Jafari S.M. General aspects of nanoemulsions and their formulation // Nanoemulsions: Academic press. 2018. P. 3–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811838-2.00001-1
Koroleva M.Y., Yurtov E.V. Nanoemulsions: The properties, methods of preparation and promising applications // Russ. Chem. Rev. 2012. V. 81. № 1. P. 21–43. https://doi.org/10.1070/RC2012v081n01ABEH004219
Koroleva M., Portnaya I., Mischenko E., Abutbul-Ionita I., Kolik-Shmuel L., Danino D. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions with solid shell: Physical and thermal stability // J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. V. 610. P. 61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.12.010
Higuchi W.I., Misra J. Physical degradation of emulsions via the molecular diffusion route and the possible prevention thereof // J. Pharm. Sci. 1962. V. 51. № 5. P. 459–466. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600510514
Koroleva M.Y., Yurtov E.V. Ostwald ripening in macro-and nanoemulsions // Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021. V. 90. № 3. P. 293–323. https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4962
Ribeiro M.D.M.M., Arellano D.B., Grosso C.R.F. The effect of adding oleic acid in the production of stearic acid lipid microparticles with a hydrophilic core by a spray-cooling process // Food Res. Int. 2012. V. 47. № 1. P. 38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.01.007
Jeitler R., Glader C., Tetyczka C., Zeiringer S., Absenger-Novak M., Selmani A., Fröhlich E., Roblegg E. Investigation of cellular interactions of lipid-structured nanoparticles with oral mucosal epithelial cells // Frontiers in Mol. Biosci. 2022. V. 9. P. 917921. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.917921
Dantas I.L., Bastos K.T.S., Machado M., Galvao J.G., Lima A.D., Gonsalves J.K.M.C., Almeida E.D.P., Araújo A.A.S., de Meneses C.T., Sarmento V.H.V., Nunes R.S., Lira A.A.M. Influence of stearic acid and beeswax as solid lipid matrix of lipid nanoparticles containing tacrolimus // J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018. V. 132. P. 1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7072-7
Pinto F., de Barros D.P., Reis C., Fonseca L.P. Optimization of nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with retinoids by central composite design // J. Mol. Liq. 2019. V. 293. P. 111468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111468
de Souza I.D., Saez V., de Campos V.E., Mansur C.R. Size and vitamin E release of nanostructured lipid carriers with different liquid lipids, surfactants and preparation methods // Macromolecular Symposia. 2019. V. 383. № 1. P. 1800011. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201800011
Almeida E.D.P., Silva L.A.S., de Araujo G.R.S., Montalvão M.M., Matos S.S., da Cunha Gonsalves J.K.M., de Souza Nunes R., de Meneses C.T., Araujo R.G.O., Sarmento V.H.V., de Lucca Junior W., Correa C.B., Rodrigues Júnior J.J., Lira A.A.M. Chitosan-functionalized nanostructured lipid carriers containing chloroaluminum phthalocyanine for photodynamic therapy of skin cancer // Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022. V. 179. P. 221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2022.09.009
Sánchez-López E., Espina M., Doktorovova S., Souto E.B., García M.L. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC): Overcoming the anatomical and physiological barriers of the eye–Part II-Ocular drug-loaded lipid nanoparticles // Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017. V. 110. P. 58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.10.013
Matarazzo A.P., Elisei L.M.S., Carvalho F.C., Bonfílio R., Ruela A.L.M., Galdino G., Pereira G.R. Mucoadhesive nanostructured lipid carriers as a cannabidiol nasal delivery system for the treatment of neuropathic pain // Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021. V. 159. P. 105698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105698
Lüdtke F.L., Stahl M.A., Grimaldi R., Forte M.B.S., Gigante M.L., Ribeiro A.P.B. Optimization of high pressure homogenization conditions to produce nanostructured lipid carriers using natural and synthetic emulsifiers // Food Res. Int. 2022. V. 160. P. 111746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111746
Kelidari H.R., Saeedi M., Akbari J., Morteza-Semnani K., Valizadeh H., Maniruzzaman M., Farmoudeh A., Nokhodchi A. Development and optimisation of spironolactone nanoparticles for enhanced dissolution rates and stability // AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2017. V. 18. P. 1469–1474. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-016-0621-0
Shirokikh A.D., Anikina V.A., Zamyatina E.A., Mishchenko E.V., Koroleva M.Y., Ivanov V.K., Popova N.R. Bioavailability of nanoemulsions modified with curcumin and cerium dioxide nanoparticles // Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math. 2023. V. 14. № 1. P. 89–97. https://doi.org/10.17586/2220-8054-2023-14-1-89-97
Gadad A.P., Tigadi S.G., Dandagi P.M., Mastiholimath V.S., Bolmal U.B. Rosuvastatin loaded nanostructured lipid carrier: For enhancement of oral bioavailability // Indian J. Pharm. Ed. Res. 2016. V. 50. № 4. P. 605–611. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.50.4.13
Moghddam S.M.M., Ahad A., Aqil M., Imam S.S., Sultana Y. Optimization of nanostructured lipid carriers for topical delivery of nimesulide using Box–Behnken design approach // Artif. Cells, Nanomed., and Biotechnol. 2017. V. 45. № 3. P. 617–624. https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2016.1167699
Becerra M.O., Contreras L.M., Lo M.H., Díaz J.M., Herrera G.C. Lutein as a functional food ingredient: Stability and bioavailability // J. Funct. Foods. 2020. V. 66. 103771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103771
Ozawa Y., Sasaki M., Takahashi N., Kamoshita M., Miyake S., Tsubota K. Neuroprotective effects of lutein in the retina // Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012. V. 18. № 1. P. 51–56. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212798919101
Ahn Y.J., Kim H. Lutein as a modulator of oxidative stress-mediated inflammatory diseases // Antioxidants. 2021. V. 10(9). P. 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091448
Wang Y., Geng M., Zhang X., Yan M., Sun L., Zhao Q. Preparation of lutein nanoemulsion by ultrasonic homogenization method: Stability and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity // Algal Res. 2023. V. 73. P. 103154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2023.103154
Lim C., Kim D.W., Sim T., Hoang N.H., Lee J.W., Lee E.S., Youn Y.S., Oh K.T. Preparation and characterization of a lutein loading nanoemulsion system for ophthalmic eye drops // J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2016. V. 36. P. 168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2016.10.009
Doost A.S., Afghari N., Abbasi H., Nasrabadi M.N., Dewettinck K., Van der Meeren P. Nano-lipid carriers stabilized by hydrophobically modified starch or sucrose stearate for the delivery of lutein as a nutraceutical beverage model // Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 2020. V. 605. P. 125349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125349
Weigel F., Weiss J., Decker E.A., McClements D.J. Lutein-enriched emulsion-based delivery systems: Influence of emulsifiers and antioxidants on physical and chemical stability // Food Chem. 2018. V. 242. P. 395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.060
Teo A., Lee S.J., Goh K.K., Wolber F.M. Kinetic stability and cellular uptake of lutein in WPI-stabilised nanoemulsions and emulsions prepared by emulsification and solvent evaporation method // Food Chem. 2017. V. 221. P. 1269–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.030
Toragall V., Srirangam P., Jayapala N., Baskaran V. Lutein encapsulated oleic-linoleic acid nanoemulsion boosts oral bioavailability of the eye protective carotenoid lutein in rat model // Mater. Today Commun. 2021. V. 28. P. 102522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102522
Lacatusu I., Mitrea E., Badea N., Stan R., Oprea O., Meghea A. Lipid nanoparticles based on omega-3 fatty acids as effective carriers for lutein delivery. Preparation and in vitro characterization studies // J. Funct. Foods. 2013. V. 5. № 3. P. 1260–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2013.04.010
Tan F., Cui H., Bai C., Qin C., Xu L., Han J. Preparation, optimization, and transcorneal permeability study of lutein-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles // J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2021. V. 62. P. 102362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102362
Liu M., Wang F., Pu C., Tang W., Sun Q. Nanoencapsulation of lutein within lipid-based delivery systems: Characterization and comparison of zein peptide stabilized nano-emulsion, solid lipid nanoparticle, and nano-structured lipid carrier // Food Chem. 2021. V. 358. P. 129840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129840
Mitri K., Shegokar R., Gohla S., Anselmi C., Müller R.H. Lipid nanocarriers for dermal delivery of lutein: Preparation, characterization, stability and performance // Int. J. Pharm. 2011. V. 414. № 1–2. P. 267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.05.008
Koroleva M., Nagovitsina T., Yurtov E. Properties of nanocapsules obtained from oil-in-water nanoemulsions // Mendeleev Commun. 2015. V. 25. P. 389–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mencom.2015.09.026
Koroleva M., Portnaya I., Mischenko E., Abutbul-Ionita I., Kolik-Shmuel L., Danino D. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions with solid shell: Physical and thermal stability // J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. V. 610. P. 61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.12.010
Izquierdo P., Feng J., Esquena J., Tadros T.F., Dederen J.C., Garcia M.J., Azemar N., Solans C. The influence of surfactant mixing ratio on nano-emulsion formation by the PIT method // J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005. V. 285. № 1. P. 388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.10.047
Tikhonov V.P., Shevchenko T.V., Rodina I.A., Beljankina E.J., Pligina K.L., Makarova M.N., Girina M.B. Method of evaluating irritating action and activity of natural, synthetic substances and ready preparations on chick embryos by method of ultrasonic dopplerography // RF patent: RU 2383888 C1. 2010.
Mishchenko E.V., Timofeeva E.E., Artamonov A.S., Portnaya I.B., Koroleva M.Y. Nanoemulsions and nanocapsules with oleic acid // Colloid J. 2022. V. 84. № 1. P. 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X22010082
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Коллоидный журнал


