Микробиология, 2023, T. 92, № 3, стр. 250-260
Анаэробные Thermodesulfovibrio и аэробные Meiothermus сосуществуют в глубинной термальной воде
А. П. Лукина a, В. В. Кадников b, И. И. Русанов c, М. Р. Авакян a, А. В. Белецкий b, А. В. Марданов b, Н. В. Пименов c, Н. В. Равин b, О. В. Карначук a, *
a Лаборатория биохимии и молекулярной биологии, Томский государственный университет
634050 Томск, Россия
b Институт биоинженерии им. К.Г. Скрябина, ФИЦ Биотехнологии РАН
119071 Москва, Россия
c Институт микробиологии им. С.Н. Виноградского, ФИЦ Биотехнологии РАН
119071 Москва, Россия
* E-mail: olga.karnachuk@green.tsu.ru
Поступила в редакцию 09.12.2022
После доработки 13.12.2022
Принята к публикации 13.12.2022
- EDN: FWKVNZ
- DOI: 10.31857/S0026365622600833
Аннотация
Изучение микроорганизмов, обитающих в подземных водоносных горизонтах, основано на отборе проб воды, поступающих из глубинных скважин, и редко учитывает физико-химические процессы в системе вода‒порода. Остается неясным, как метаболизируют аэробные прокариоты, обнаруживаемые под землей молекулярными методами. Для прямого определения отношения прокариот к кислороду необходимо культивирование. В настоящем исследовании проведено целевое выделение аэробных и анаэробных бактерий, обнаруженных в термальных радоновых водах на курорте Белокуриха молекулярными методами. Профилирование по гену 16S рРНК выявило доминирование представителей группы Deionococcus‒Thermus, относящихся к роду Meiothermus (17.6% чтений) и считающихся строгими аэробами. Одновременно в воде присутствовали анаэробные сульфатредуцирующие Thermodesulfovibrio. Вода характеризовалась восстановительными и щелочными условиями. Целевое культивирование позволило выделить растущий аэробно Meiothermus sp. 1165, являющийся близким родственником Meiothermus cerbereus. Одновременно выделен алкалофильный анаэробный сульфатредуктор Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176. Измерение в воде Белокурихи интенсивности сульфатредукции с ${\text{Na}}_{{\text{2}}}^{{\,\,{\text{35}}}}{\text{S}}{{{\text{O}}}_{{\text{4}}}}$ продемонстрировало активный процесс, протекающий со скоростью 41.4 ± 1.06 мкг Sвосст/л/сут (1.29 нмоль S/мл/сут). Анализ генома штамма 1176 выявил присутствие различных механизмов, обеспечивающих относительную устойчивость к кислороду и окислительному стрессу и включающих супероксид редуктазу, рубредоксин, супероксид дисмутазу Fe-Mn семейства, каталазу-пероксидазу KatG и цитохром bd убихинол оксидазу. Низкий окислительно-восстановительный потенциал и интенсивный процесс анаэробной сульфатредукции подтверждают, что, в целом, подземные горизонты в Белокурихе характеризуются восстановительными условиями. Можно предположить пространственное разобщение аэробов и анаэробов в системе вода‒порода, как это происходит в наземных микробных матах, а также протекание аэробных процессов в микрозонах.
Современные оценки предполагают, что 15% всей биомассы Земли приходится на обитающих в подземных горизонтах бактерий и архей (Bar-On et al., 2018). Микроорганизмы подземных водоносных горизонтов остаются наименее изученной частью микробиоты планеты, прежде всего, в силу малой доступности подземных местообитаний для исследований. Отбор проб водоносных горизонтов возможен через глубинные скважины, которые образно называют “окнами в подземный мир” (Pedersen, 2000). Особое значение имеют артезианские скважины, из которых вода поступает под давлением, что исключает возможность контаминации наземными микроорганизмами. Однако один только отбор проб воды недостаточен для понимания активности прокариот, связанной с физическими и геологическими характеристиками биотопов. Подземные горизонты представляют насыщенные водой проницаемые породы. Взаимодействие вода‒порода является важным фактором, определяющим распространение и активность прокариот. Современные исследования показывают, что минеральная компонента, например, содержание глины, влияет на скорость роста различных таксонов бактерий в почве (Finley et al., 2022). Увеличение содержания минералов ближнего порядка (аллофана, имоголита, ферригидрита) угнетало рост бактерий. Одна из нерешенных загадок “подземной биосферы” ‒ вопрос о возможности присутствия кислорода в глубинных слоях и использования его аэробными микробами. Традиционно считают, что глубинные горизонты изолированы от атмосферы и характеризуются восстановительными и олиготрофными условиями (Lovley, Chapelle, 1995; Kieft et al., 2005). В условиях “подземной биосферы” энергетический метаболизм ограничивается анаэробным дыханием и брожением.
В предварительных исследованиях термальной воды из подземных водоносных горизонтов, используемых в бальнеологических целях на курорте Белокуриха (Алтайский край), мы обнаружили, что значительную часть микробного сообщества составляет группа Deionococcus‒Thermus, для которых предпочтительным является аэробный метаболизм. Одновременно вода характеризовалась отрицательными значениями окислительно-восстановительного потенциала и присутствием сульфатредуцирующих бактерий, включая Thermodesulfovibrio. Молекулярное профилирование сообщества прокариот позволяет определить таксономическое положение филотипов и определить их возможное отношение к присутствию/отсутствию кислорода в среде. Однако для окончательного подтверждения характера роста необходимы эксперименты с культурами.
Настоящее исследование посвящено целевому культивированию доминирующих филотипов бактерий, совмещенному с параллельным профилированием сообщества прокариот по гену 16S рРНК, и выяснению особенностей метаболизма путем измерения скорости процесса сульфатредукции и анализа генома.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Отбор проб, измерение физико-химических характеристик. Отбор проб воды проводили из скважины, обозначаемой 4Э и используемой в качестве источника минеральной радоновой воды на курорте Белокуриха. Пробы были отобраны дважды; для молекулярного анализа использовали воду, отобранную 08.08.2019. Для культивирования, измерения скорости сульфатредукции и параллельного молекулярного анализа пробы воды были отобраны 13.08.2021. Пробы воды отбирали на месте излива скважины 4Э. Физико-химические параметры воды, pH, температуру и окислительно-восстановительный потенциал измеряли рН-метром HI18314F (“Hanna Instruments”, Германия). Элементный состав воды определяли масс-спектрометрией с индуктивно связанной плазмой, как описано ранее (Карначук и соавт., 2015).
Измерение скорости сульфатредукции. Для измерения скорости сульфатредукции в условиях, приближенных к in situ, пробы воды разливали в пенициллиновые флаконы объемом 30 мл и закрывали резиновой пробкой без доступа воздуха. Аликвоты (300 мкл) Na235SO4 (4 мкКи; “PerkinElmer”, США) вносили в пенициллиновые флаконы шприцем через резиновую пробку. Все измерения скорости сульфатредукции проводили в трех повторностях. Инкубировали флаконы в течение 24 ч при температуре 42°С, после чего фиксировали 1 мл 1 N раствора KOH. В лаборатории проводили разделение восстановленных форм серы кислотной перегонкой (кислото-растворимые сульфиды) и восстановлением CrCl2 (элементная, пиритная и органическая сера), как описано ранее (Карначук и соавт., 2006).
Выделение чистых культур. Для культивирования концентрировали инокулят путем фильтрования через мембранный фильтр с диаметром пор 0.22 мкм. Для получения накопительных культур аэробных представителей группы Deionococcus‒ Thermus были использованы среды DSMZ256, DSMZ86 и DSMZ1004. Получение накопительных культур проводили на агаризованной среде DSMZ256, DSMZ86 и жидкой среде DSMZ1004. Накопительные культуры инкубировали при температуре 45, 50, 55 и 60°С.
Среда DSMZ1004 была модифицирована добавлением 1 мл/л раствора микроэлементов по Волину (Modified Wolin’s mineral solution, DSMZ141) и 2 мл/л раствора витаминов по Видделю (Widdel, Bak, 1992). Также вносили 1 мл/л раствор селената и вольфрамата и 2 мл/л раствора сульфида натрия по Видделю‒Баку (Widdel, Bak, 1992). В качестве донора электронов использовали глюкозу (10 мM); рН среды доводили раствором NaHCO3 (8%) до 7.5.
Для получения культуры Thermodesulfovibrio использовали пресноводную среду Видделя‒Бака (Widdel, Bak, 1992), содержащую (в г/л): Na2SO4 ‒ 4, KH2PO4 ‒ 0.2, NH4Cl ‒ 0.25, NaCl ‒ 1, MgCl2 · · 6H2O ‒ 0.4, KCl ‒ 0.5, CaCl2 ‒ 0.113, 2 мл раствора витаминов, 1 мл раствора микроэлементов, по 1 мл раствора Na2SeO3 и Na2WO4. Формиат (7.5 мМ) и ацетат (9 мМ) использовали в качестве донора электронов и Na2S · 9H2O – в качестве восстановителя.
Для определения филогенетического положения изолятов секвенировали ген 16S рРНК, амплифицированый с праймерами 27F-1492R. Выделение ДНК и условия амплификации аналогичны описанным ранее (Frank et al., 2016). Последовательности генов 16S рРНК штаммов Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176 и Meiothermus sp. 1165 депонированы в GenBank NCBI под номерами OP919603 и OP926023 соответственно.
Анализ состава микробного сообщества. Образцы воды (объемом 50 л) фильтровали через фильтр с диаметром пор 0.22 мкм. Фильтры гомогенизировали, растирая с жидким азотом; препарат метагеномной ДНК выделяли с помощью Power Soil DNA Isolation Kit (“MO BIO Laboratories Inc.”, Carlsbad, США).
Состав сообщества прокариот определяли на основании анализа последовательностей вариабельного региона V3–V4 гена 16S рРНК, амплифицированного с помощью ПЦР с использованием праймеров PRK341F (5'-CCTACGGGRBGCASCAG-3') и PRK806R (5'-GGACTACYVGGGTATCTAAT-3'). Полученные ПЦР фрагменты использовали для приготовления библиотеки для секвенирования с помощью набора Nextera XT DNA Library Prep Kit (“Illumina”, США) по протоколам производителя. Полученную библиотеку секвенировали на MiSeq (“Illumina”) с использованием набора MiSeq Reagent Kit v.3 (в формате парных чтений, 2 × 300 нт). Полученные пересекающиеся чтения объединяли с помощью программы FLASH v 1.2.11 (Magoč, Salzberg, 2011). В результате для образцов 2019 г. и 2021 г. было получено 137 780 и 13 979 последовательностей фрагментов генов 16S рРНК соответственно.
Последовательности фрагментов генов 16S рРНК кластеризовали в операционные таксономические единицы (ОТЕ) на уровне 97% идентичности с помощью программы USEARCH v. 11 (Edgar, 2010). Прочтения низкого качества, химерные последовательности и синглтоны удалялись алгоритмами USEARCH. Чтобы рассчитать относительные представленности ОТЕ, все полученные чтения были картированы на ОТЕ с глобальным порогом идентичности 97% с помощью USEARCH. Таксономическую классификацию OTЕ проводили по базе последовательностей рРНК SILVA v. 138 с использованием алгоритма VSEARCH v. 2.14.1 (Rognes et al., 2016).
Полученные последовательности фрагментов генов 16S рРНК депонированы в базу NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) под номерами SR-RХХХХХ (образец 2019 г.) и SRRХХХХХ (образец 2021 г.).
Секвенирование генома штамма Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176. Геномную ДНК выделяли с использованием набора Power Soil (“MO BIO Laboratories”, Carlsbad, CA, США) и секвенировали с использованием платформы Illumina MiSeq. Библиотеку готовили с использованием набора NEBNext Ultra II (“New England BioLabs”, Ipswitch, MA, США). В результате секвенирования этой библиотеки на Illumina MiSeq с использованием реагентов MiSeq Reagent Kit v.3 (в формате парных чтений, 2 × 300 нт) получено 1 051 896 чтений. Перекрывающиеся парные чтения были объединены с помощью FLASH v1.2.11 (Magoč, Salzberg, 2011), а последовательности с низким качеством были удалены с помощью Sickle v1.33 (https:// github.com/najoshi/sickle/). Чтения Illumina собирали в контиги с помощью SPAdes v.3.11.1 (Nurk et al., 2013). Поиск и аннотацию генов проводили с помощью сервера RAST (Brettin et al., 2015). Полноту драфт генома оценивали с помощью программы CheckM (Parks et al., 2015).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Физико-химические характеристики воды из скважины 4Э и скорость сульфатредукции. Температура воды скважины 4Э в момент отбора проб 08.08.2019 составляла 38.0°C, рН ‒ 9.12 (табл. 1). Измеренный окислительно-восстановительный потенциал, ‒40 мВ, мог быть несколько завышен в силу того, что из-за конструкции подводящих путей не было возможности провести измерения непосредственно на изливе скважины. Измерения проводили в бутыли с пробой воды. Концентрация сульфата в воде изменялась от 88.6 мг/л в 2019 г., до 57.0 мг/л – в 2021 г. Заметной особенностью микроэлементного состава воды была высокая концентрация вольфрама, достигавшая 140 мкг/л. Также высокой была концентрация молибдена, составлявшая 38 мкг/л.
Таблица 1.
Физико-химические параметры воды скважины 4Э
| Параметры и единицы измерения | Значения |
|---|---|
| рН | 9.12 |
| Температура, °C | 38.0 |
| Eh, мВ | ‒40 |
| Содержание в воде, мг/л: | |
| ${\text{SO}}_{4}^{{2 - }}$ | 88.6 |
| Cl– | 11.3 |
| ${\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - }$ | 4.6 |
| F– | 17.6 |
| Na | 69.3 |
| Mg | 0.0017 |
| Ca | 2.75 |
| Si | 26.2 |
| K | 1.06 |
| Sr | 0.070 |
| W | 0.140 |
| Mo | 0.038 |
| Cs | 0.030 |
| B | 0.29 |
| Li | 0.50 |
| Fe | <0.02 |
| Ba | 0.00025 |
| Se | 0.00083 |
| P | <0.2 |
| Rb | 0.012 |
| Mn | 0.000068 |
| Al | 0.0024 |
| Ge | 0.0050 |
| Zn | 0.0013 |
| Cr | <0.0005 |
| As | 0.0026 |
Средняя скорость сульфатредукции, измеренная в пробах воды в августе 2021 г., составляла 41.4 ± 1.06 мкг Sвосст/л/сут (1.29 нмоль S/мл/сут). Большая часть (92.5%) восстановленной серы находилась в форме сероводорода (кислоторастворимая сера, КРС). Остальная часть метки находилась в форме серы, восстанавливаемой CrCl3 (ХВС), которая может включать пирит (FeS2), элементную и органическую серу.
Состав микробного сообщества. В микробном сообществе воды, отобранной из скважины 4Э в 2019 г., доминировали бактерии, доля архей составляла лишь 0.3% всех последовательностей генов 16S рРНК. На уровне филумов доминировали представители Proteobacteria (32.5%), Deinococcota (18.5%), Candidatus Eremiobacterota (13.8%), Chloroflexi (10.3%), Patescibacteria (6.8%), Actinobacteriota (4.2%), Armatimonadota (3.4%), Planctomycetota (2.6%), Acidobacteriota (2.5%), Bacteroidota (1.6%); доли остальных линий уровня филума не превышали 1% (рис. 1).
Рис. 1.
Состав микробного сообщества на уровне филумов по данным профилирования гена 16S рРНК в 2019 и 2021 гг.
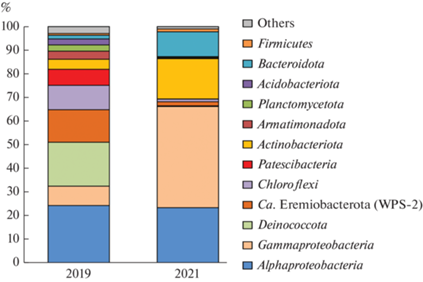
Большинство протеобактерий представляли классы альфа (24.3%) и гамма (8.2%). Наиболее многочисленная ОТЕ альфапротеобактерий, представлявшая 9.9% сообщества, имела 97.6%-ю гомологию последовательности гена 16S рРНК с Parvibaculum lavamentivorans, ‒ аэробной гетеротрофной бактерией, идентифицированной в сточных водах (Schleheck et al., 2004). Также среди альфапротеобактерий были обнаружены представители порядков Caulobacterales (2.0%), Rhizobiales (3.4%), Rhodobacterales (1.6%), Sphingomonadales (5.5%), Acetobacterales (0.3%) и Azospirillales (0.4%). На уровне рода были идентифицированы Brevundimonas (1.8%), Rubellimicrobium (1.3%), Novosphingobium (2.4%), Sphingomonas (2.9%), среди культивируемых представителей которых преобладают аэробные гетеротрофы, встречающиеся в почвах и водоемах (Dastager et al., 2008; Asaf et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021). Среди гаммапротеобактерий были обнаружены семейства Comamonadaceae (2.3%) и Hydrogenophilaceae (5.4%); последнее включало род Thiobacillus (3.8%) и неклассифицируемые на уровне рода филотипы. Представители Thiobacillus являются хемолитоавтотрофами, способными окислять железо или восстановленные соединения серы (Rawlings, Kusano, 1994).
Во втором по относительной численности филуме, Deinococcota, доминировал род Meiothermus (17.6%), наиболее многочисленный филотип которого (15.4%) был близок к Meiothermus ruber (99.1% идентичности по 16S рРНК). Представители этого рода – умеренно термофильные гетеротрофы, встречающиеся в термальных водах, включая подземные (Tindall et al., 2010). Около 0.9% сообщества составляли представители семейства Deinococcaceae.
Третья по численности линия, кандидатный филум Eremiobacterota (WPS-2), был представлен одной ОТЕ. Этот филум включает представителей с разнообразными путями метаболизма, включая аноксигенный фотосинтез, автотрофный рост за счет окисления атмосферного водорода и СО, анаэробное дыхание и органотрофию (Ji et al., 2021).
Около 6.8% сообщества составляют Patescibacteria, большая часть которых относится к одной ОТЕ кандидатного класса WWE3 (по таксономии Silva). Возможно, реальное содержание Patescibacteria даже выше, поскольку из-за небольших размеров клеток представителей этого филума часть их может теряться при использовании для сбора биомассы 0.2 мкм фильтра (Herrmann et al., 2019). Представители Patescibacteria характерны для грунтовых вод и преимущественно распространены в бескислородных средах, реже встречаются в подземных водах, содержащих кислород (Nelson, Stegen, 2015). Patescibacteria обладают небольшими геномами (обычно менее ~1 млн нт) и лишены многих ключевых биосинтетических путей (Brown et al., 2015). Предположительно, Patescibacteria являются паразитами или симбионтами других микроорганизмов (Ji et al., 2022).
Остальные филумы бактерий были в основном представлены линиями гетеротрофов, характерных для почв и подземных вод. Это Chloroflexi (в основном класс Anaerolineae), Actinobacteria (в основном Corynebacteriales, Micrococcales и Solirubrobacterales), Armatimonadetes (Fimbriimonadales), Planctomycetes (Phycisphaerales, Gemmatales и Isosphaerales), Acidobacteria (Bryobacterales и Blastocatellales) и Bacteroidota.
Среди известных линий диссимиляционных сульфатредукторов были детектированы представители порядка Desulfitobacteriales филума Firmicutes, ‒ Desulfosporosinus, Desulfotomaculum и Desulfurispora, но их суммарная доля составляла менее 0.02%. Около 0.03% сообщества представлял ‘Desulforudis audaxviator’, ‒ эндемичная для глубинной подземной биосферы бактерия, ранее выделенная нами из подземных вод Западно-Сибирского региона (Karnachuk et al., 2019). Потенциальными сульфатредукторами также могут быть представители класса Thermodesulfovibrionia филума Nitrospirota (0.6% сообщества), который включает термофильных сульфатредукторов рода Thermodesulfovibrio. Однако детектированные ОТЕ были филогенетически удалены от культивируемых Thermodesulfovibrio и не были классифицированы даже на уровне порядка. Отметим, что известные сульфатредукторы филума Desulfiobacterota не были обнаружены.
Микробное сообщество воды, отобранной в 2021 г., содержало те же основные таксономические группы микроорганизмов, хотя их соотношения заметно отличались. Преобладали представители трех филумов Proteobacteria (66.3%, в основном класса гамма), Actinobacteriota (17.1%) и Bacteroidota (10.5%), доли филумов Deinococcota, Candidatus Eremiobacterota, Chloroflexi и Patescibacteria были намного ниже, чем в образцах 2019 г. (0.3, 1.7, 1.1 и 0.03% соответственно). Наиболее многочисленный филотип 2021 г. (21.9%), представляющий род Cavicella семейства Moraxellaceae, не был детектирован в 2019 г. Представитель этого рода, Cavicella subterranea, является органотрофным аэробом и был выделен из подземного водоносного горизонта глубиной 150 м в Португалии (França et al., 2015). Второй по численности филотип, актинобактерии рода Dietzia, представители которого могут окислять углеводороды (Ali et al., 2022), составляли 16.7% сообщества в 2021 г. и лишь 0.7% в 2019 г. Тем не менее, представители рода Meiothermus и неклассифицируемые Thermodesulfovibrionia были обнаружены и в образцах 2021 г., составляя, соответственно, 0.3 и 0.2% сообщества.
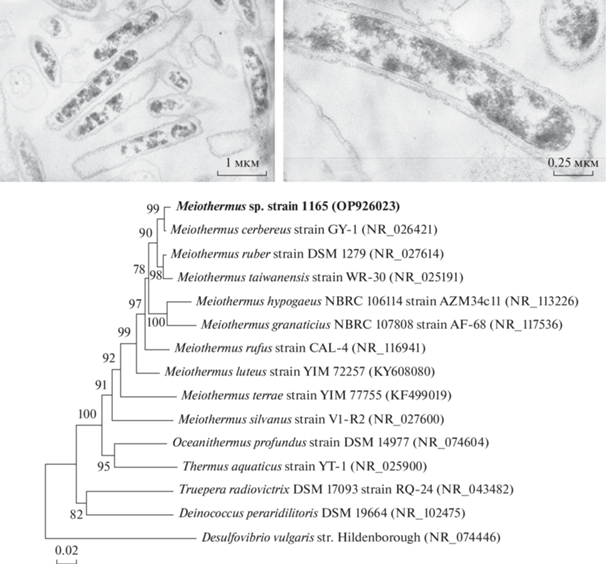
Выделение чистых культур. Учитывая результаты профилирования по гену 16S рРНК, полученные в 2019 г., целевыми филотипами для выделения в культуру были выбраны аэробные Meiothermus и строго анаэробные Thermodesulfovibrio. Для получения накопительных культур аэробных Meiothermus была использована среда DSMZ256, содержащая пептон и крахмал, и DSMZ86, содержащая триптон. Однако рост на агаризованной среде в условиях температур от 45 до 60°C отсутствовал. Одновременно наблюдали присутствие морфологически однородных палочковидных клеток, образующих тяжи, на среде DSMZ1004 с глюкозой для Chloroflexi при культивировании в анаэробных условиях при температуре 50°C. Последующее культивирование накопительной культуры в аэробных условиях на качалке (160 об./мин) на модифицированной среде DSMZ1004 привело к выделению чистой культуры, обозначенной как штамм 1165. Филогенетический анализ последовательности гена 16S рРНК штамма 1165 показал, что он относится к роду Meiothermus (рис. 2). Ближайшими родственниками являются Meiothermus cerbereus и Meiothermus ruber со сходством последовательностей гена 16S рРНК 99.13 и 97.8% соответственно. Штамм рос в узком диапазоне температур от 40 до 50°C, оптимальная температура роста составляла 50°C. При росте на жидкой среде штамм 1165 мог использовать в качестве субстрата крахмал, глюкозу, сахарозу, фруктозу, триптон, пептон и соевый пептон.
Рис. 2.
Микрофотографии ультратонких срезов клеток и дерево, показывающее филогенетическое положение штамма Meiothermus sp. 1165 на основе анализа последовательностей гена 16S рРНК, определенное методом Neighbor-Joining. Бутстрепы рассчитаны из 1000 итераций.
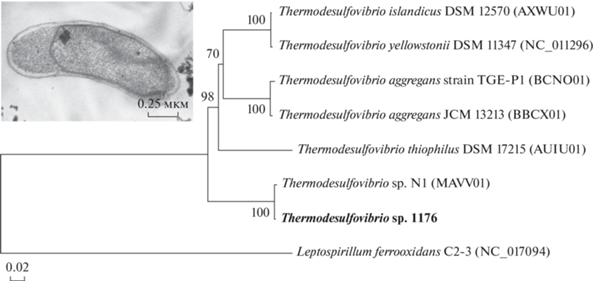
Целевое выделение Thermodesulfovibrio проводили на пресноводной среде Видделя‒Бака с формиатом и ацетатом в качестве донора электронов и источника углерода и сульфитом в качестве акцептора, при 70○C; рН среды увеличивали до 8.5 с учетом щелочной реакции среды в термальной воде. Полученный сульфидоген был обозначен как штамм 1176. Филогенетический анализ последовательности гена 16S рРНК штамма 1176 подтвердил, что бактерия относится к роду Thermodesulfovibrio (рис. 3). Ближайшим родственником штамма 1176 является алкалотолерантный Thermodesulfovibrio sp. N1, выделенный из термальных подземных вод мезозойских отложений в поселке Белый Яр Томской области (Frank et al., 2016). Проведенный анализ сходства нуклеотидных последовательностей геномов показал, что среднее сходство (ANI) штаммов 1176 и N1 составляет 99.13% и не превышает порог 95%, предложенный для разграничения видов (Chun et al., 2018). Молекулярные данные свидетельствуют о принадлежность штаммов N1 и 1176 к одному виду. Штамм 1176 рос в диапазоне температур от 37 до 65○C с оптимумом при 55○C. Штамм характеризовался широким диапазоном рН для роста от 5.5 до 12, с оптимумом 10.5.
Рис. 3.
Микрофотографии ультратонких срезов клеток и дерево, показывающее филогенетическое положение штамма Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176 на основе анализа конкатенированных аминокислотных последовательностей 120 однокопийных белков-маркеров. Дерево построено методом Neighbor-Joining. Бутстрепы рассчитаны из 1000 итераций. Неясные позиции были удалены для каждой пары последовательностей (pairwise deletion option). Общее количество позиций – 5040. Эволюционный анализ проведен в MEGA11.
Анализ генома Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176. Геном штамма Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176 был получен в виде 32 контигов суммарной длиной 2 083 381 нт. Полнота собранного драфт генома оценивается СheckM в 99.1%. Проведенный анализ сходства нуклеотидных последовательностей геномов показал, что ANI между геномами штаммов 1176 и N1 (GCA_001707915) составляет 99.61%, что указывает на их принадлежность к одному виду (Chun et al., 2018). В геноме предсказано 2222 белок-кодирующих гена, 3 гена рРНК и 46 генов транспортных РНК (тРНК). Сравнение геномов этих штаммов выявили минимальные отличия в наборах присутствующих у них генов; штамм-специфические гены, в основном, кодировали белки мобильных элементов и гипотетические белки с неизвестными функциями.
Анализ генома штамма 1176 показал, что он содержит набор генов диссимиляционной сульфатредукции, включая сульфатаденил трансферазу, аденозин-фосфосульфат редуктазу AprAB, мембранно-связанный электрон-транспортный комплекс QmoABC, диссимиляционную сульфитредуктазу DsrABC и ассоциированный с ней комплекс DsrMKJOP. Наличие поглощающей гидрогеназы и формиатдегидрогеназы указывает на возможность окисления водорода и формиата. Помимо сульфата, штамм 1176 может использовать в качестве акцепторов электронов нитрит и тиосульфат, о чем свидетельствует присутствие соответствующих мембранно-связанных оксидоредуктаз. В отличие от T. yellowstonii, T. aggregans и T. islandicus, у штамма 1176, как и у штамма N1, отсутствует нитрогеназа. Общим для штаммов 1176 и N1 адаптивным признаком, связанным с алкалофилией, является наличие мультисубъединичного Na+/H+ антипортера Mnh семейства.
У штамма 1176 имеются различные механизмы, которые могут обеспечивать его относительную устойчивость к кислороду и окислительному стрессу. Наряду с обычно встречающимися у анаэробов супероксид редуктазой и рубредоксином, в геноме кодируются характерные для аэробов супероксиддисмутаза Fe-Mn семейства и каталаза-пероксидаза KatG, которые могут обеспечивать детоксификацию супероксид-радикала. Также у штамма 1176 имеется мембранно-связанная цитохром bd убихинол оксидаза. Эти ферменты имеют высокое сродство к кислороду (Jünemann, 1997) и могут обеспечивать не только защиту от окислительного стресса в микроаэробных условиях (Borisov et al., 2021), но и генерацию трансмембранного протонного градиента. Наряду с ферментативными механизмами, толерантность штамма 1176 к кислороду может обеспечиваться за счет внеклеточного полисахаридного матрикса. Его формирование возможно благодаря bcsABZC-оперону, кодирующему целлюлоз-синтазу. Помимо штамма 1176, это оперон имеется у родственного штамма N1 и у T. aggregans (Frank et al., 2016), но отсутствует у других видов Thermodesulfovibrio.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Молекулярный анализ термальной радоновой воды выявил присутствие как аэробных, так и анаэробных бактерий. Однако для окончательного подтверждения характера роста необходимы эксперименты с культурами. Несмотря на снижение численности Meiothermus в воде в 2021 г., представитель этого рода, штамм 1165, был успешно культивирован, и продемонстрирован его аэробный рост на сахарах и белках. Meiothermus sp. 1165 сохранял жизнеспособность и в анаэробных условиях. До последнего времени представителей Meiothermus рассматривали как строго аэробных умеренно термофильных гетеротрофов (Habib et al., 2017). Некоторые представители Meiothermus могут использовать нитрат в качестве акцептора электронов. Достаточное для протекания нитратредукции количество NO3 (4.6 мг/л) обнаружено в воде скважины 4Э.
Представители Meiothermus устойчивы к радиации (Masurat et al., 2005). Авторы обнаружили биопленки Meiothermus внутри системы для хранения отходов отработанного ядерного топлива. Анализ по гену 16S рРНК показал, что Meiothermus, образующий микробные обрастания в радиоактивных местообитаниях, представляет удаленную ветвь внутри рода, но его ближайшим родственником является M. cerbereus. Дальнейшего описания бактерии не было проведено. Термальные воды курорта Белокуриха содержат радон и природную радиоактивность. Содержание радона в скважине 4Э составляет 5–8 нKи/л (Джабарова и соавт., 2016). Возможная устойчивость штамма 1165 к радиоактивности обусловливает его распространение в воде подземных горизонтов. Сходство последовательностей генов 16S рРНК штамма 1165 и M. cerbereus составляло 99.13% и превышало установленный порог для разграничения видов 98.7% (Kim et al., 2014). Вероятно, бактерия, выделенная из термальных вод в Белокурихе, представляет новый штамм M. cerbereus. Штамм 1165 отличается от типового штамма GY-1 активным ростом на жидкой среде, в то время как вид получил свое латинское название “cerbereus” из-за трудностей, связанных с выращиванием на жидкой среде (Chung et al., 1997). Штамм 1165 рос только на жидкой среде и не поддавался культивированию на агаризованных средах.
Несмотря на более ранние представления об отсутствии кислорода и существовании восстановленных условий в подземных горизонтах, последние исследования демонстрируют возможность существования низкого парциального давления О2. В частности, 0.42–2.3 мл/л растворенного O2 было обнаружено в водах шахты по добыче золота в Южной Африке (Weinstein et al., 2019) на глубине 1.3 км. Из этого биотопа была выделена подземная нематода Halicephalobus mephisto (Borgonie et al., 2011). Нематода поддерживала аэробный метаболизм в условиях гипоксии при парциальном давлении кислорода всего 0.4 кПа. Авторы предполагают, что нематода питается населяющими глубинные слои прокариотами. Для поддержания энергетического метаболизма животное должно находиться в микробных биопленках, развивающихся во вмещающих породах. Наши исследования подземной термофильной спирохеты Longinema margulisae предполагают возможность образования микробных обрастаний в глубинных водоносных горизонтах, аналогичных развивающимся в наземных условиях микробным матам (Karnachuk et al., 2021). Прямые доказательства существования сестонных форм в подземной биосфере были получены при изучении колонок фракционных пород (Wanger et al., 2006). Авторы наблюдали участки органического вещества и микроколонии клеток, связанные с породой в колонках фракционной зоны шахты Мпоненг в Южной Африке, в водах которой ранее был обнаружен ‘Desulforudis audaxviator’.
Несмотря на общепризнанный факт широкого распространения сульфатредуцирующих прокариот в термальных подземных водоносных горизонтах (Bell et al., 2020), измерение скорости процесса сульфатредукции в этих биотопах фактически не проводили. Нам известно единственное сообщение об определении скорости сульфатредукции с использованием радиоактивного сульфата в воде офолитов Самаил (Samail Ophiolite) в султанате Оман (Glombitza et al., 2021). Авторы провели измерение скорости процесса в воде, полученной из 12 скважин, глубиной от 78 до 472 м и температурой от 30.0 до 35.7○C. Скорость сульфатредукции была низкой, максимальная величина составляла 2.1 пмоль мл/сут, что было на три порядка меньше измеренной нами в воде Белокурихи. Интересно отметить, что профилирование микробного сообщества по гену 16S рРНК в водах офолитов выявило доминирование представителей Meiothermus (6.78% всех чтений) и Thermodesulfovibrio (5.33% всех чтений) (Rempfert et al., 2017). Подземную воду офолитов и изученную нами радоновую подземную воду объединяет щелочная реакция среды; рН в воде скважин офолитов Самаил изменялась в пределах от 7.6 до 11.4. Meiothermus также доминировали в щелочной термальной воде офолитов Замбала (Zambala) на Филлипинах (Woycheese et al., 2015), где они составляли 45% всего сообщества. Исследованные пробы воды характеризовались низкими значениями окислительно-восстановительного потенциала (от ‒194 до –580 мВ) и рН около 10.
Высокие концентрации вольфрама и молибдена, зафиксированные в воде скважины 4Э в Белокурихе, известны для геотермальных вод (Planer-Friedrich et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2021). Интересно отметить, что оба металла являются важными кофакторами формиатдегидрогеназ у классических сульфатредукторов Desulfovibrionales (Zhang, Gladyshev, 2008). Недавно на примере модельного Desulfovibrio vulgaris Heldenborough были описаны новые регуляторы транскрипции TaoR, контролирующие экспрессию транспортеров вольфрама и молибдена (Rajeev et al., 2018). Оба микроэлемента используются в питательных средах для выращивания сульфатредукторов (Widdel, Bak, 1992), и их доступность в подземной воде может быть дополнительным фактором, способствующим развитию СРБ.
Таким образом, наши результаты свидетельствуют в пользу существования гетерогенных условий в глубинных водоносных горизонтах в Белокурихе, что обеспечивает одновременное присутствие аэробных Meiothermus и анаэробных Thermodesulfovibrio. Низкий окислительно-восстановительный потенциал и интенсивный процесс анаэробной сульфатредукции подтверждают, что, в целом, подземные горизонты характеризуются восстановительными условиями. Можно предположить пространственное разобщение аэробов и анаэробов в системе вода‒порода, как это происходит в наземных микробных матах. Кроме того, выделенный нами Thermodesulfovibrio sp. 1176 может образовывать внеклеточные полисахариды, благодаря bcsABZC оперону, кодирующему целлюлоз-синтазу. Очевидно, что гетерогенность водоносных горизонтов может обеспечивать существование микрозон, известных для морских осадков. Только в случае анаэробных водоносных горизонтов, характеризующихся восстановительными условиями, можно ожидать существование микрозон с низким парциальным давлением кислорода.
Список литературы
Джабарова Н.К., Яковенко Э.С., Сидорина Н.Г., Коханенко А.А., Воробьев В.А., Зайцев А.А., Коваленко Т.С., Жиляков И.В. Перспективы развития Белокурихинской курортной зоны Алтайского края // Вопросы курортологии, физиотерапии и лечебной физической культуры. 2016. № 2. С. 43‒47.
Карначук О.В., Пименов Н.В., Юсупов С.К., Франк Ю.А. Пухакка Я.А., Иванов М.В. Распределение, разнообразие и активность сульфатредуцирующих бактерий в водной толще озера Гек-Гель, Азербайджан // Микробиология. 2006. Т. 75. С. 101‒109.
Karnachuk O.V., Pimenov N.V., Yusupov S.K., Frank Yu.A., Puhakka Ya.A., Ivanov M.V. Distribution, diversity, and activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the water column in Gek-Gel Lake, Azerbaijan // Microbiology (Moscow). 2006. V. 75. P. 82‒89.
Карначук О.В., Курганская И.А., Авакян М.Р., Франк Ю.А., Иккерт О.П., Филенко Р.А., Данилова Э.В., Пименов Н.В. Ацидофильный Desulfosporosinus из окисленных отходов добычи металлов в Забайкальском крае // Микробиология. 2015. Т. 84. С. 595‒605.
Karnachuk O.V., Kurganskaya I.A., Avakyan M.R., Frank Y.A., Ikkert O.P., Filenko R.A., Danilova E.V., Pimenov N.V. An acidophilic Desulfosporosinus isolated from the oxidized mining wastes in the Transbaikal area // Microbiology (Moscow). 2015. V. 84. P. 677‒686.
Ali N., Khanafer M., Al-Awadhi H. Indigenous oil-degrading bacteria more efficient in soil bioremediation than microbial consortium and active even in super oil-saturated soils // Front. Microbiol. 2022. V. 13. Art. 950051.
Asaf S., Numan M., Khan A.L., Al-Harrasi A. Sphingomonas: from diversity and genomics to functional role in environmental remediation and plant growth // Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020. V. 40. P. 138‒152.
Bar-On Y.M., Phillips R., Milo R. The biomass distribution on Earth // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018. V. 115. P. 6506‒6511.
Bell E., Lamminmäki T., Alneberg J., Andersson A.F., Qian C., Xiong W., Hettich R.L., Frutschi M., Bernier-Latmani R. Active sulfur cycling in the terrestrial deep subsurface // ISME J. 2020. V. 14. P. 1260‒1272.
Borgonie G., García-Moyano A., Litthauer D., Bert W., Bester A., van Heerden E., Möller C., Erasmus M., Onstott T.C. Nematoda from the terrestrial deep subsurface of South Africa // Nature. 2011. V. 474. P. 79‒82.
Borisov V.B., Siletsky S.A., Nastasi M.R., Forte E. ROS defense systems and terminal oxidases in bacteria // Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. V. 10. Art. 839.
Brettin T., Davis J.J., Disz T., Edwards R.A., Gerdes S., Olsen G.J., Olson R., Overbeek R., Parrello B., Pusch G.D., Shukla M., Thomason J.A. 3rd, Stevens R., Vonstein V., Wattam A.R., Xia F. RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes // Sci. Rep. 2015. V. 5. Art. 8365.
Brown C.T., Hug L.A., Thomas B.C., Sharon I., Castelle C.J., Singh A., Wilkins M.J., Wrighton K.C., Williams K.H., Banfield J.F. Unusual biology across a group comprising more than 15% of domain Bacteria // Nature. 2015. V. 523. P. 208.
Chun J., Oren A., Ventosa A., Christensen H., Arahal D.R., da Costa M.S., Rooney A.P., Yi H., Xu X.W., De Meyer S., Trujillo M.E. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes // Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018. V. 68. P. 461‒466.
Chung A.P., Rainey F., Nobre M.F., Burghardt J., da Costa M.S. Meiothermus cerbereus sp. nov., a new slightly thermophilic species with high levels of 3-hydroxy fatty acids // Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997. V. 47. P. 1225‒1230.
Dastager S.G., Lee J.C., Ju Y.J., Park D.J., Kim C.J. Rubellimicrobium mesophilum sp. nov., a mesophilic, pigmented bacterium isolated from soil // Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008. V. 58. P. 1797‒1800.
Edgar R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST // Bioinformatics 2010. V. 26. P. 2460‒2461.
Finley B.K., Mau R.L., Hayer M., Stone B.W., Morrissey E.M., Koch B.J., Rasmussen C., Dijkstra P., Schwartz E., Hungate B.A. Soil minerals affect taxon-specific bacterial growth // ISME J. 2022. V. 16. P. 1318‒1326.
França L., Albuquerque L., da Costa M.S. Cavicella subterranea gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a deep mineral-water aquifer, and emended description of the species Perlucidibaca piscinae // Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015. V. 65. P. 3812‒3817.
Frank Y.A., Kadnikov V.V., Lukina A.P., Banks D., Beletsky A.V., Mardanov A.V., Sen’kina E.I., Avakyan M.R., Karnachuk O.V., Ravin N.V. Characterization and genome analysis of the first facultatively alkaliphilic Thermodesulfovibrio isolated from the deep terrestrial subsurface // Front. Microbiol. 2016. V. 7. Art. 2000.
Glombitza C., Putman L.I., Rempfert K.R., Kubo M.D., Schrenk M.O., Templeton A.S., Hoehler T.M. Active microbial sulfate reduction in fluids of serpentinizing peridotites of the continental subsurface // Commun. Earth Environ. 2021. V. 2. Art. 84.
Habib N., Khan I.U., Hussain F., Zhou E.M., Xiao M., Dong L., Zhi X.Y., Li W.J. Meiothermus luteus sp. nov., a slightly thermophilic bacterium isolated from a hot spring // Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017. V. 67. P. 2910‒2914.
Herrmann M., Wegner C.E., Taubert M., Geesink P., Lehmann K., Yan L., Lehmann R., Totsche K.U., Küsel K. Predominance of Cand. Patescibacteria in groundwater is caused by their preferential mobilization from soils and flourishing under oligotrophic conditions // Front. Microbiol. 2019. V. 10. Art. 1407.
Ji M., Williams T.J., Montgomery K., Wong H.L., Zaugg J., Berengut J.F., Bissett A., Chuvochina M., Hugenholtz P., Ferrari B.C. Candidatus eremiobacterota, a metabolically and phylogenetically diverse terrestrial phylum with acid-tolerant adaptations // ISME J. 2021. V. 15. P. 2692‒2707.
Ji Y., Zhang P., Zhou S., Gao P., Wang B., Jiang J. Widespread but poorly understood bacteria: Candidate Phyla Radiation // Microorganisms. 2022. V. 10. Art. 2232.
Jünemann S. Cytochrome bd terminal oxidase // Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997. V. 1321. P. 107‒127.
Karnachuk O.V., Frank Y.A., Lukina A.P., Kadnikov V.V., Beletsky A.V., Mardanov A.V., Ravin N.V. Domestication of previously uncultivated Candidatus Desulforudis audaxviator from a deep aquifer in Siberia sheds light on its physiology and evolution // ISME J. 2019. V. 13. P. 1947‒1959.
Karnachuk O.V., Lukina A.P., Kadnikov V.V., Sherbakova V.A., Beletsky A.V., Mardanov A.V., Ravin N.V. Targeted isolation based on metagenome-assembled genomes reveals a phylogenetically distinct group of thermophilic spirochetes from deep biosphere // Environ. Microbiol. 2021. V. 23. P. 3585‒3598.
Kieft T.L., McCuddy S.M., Onstott T.C., Davidson M., Lin L.-H., Mislowack B., Pratt L., Boice E., Lollar B.S., Lippmann-Pipke J., Pfiffner S.M., Phelps T.J., Gihring T., Moser D., van Heerden A. Geochemically generated, energy-rich substrates and indigenous microorganisms in deep, ancient groundwater // Geomicrobiol. J. 2005. V. 22. P. 325–335.
Kim M., Oh H.S., Park S.C., Chun J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rR-NA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes // Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014. V. 64. P. 346‒351.
Liu L., Feng Y., Wei L., Zong Z. Genome-based taxonomy of Brevundimonas with reporting Brevundimonas huaxiensis sp. nov. // Microbiol. Spectr. 2021. V. 9. e0011121.
Lovley D.R., Chapelle F.H. Deep subsurface microbial processes // Rev. Geophys. 1995. V. 33. P. 365–381.
Magoc T., Salzberg S.L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies // Bioinformatics. 2011. V. 27. P. 2957–2963.
Masurat P., Fru E.C., Pedersen K. Identification of Meiothermus as the dominant genus in a storage system for spent nuclear fuel // J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005. V. 98. P. 727‒740.
Nelson W.C., Stegen J.C. The reduced genomes of Parcubacteria (OD1) contain signatures of a symbiotic lifestyle // Front. Microbiol. 2015. V. 6. Art. 713.
Nurk S., Bankevich A., Antipov D., Gurevich A.A., Korobeynikov A., Lapidus A., Prjibelski A.D., Pyshkin A., Sirotkin A., Sirotkin Y., Stepanauskas R., Clingenpeel S.R., Woyke T., McLean J.S., Lasken R., Tesler G., Alekseyev M.A., Pevzner P.A. Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products // J. Comput. Biol. 2013. V. 20. P. 714‒737.
Parks D.H., Imelfort M., Skennerton C.T., Hugenholtz P., Tyson G.W. CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes // Genome Res. 2015. V. 25. P. 1043‒1055.
Pedersen K. Exploration of deep intraterrestrial microbial life: current perspectives // FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000. V. 185. P. 9‒16.
Planer-Friedrich B., Forberg J., Lohmayer R., Kerl C.F., Boeing F., Kaasalainen H., Stefánsson A. Relative abundance of thiolated species of As, Mo, W, and Sb in hot springs of Yellowstone National Park and Iceland // Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020. V. 54. P. 4295‒4304.
Rajeev L., Garber M.E., Zane G.M., Price M.N., Dubchak I., Wall J.D., Novichkov P.S., Mukhopadhyay A., Kazakov A.E. A new family of transcriptional regulators of tungstoenzymes and molybdate/tungstate transport // Environ. Microbiol. 2019. V. 21. P. 784‒799.
Rawlings D.E., Kusano T. Molecular genetics of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans // Microbiol. Rev. 1994. V. 58. P. 39‒55.
Rempfert K.R., Miller H.M., Bompard N., Nothaft D., Matter J.M., Kelemen P., Fierer N., Templeton A.S. Geological and geochemical controls on subsurface microbial life in the Samail Ophiolite, Oman // Front. Microbiol. 2017. V. 8. Art. 56.
Rognes T., Flouri T., Nichols B., Quince C., Mahé F. VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics // Peer J. Preprints. 2016. V. 4. e2409v1.
Schleheck D., Tindall B.J., Rosselló-Mora R., Cook A.M. Parvibaculum lavamentivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel heterotroph that initiates catabolism of linear alkylbenzenesulfonate // Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004. V. 54. P. 1489‒1497.
Tindall B.J., Sikorski J., Lucas S., Goltsman E., Copeland A., Glavina Del Rio T., Nolan M., Tice H., Cheng J.F., Han C., Pitluck S., Liolios K., Ivanova N., Mavromatis K., Ovchinnikova G., Pati A., Fähnrich R., Goodwin L, Chen A., Palaniappan K., Land M., Hauser L., Chang Y.J., Jeffries C.D., Rohde M., Göker M., Woyke T, Bristow J., Eisen J.A., Markowitz V., Hugenholtz P., Kyrpides N.C., Klenk H.P., Lapidus A. Complete genome sequence of Meiothermus ruber type strain (21) // Stand. Genomic Sci. 2010. V. 3. P. 26‒36.
Wanger G., Southam G. Onstott T.C. Structural and chemical characterization of a natural fracture surface from 2.8 kilometers below land surface: biofilms in the deep subsurface // Geomicrobiol. J. 2006. V. 23. P. 443‒452.
Weinstein D.J., Allen S.E., Lau M.C.Y., Erasmus M., Asalone K.C., Walters-Conte K., Deikus G., Sebra R., Borgonie G., van Heerden E., Onstott T.C., Bracht J.R. The genome of a subterrestrial nematode reveals adaptations to heat // Nat. Commun. 2019. V. 10. Art. 5268.
Widdel F.F., Bak R. Gram negative mesophilic sulfate reducing bacteria // The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Ecophysiology, Isolation, Identification, Applications / Eds. Balows A. et al. Berlin: Springer, 1992. P. 3352–3378.
Woycheese K.M., Meyer-Dombard D.R., Cardace D., Argayosa A.M., Arcilla C.A. Out of the dark: transitional subsurface-to-surface microbial diversity in a terrestrial serpentinizing seep (Manleluag, Pangasinan, the Philippines) // Front. Microbiol. 2015. V. 6. Art. 44.
Zhang Y., Gladyshev V.N. Molybdoproteomes and evolution of molybdenum utilization // J. Mol. Biol. 2008. V. 379. P. 881‒899.
Zhao Q., Guo Q., Luo L., Yan K. Tungsten accumulation in hot spring sediments resulting from preferred sorption of aqueous polytungstates togGoethite // Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021. V. 18. P. 12629.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.


