Биологические мембраны: Журнал мембранной и клеточной биологии, 2022, T. 39, № 6, стр. 431-439
Прокоагулянтные свойства внеклеточных везикул при нормальной и патологической беременности
Е. М. Кольцова a, b, *, А. А. Мартьянов a, b, c, Н. А. Подоплелова a, b
a Национальный медицинский исследовательский центр детской гематологии,
онкологии и иммунологии им. Дмитрия Рогачева
117997 Москва, Россия
b Центр теоретических проблем физико-химической фармакологии РАН
109029 Москва, Россия
c Институт биохимической физики им. Н.М. Эмануэля РАН
119334 Москва, Россия
* E-mail: ekaterina_koltsova@bk.ru
Поступила в редакцию 25.11.2021
После доработки 16.04.2022
Принята к публикации 17.04.2022
- EDN: HEWYKG
- DOI: 10.31857/S023347552206007X
Аннотация
Внеклеточные везикулы – это двухслойные мембранные липидные структуры без ядер, которые высвобождаются из различных клеток в результате физиологических и метаболических изменений. Они играют важную роль в межклеточной коммуникации посредством передачи широкого спектра биоактивных молекул, способствуя регуляции различных физиологических и патологических процессов. Внеклеточные везикулы могут обладать прокоагулянтными свойствами вследствие наличия фосфатидилсерина, ускоряющего реакции свертывания, на внешнем слое мембраны, а также экспрессии тканевого фактора, активирующего свертывание по внешнему пути, на поверхности некоторых везикул. В большом количестве клинических и экспериментальных исследований показано, что при различных патологиях и специфических физиологических состояниях, включая состояние беременности, концентрации внеклеточных везикул существенно превышают концентрации у здоровых добровольцев, что теоретически может являться одним из факторов развития гиперкоагуляционных состояний. Данный обзор будет сосредоточен на описании прокоагулянтных свойств внеклеточных везикул различного происхождения при нормальной и патологической беременности.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Внеклеточные везикулы представляют собой двухслойные мембранные липидные структуры без ядер, которые высвобождаются из различных клеток в результате физиологических и метаболических изменений [1]. Их можно разделить на три основные класса: экзосомы, эктосомы или микровезикулы и апоптотические тельца [2]. Разделение на классы происходит исходя из размера частиц, их происхождения, внутреннего содержимого и выполняемых функций [3, 4]. Экзосомы имеют сравнительно небольшие размеры от ~40 до 160 нм и высвобождаются из мультивезикулярных телец при экзоцитозе (т.е. при слиянии мембраны телец с плазматической мембраной) [5, 6]. Эктосомы или микровезикулы довольно крупные частицы размером от ~50 нм до 1 мкм образуются из выпячиваний плазматической мембраны [7]. Отличительной чертой эктосом является наличие фосфатидилсерина (ФС) на внешнем слое мембраны. Апоптотические тельца высвобождаются клетками, подвергающимися апоптозу, и имеют размер от 1 мкМ и больше [8].
Изменение качественного и количественного состава внеклеточных везикул сопровождает широкий круг физиологических и патологических состояний. Особенную роль внеклеточные везикулы играют при беременности, поскольку они опосредуют взаимодействие плода и матери и участвуют во многих важных физиологических процессах, включая имплантацию эмбриона и развитие эмбриональных кровеносных сосудов, а также вследствие появления нового органа – плаценты, который также является источником внеклеточных везикул в кровотоке матери [9–12]. В последних публикациях указывается на изменение качественного и количественного состава внеклеточных везикул при развитии патологических состояний у беременных женщин (преэклампсия [13], сахарный диабет [14], преждевременные роды и выкидыш [15]). Физиологическая гиперкоагуляция, характерная для нормальной беременности, имеет неясное происхождение, а повышенные риски тромботических осложнений как в группе здоровых беременных, так и в группе с различными акушерскими патологиями, привлекает внимание к исследованию возможных причин возникновения гиперкоагуляции при беременности.
Данный обзор будет сосредоточен на описании прокоагулянтных свойств внеклеточных везикул различного происхождения при нормальной и патологической беременности.
ВЕЗИКУЛЫ ИЗ КЛЕТОК КРОВИ И ЭНДОТЕЛИЯ И ИХ ПРОКОАГУЛЯНТНЫЕ СВОЙСТВА
Несмотря на то, что беременность является физиологическим состоянием женщины, она сама по себе характеризуется сдвигом гемостаза в сторону гиперкоагуляции и склонности к тромботическим осложнениям. Развитие патологических состояний у беременных женщин (преэклампсия, сахарный диабет, преждевременные роды и выкидыш) существенно влияет на состав и свойства внеклеточных везикул в кровотоке, в том числе внеклеточных везикул из клеток крови, что, в свою очередь, может влиять на баланс системы гемостаза.
В целом, все типы клеток способны формировать и высвобождать во внеклеточное пространство различные типы везикул. Согласно ряду исследований, наиболее представленными в кровотоке являются внеклеточные везикулы тромбоцитарного происхождения [16]. По данным криоэлектронной микроскопии примерно 30% всех внеклеточных везикул в свободной от тромбоцитов плазме положительны по CD41 [17]. Для идентификации тромбоцитарных внеклеточных везикул могут применяться как маркеры характерные для всех тромбоцитов (CD41, CD42b), так и маркеры специфичные исключительно для активированных тромбоцитов (CD62P или антитела к активной форме интегрина αIIbβ3) [18]. Так же могут быть использованы и менее специфичные маркеры CD31 и CD61, оба из которых также экспрессируются на эндотелиальных внеклеточных везикулах. Полный список маркеров, используемых для идентификации происхождения внеклеточных везикул представлен на рис. 1.
Рис. 1.
Схематический рисунок, обобщающий наиболее распространенные маркеры, используемые для характеристики происхождения внеклеточных везикул, с акцентом на клетки, участвующие в свертывании крови.
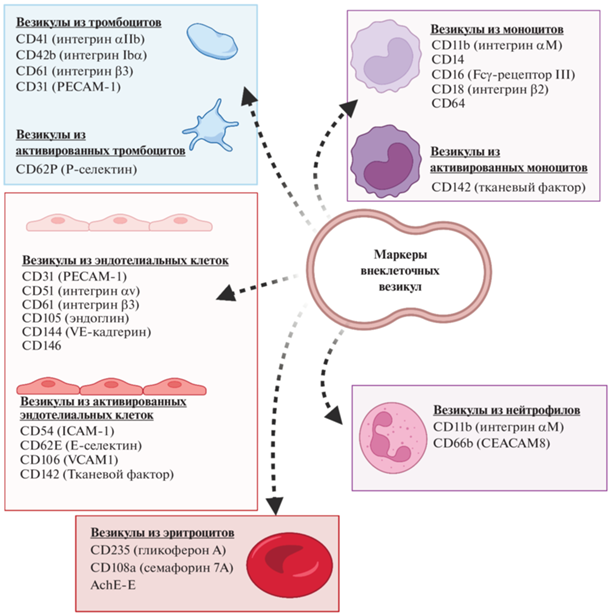
Также важным источником внеклеточных везикул являются эндотелиальные клетки. Было показано, что до 10% внеклеточных везикул, циркулирующих в кровотоке здоровых добровольцев, имеют эндотелиальное происхождение [19]. При этом активация или повреждение эндотелия в результате травмы или патологии приводит к существенному росту количества данных везикул в кровотоке. Фактически эндотелиальные внеклеточные везикулы могут использоваться в качестве маркера дисфункции эндотелия [20]. В качестве основных маркеров для идентификации эндотелиальных внеклеточных везикул могут использоваться CD31, CD105 и CD144, или CD62E и CD106 (васкулярная молекула клеточной адгезии 1, VCAM-1) в случае активации эндотелия [21]. Поскольку некоторые из маркеров, такие как CD31, также экспрессируются на других типах клеток (например, тромбоцитах и лейкоцитах), рекомендуется использование нескольких маркеров из данного списка.
Важным источником внеклеточных везикул являются иммунные клетки, в частности лейкоциты. Данный тип внеклеточных везикул является минорным в кровотоке здоровых доноров, однако при патологиях их количество может возрастать. Это делает данные внеклеточные везикулы перспективными для исследования в качестве возможного маркера различных заболеваний [22].
Помимо эндотелиальных клеток, тромбоцитов и лейкоцитов, эритроциты также могут быть источником внеклеточных везикул [23]. Эритроцитарные внеклеточные везикулы в больших количествах были обнаружены в эритроконцентратах при длительном хранении или использовании жестких методов обработки [24]. Считается, что данные внеклеточные везикулы ответственны как за положительные, так и за отрицательные эффекты, наблюдаемые после переливания крови [25].
Прокоагулянтные свойства внеклеточных везикул в первую очередь связывают с наличием на их мембране белка тканевого фактора (ТФ) [26] и/или отрицательно заряженных фосфолипидов, в частности ФС [27]. Присутствие этих прокоагулянтных молекул напрямую связано с источником и механизмом образования везикул.
ТФ является одним из цитокиновых рецепторов и экспрессируется большинством несосудистых и периваскулярных клеток. Он активирует свертывание после сосудистого повреждения [28]. Помимо своей непосредственной роли в свертывании, ТФ необходим для развития эмбриональных кровеносных сосудов, миграции и пролиферации гладкомышечных клеток сосудистой стенки и регуляции воспаления [29, 30]. Считается, что в нормальных условиях клетки, контактирующие с кровью, не экспрессируют физиологически активный ТФ, поскольку даже его субпикомолярных концентраций достаточно для запуска свертывания [31]. Микровезикулы плазмы в норме также не несут на себе ТФ, однако присутствие внеклеточных везикул (в основном микровезикул), несущих на себе ТФ, подтверждено при различных патологических состояниях, связанных с тромботическими осложнениями, таких как сепсис, рак и сердечно-сосудистые заболевания [32].
Моноциты являются основным источников внеклеточных везикул, несущих на себе ТФ [33, 34]. Внеклеточные везикулы тромбоцитарного происхождения не несут ТФ и не участвуют в запуске каскада свертывания по внешнему пути [18].
Вторым важным источником прокоагулянтной активности внеклеточных везикул является наличие ФС на внешнем слое мембраны, так как все основные реакции свертывания крови протекают на отрицательно заряженных фосфолипидных мембранах [27]. Кроме того, ФС-положительные везикулы могут напрямую активировать свертывание крови через фактор свертывания XII и контактный путь [35].
Было показано, что при нормальной неосложненной беременности уже начиная с первого триместра наблюдается повышение количества циркулирующих в кровотоке матери внеклеточных везикул, в основном в исследованиях упоминаются микровезикулы размером до 1 мкм [36, 37]. При этом их количество увеличивается по мере развития беременности и достигает своего максимума в третьем триместре [38]. Наблюдается значительное увеличение концентраций микровезикул тромбоцитарного, лейкоцитарного, эндотелиального происхождения при нормальной беременности и при преэклампсии [38, 39]. Однако только данными тремя источниками невозможно объяснить высокие уровни ФС-положительных прокоагулянтных микровезикул в кровотоке беременных. Это указывает на возможную роль плацентарных внеклеточных везикул как источника прокоагулянтной поверхности [40, 41].
ВЕЗИКУЛЫ ПЛАЦЕНТАРНОГО ПРОИСХОЖДЕНИЯ ПРИ БЕРЕМЕННОСТИ И ИХ ПРОКОАГУЛЯНТНЫЕ СВОЙСТВА
В крови беременных женщин циркулирует большое количество везикул плацентарного происхождения. В плаценте человека присутствует три подтипа трофобластов: ворсинчатый цитотрофобласт, вневорсинчатый трофобласт (ВВТ) и синцитиотрофобласт (СТФ). СТФ представляет собой многоядерную одиночную клетку-симпласт [42], которая покрывает обращенную к матери часть плаценты. Он формируется на ранних стадиях развития эмбриона путем начального слияния мононуклеарных цитотрофобластов, а затем обновляется на протяжении всей беременности за счет рекрутирования нижележащих клеток цитотрофобласта [43]. СТФ непосредственно контактирует с материнским кровотоком и, по сути, представляет собой границу между кровообращением матери и плода, обеспечивая транспорт питательных веществ и кислорода к развивающемуся эмбриону и вырабатывая гормоны, поддерживающие беременность [44]. СТФ также функционирует как защитный иммунологический барьер, поскольку никогда не экспрессирует молекулы человеческого лейкоцитарного антигена (HLA), а это означает, что, несмотря на присутствие аллогенного плода, циркулирующие иммунные клетки не распознают СТФ как мишень [45]. Именно СТФ является источником микровезикул (200–1000 нм) и нановезикул (<200 нм). Кроме того, благодаря своей многоядерной природе СТФ также способен продуцировать третий тип везикул, уникальных для плаценты человека – макровезикулы [46, 47]. Макровезикулы содержат в себе в среднем 60 ядер и имеют размер от 20 до 500 мкм [47]. Макровезикулы плаценты перемещаются по крупным венам матери в легкие, где они сталкиваются с системой мелких капилляров и застревают из-за своего физического размера. В мелких сосудах периферии макровезикулы обнаруживаются крайне редко [48] в отличие от микро- и нановезикул.
Наличие активного ТФ на самом СТФ и его везикулах, на данный момент является спорным вопросом. Хотя неоднократно сообщалось, что ТФ присутствует на мембранах, полученных обработкой ультразвуком ворсин плаценты [49], клеточных линий хориокарциномы [50] и СТФ, дифференцированных in vitro из первичных трофобластов ворсинок [51], гистологические исследования показывают, что ТФ присутствует в высокой концентрации в децидуальной оболочке, но отсутствует в самих СТФ [52, 53]. Тем не менее, группа Teng и др. [54] сообщила о повышенных уровнях антигена ТФ в СТФ у женщин с преэклампсией. Активность ТФ СТФ была функционально оценена группой Gardiner и др. [55], которая показала, что добавление микровезикул, полученных из СТФ в плазму достоверно сдвигает свертывание в область гиперкоагуляции в тесте генерации тромбина у женщин с преэклампсией по сравнению с женщинами с нормально протекающей беременностью, и данный сдвиг связан с повышенной экспрессией ТФ на мембранах микровезикул СТФ при преэлампсии. Принимая во внимание тот факт, что помимо качественной разницы в уровне экспрессии ТФ, существует еще и количественное превышение в 2–10 раз продукции микровезикул при преэклампсии [56–60] по сравнению со здоровой беременностью, можно предположить, что в совокупности это является одним из факторов тромботического риска. К сожалению, на данный момент трудно сказать, какую роль микровезикулы СТФ играют в гиперкоагуляции, характерной для нормально протекающей беременности.
Помимо непосредственной активации от ТФ, СТФ является потенциально прокоагулянтным за счет экстернализации ФС на поверхности материнской мембраны во время формирования многоядерного СТФ путем слияния клеток цитотрофобласта [61], поскольку экстернализация ФС необходима для формирования миотрубки [62]. Несмотря на эти наблюдения, в норме свертывания в области ворсин не происходит, поскольку трофобласты продуцируют антикоагулянтные белки тромбомодулин и аннексин V, причем тромбомодулин ассоциирован с микроворсинками СТФ [63], а аннексин V связывается с ФС. На данный момент не существует убедительных данных о том, что микровезикулы СТФ несут на себе ФС, однако их наличие является потенциально возможным в патологических условиях, например, при антифосфолипидном синдроме, поскольку синтез аннексина V при данной патологии сильно снижен [64]. Ингибитор активатора плазминогена (PAI-2), который является ингибитором фибринолиза, специфичным для беременности, был также обнаружен на микровезикулах СТФ [65].
Что касается опосредованного влияния микровезикул плацентарного происхождения на гемостаз матери, то здесь следует отдельно отметить влияние на функцию эндотелия. Нарушение функции эндотелия значительно увеличивает риск сосудистых осложнений во время беременности, особенно при преэклампсии [66]. Fms-подобная тирозинкиназа-1 (Flt-1), которая является антиангиогенным фактором, присутствует на поверхности микровезикул СТФ и, как предполагается, участвует в повреждении эндотелия у пациенток с преэклампсией [67]. Содержание растворимого Flt-1 и растворимого эндоглина (sEng) были увеличены в микровезикулах, выделенных из плазмы пациентов с преэклампсией, по сравнению с нормальным контролем. Кроме того, Chang и др. показали, что микровезикулы обеспечивают эффективный перенос sFlt-1 и sEng в эндотелиальные клетки, что ослабляет пролиферацию, миграцию и образование микротрубочек в эндотелиальных клетках in vitro [68]. Экспрессия на микровезикулах СТФ молекул адгезии, таких как молекула межклеточной адгезии 1 (ICAM-1), VCAM-1, E-селектин, P-селектин и витронектин, может влиять на адгезию этих микровезикул к различным клеткам-мишеням и способствовать их взаимодействию [13]. Исследования in vitro показали, что микроРНК-155 может переноситься из микровезикул СТФ в клетки эндотелия и может подавлять экспрессию эндотелиальной синтазы оксида азота (eNOS) [69].
Помимо влияния на эндотелий, микровезикулы СТФ также in vitro вызывают агрегацию тромбоцитов и ускоряют скорость образования тромбов при исследовании в потоке [70], а также влияют на функцию моноцитов и макрофагов, вызывая продукцию провоспалительных цитокинов [71].
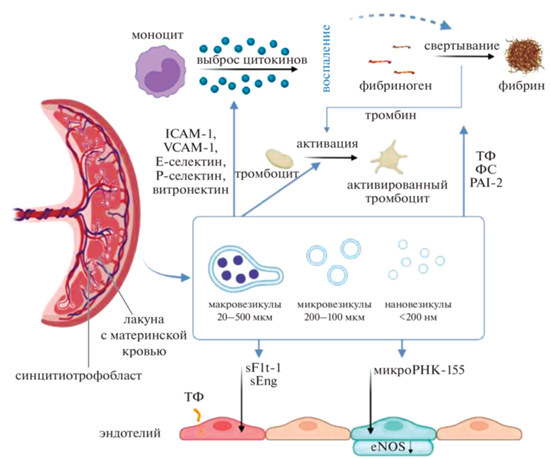
Схема воздействия везикул плацентарного происхождения на гемостаз представлена на рис. 2.
Рис. 2.
Механизмы возникновения эндотелиальной дисфункции и гиперкоагуляции при беременности. Плацентарные везикулы синцитиотрофобласта несут на своей поверхности различные молекулы адгезии, потенциально увеличивая способность к взаимодействию с клетками-мишенями и их последующей активации (например, моноцитами и тромбоцитами). Кроме того, на своей поверхности везикулы несут ТФ, ФС и PAI-2, которые активируют, либо усиливают свертывание и снижают фибринолиз. Плацентарные везикулы напрямую взаимодействуют с эндотелиальными клетками, вызывая эндотелиальную дисфункцию, частично за счет переноса fms-подобной тирозинкиназы-1 (sFlt-1) и эндоглина (sEng). Путем переноса своих микроРНК плацентарные везикулы влияют на уровни экспрессии eNOS (микроРНК-155) Сокращения: eNOS – эндотелиальная синтаза оксида азота; ICAM-1 – молекула межклеточной адгезии 1; ФС – фосфатидилсерин; PAI-2 – ингибитор активатора плазминогена-2; sFlt – растворимая fms-подобная тирозинкиназа-1; sEng – растворимый эндоглин; ТФ – тканевый фактор; VCAM-1– васкулярная молекула клеточной адгезии 1.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Повышение концентрации прокоагулянтных внеклеточных везикул при беременности, происходящих как из клеток крови, так и из плаценты, подтверждаются клиническими и экспериментальными исследованиями. Это может являться одним из компонентов физиологической гиперкоагуляции, возникающей при данном состоянии. Таким образом, повышение концентраций прокоагулянтных везикул может являться одним из факторов, обуславливающих повышенный риск тромбоза во время беременности, однако данный факт все еще не доказан напрямую. Для выявления роли внеклеточных везикул в тромбообразовании у беременных необходимо проведение проспективных исследований в данной группе.
Конфликт интересов. Авторы заявляют, что у них нет конфликта интересов.
Источники финансирования. Автор Е.М. Кольцова поддержана грантом Президента МК-432.2020.7 (соглашение № 075-15-2020-181), автор А.А. Мартьянов поддержан стипендией Президента СП-2675.2019.4, автор Н.А. Подоплелова поддержана грантом Президента МК-6271.2021.1.4 (соглашение № 075-15-2021-413).
Соответствие принципам этики. Настоящая статья не содержит описания каких-либо исследований с участием людей или животных в качестве объектов.
Список литературы
Théry C., Witwer K.W., Aikawa E., Alcaraz M.J., Anderson J.D., Andriantsitohaina R., Antoniou A., Arab T., Archer F., Atkin-Smith G.K., Ayre D.C., Bach J.M., Bachurski D., Baharvand H., Balaj L., et al. 2018. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. vesicles. 7 (1), 1535750. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
Yáñez-Mó M., Siljander P.R., Andreu Z., Zavec A.B., Borràs F.E., Buzas E.I., Buzas K., Casal E., Cappello F., Carvalho J., Colás E., Cordeiro-da Silva A., Fais S., Falcon-Perez J.M., Ghobrial I.M., et al. 2015. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. vesicles. 4 (2015), 27066. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27066
Colombo M., Raposo G., Théry C. 2014. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 30, 255–289. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326
Rojalin T., Phong B., Koster H.J., Carney R.P. 2019. Nanoplasmonic approaches for sensitive detection and molecular characterization of extracellular vesicles. Front. Chem. 7, 279. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00279
Raposo G., Stoorvogel W. 2013. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 200 (4), 373–383. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211138
Bebelman M.P., Smit M.J., Pegtel D.M., Baglio S.R. 2018. Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 188, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.013
Cretoiu D., Xu J., Xiao J., Cretoiu S.M. 2016. Telocytes and their extracellular vesicles-evidence and hypotheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 (8), 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081322
Wickman G., Julian L., Olson M.F. 2012. How apoptotic cells aid in the removal of their own cold dead bodies. Cell Death Differ. 19 (5), 735–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.25
Tannetta D., Dragovic R., Alyahyaei Z., Southcombe J. 2014. Extracellular vesicles and reproduction–promotion of successful pregnancy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 11 (6), 548–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.42
Burnett L.A., Nowak R.A. 2016. Exosomes mediate embryo and maternal interactions at implantation and during pregnancy. Front. Biosci. 8 (1), 79–96. https://doi.org/10.2741/s448
Chiarello D.I., Salsoso R., Toledo F., Mate A., Vázquez C.M., Sobrevia L. 2018. Foetoplacental communication via extracellular vesicles in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. Mol. Aspects Med. 60, 69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2017.12.002
Sheller-Miller S., Choi K., Choi C., Menon R. 2019. Cyclic-recombinase-reporter mouse model to determine exosome communication and function during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 221 (5), 502.e1–502.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2019.06.010
Han C., Han L., Huang P., Chen Y., Wang Y., Xue F. 2019. Syncytiotrophoblast-derived extracellular vesicles in pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Front. Physiol. 10, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01236
James-Allan L.B., Devaskar S.U. 2021. Extracellular vesicles and their role in gestational diabetes mellitus. Placenta. 113, 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2021.02.012
Menon R, Shahin H. 2021. Extracellular vesicles in spontaneous preterm birth. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 85(2), 139–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/aji.13353
Weiss R., Gröger M., Rauscher S., Fendl B., Eichhorn T., Fischer M.B., Spittler A., Weber V. 2018. Differential interaction of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles with leukocyte subsets in human whole blood. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 6598. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25047-x
Arraud N., Linares R., Tan S., Gounou C., Pasquet J.M., Mornet S., Brisson A.R. 2014. Extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: Determination of their morphology, size, phenotype and concentration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 12 (5), 614–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12554
Koltsova E.M., Sorokina M.A., Pisaryuk A.S., Povalyaev N.M., Ignatova A.A., Polokhov D.M., Kotova E.O., Balatskiy A.V., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A., Kobalava Z.D., Balandina A.N. 2021. Hypercoagulation detected by routine and global laboratory hemostasis assays in patients with infective endocarditis. PLoS One. 16 (12), e0261429. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261429
Combes V., Simon A.C., Grau G.E., Arnoux D., Camoin L., Sabatier F., Mutin M., Sanmarco M., Sampol J., Dignat-George F. 1999. In vitro generation of endothelial microparticles and possible prothrombotic activity in patients with lupus anticoagulant. J. Clin. Invest. 104 (1), 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI4985
Dickhout A., Koenen R.R. 2018. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in cardiovascular disease: Chances and risks. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 5, 113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2018.00113
Dignat-George F., Boulanger C.M. 2011. The many faces of endothelial microparticles. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31(1), 27–33. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.218123
Sedgwick A.E., D’Souza-Schorey C. 2018. The biology of extracellular microvesicles. Traffic. 19 (5), 319–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12558
Thangaraju K., Neerukonda S.N., Katneni U., Buehler P.W. 2020. Extracellular vesicles from red blood cells and their evolving roles in health, coagulopathy and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (1), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010153
Gamonet C., Desmarets M., Mourey G., Biichle S., Aupet S., Laheurte C., François A., Resch E., Bigey F., Binda D., Bardiaux L., Naegelen C., Marpaux N., Delettre F.A., Saas P., Morel P., Tiberghien P., Lacroix J., Capellier G., Vidal C., Garnache-Ottou F. 2020. Processing methods and storage duration impact extracellular vesicle counts in red blood cell units. Blood Adv. 4 (21), 5527–5539. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001658
Jy W., Ricci M., Shariatmadar S., Gomez-Marin O., Horstman L.H., Ahn Y.S. 2011. Microparticles in stored red blood cells as potential mediators of transfusion complications. Transfusion. 51 (4), 886–893. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03099.x
Giesen P.L.A., Rauch U., Bohrmann B., Kling D., Roqué M., Fallon J.T., Badimon J.J., Himber J., Riederer M.A., Nemerson Y. 1999. Blood-borne tissue factor: Another view of thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96 (5), 2311–2315. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.5.2311
Reddy E.C., Rand M.L. 2020. Procoagulant phosphatidylserine-exposing platelets in vitro and in vivo. Front Cardiovasc. Med. 7 (15), 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.00015
Mackman N. 2009. The many faces of tissue factor. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7, 136–139. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03368.x
Ruf W., Dorfleutner A., Riewald M. 2003. Specificity of coagulation factor signaling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 1 (7), 1495–1503. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00300.x
Monroe D.M., Key N.S. 2007. The tissue factor-factor VIIa complex: Procoagulant activity, regulation, and multitasking. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5(6), 1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02435.x
Butenas S., Orfeo T., Mann K.G. 2009. Tissue factor in coagulation: Which? Where? When? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 29 (12), 1989–1996. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.177402
Mackman N., Tilley R.E., Key N.S. 2007. Role of the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation in hemostasis and thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27 (8), 1687–1693. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.141911
Andrews A.M., Rizzo V. 2016. Microparticle-induced activation of the vascular endothelium requires caveolin-1/caveolae. PLoS One. 11 (2), e0149272. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149272
Shustova O.N., Antonova O.A., Golubeva N.V., Khaspekova S.G., Yakushkin V.V., Aksuk S.A., Alchinova I.B., Karganov M.Y., Mazurov A.V. 2017. Differential procoagulant activity of microparticles derived from monocytes, granulocytes, platelets and endothelial cells: Impact of active tissue factor. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis. 28 (5), 373–382. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBC.0000000000000609
Yang A., Chen F., He C., Zhou J., Lu Y., Dai J., Birge R.B., Wu Y. 2017. The procoagulant activity of apoptotic cells is mediated by interaction with factor XII. Front. Immunol. 8, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01188
Bretelle F., Sabatier F., Desprez D., Camoin L., Grunebaum L., Combes V., D’Ercole C., Dignat-George F. 2003. Circulating microparticles: A marker of procoagulant state in normal pregnancy and pregnancy complicated by preeclampsia or intrauterine growth restriction. Thromb. Haemost. 89 (3), 486–492. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1613378
Alijotas-Reig J., Palacio-Garcia C., Farran-Codina I., Zarzoso C., Cabero-Roura L., Vilardell-Tarres M. 2011. Circulating cell-derived microparticles in women with pregnancy loss. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 66 (3), 199–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00972.x
Radu C.M., Campello E., Spiezia L., Dhima S., Visentin S., Gavasso S., Woodhams B., Cosmi E., Simioni P. 2015. Origin and levels of circulating microparticles in normal pregnancy: A longitudinal observation in healthy women. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 75 (6), 487–495. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365513.2015.1052551
Zhang Y., Zhao C., Wei Y., Yang S., Cui C., Yang J., Zhang J., Qiao R. 2018. Increased circulating microparticles in women with preeclampsia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 40 (3), 352–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12796
Alijotas-Reig J., Palacio-Garcia C., Llurba E., Vilardell-Tarres M. 2013. Cell-derived microparticles and vascular pregnancy complications: A systematic and comprehensive review. Fertil. Steril. 99 (2), 441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.10.009
Aharon A., Brenner B. 2011. Microparticles and pregnancy complications. Thromb. Res. 127, S67–S71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-3848(11)70019-6
Burton G.J., Fowden A.L. 2015. The placenta: A multifaceted, transient organ. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 370 (1663), 20140066. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0066
Huppertz B., Kadyrov M., Kingdom J.C.P. 2006. Apoptosis and its role in the trophoblast. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 195 (1), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2005.07.039
Haider S., Meinhardt G., Saleh L., Kunihs V., Gamperl M., Kaindl U., Ellinger A., Burkard T.R., Fiala C., Pollheimer J., Mendjan S., Latos P.A., Knöfler M. 2018. Self-renewing trophoblast organoids recapitulate the developmental program of the early human placenta. Stem Cell Reports. 11 (2), 537–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.07.004
Moffett A., Loke C. 2006. Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6 (8), 584–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1897
Askelund K.J., Chamley L.W. 2011. Trophoblast deportation part I: Review of the evidence demonstrating trophoblast shedding and deportation during human pregnancy. Placenta. 32 (10), 716–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2011.07.081
Holland O., Kroneis T., El-Heliebi A., McDowell-Hook M., Stone P., Sedlmayr P., Chamley L. 2017. Detection of fetal sex, aneuploidy and a microdeletion from single placental syncytial nuclear aggregates. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 41 (1), 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445112
Johansen M., Redman C.W., Wilkins T., Sargent I.L. 1999. Trophoblast deportation in human pregnancy – its relevance for pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 20 (7), 531–539. https://doi.org/10.1053/plac.1999.0422
Reverdiau P., Jarousseau A.C., Thibault G., Khalfoun B., Watier H., Lebranchu Y., Bardos P., Gruel Y. 1995. Tissue factor activity of syncytiotrophoblast plasma membranes and tumoral trophoblast cells in culture. Thromb. Haemost. 73 (1), 49–54. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1653724
Teng Y.C., Lin Q.De., Lin J.H., Ding C.W., Zuo Y. 2009. Coagulation and fibrinolysis related cytokine imbalance in preeclampsia: The role of placental trophoblasts. J. Perinat. Med. 37 (4), 343–348. https://doi.org/10.1515/JPM.2009.060
Aharon A., Brenner B., Katz T., Miyagi Y., Lanir N. 2004. Tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in trophoblast cells: Implications for placental hemostasis. Thromb. Haemost. 92 (4), 776–786. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH04-01-0033
Lakasing L., Campa J.S., Poston R., Khamashta M.A., Poston L. 1999. Normal expression of tissue factor, thrombomodulin, and annexin V in placentas from women with antiphospholipid syndrome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 181 (1), 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70457-6
Faulk W.P., Labarrere C.A., Carson S.D. 1990. Tissue factor: Identification and characterization of cell types in human placentae. Blood. 76(1), 86–96.
Teng Y., Jiang R., Lin Q., Ding C., Ye Z. 2010. The relationship between plasma and placental tissue factor, and tissue factor pathway inhibitors in severe pre-eclampsia patients. Thromb. Res. 126 (1), e41–e45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2010.02.012
Gardiner C., Tannetta D.S., Simms C.A., Harrison P., Redman C.W.G., Sargent I.L. 2011. Syncytiotrophoblast microvesicles released from pre-eclampsia placentae exhibit increased tissue factor activity. PLoS One. 6 (10), e26313. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026313
Ng E.K.O., Leung T.N., Tsui N.B.Y., Lau T.K., Panesar N.S., Chiu R.W.K., Lo Y.M.D. 2003. The concentration of circulating corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in maternal plasma is increased in preeclampsia. Clin. Chem. 49 (5), 727–731. https://doi.org/10.1373/49.5.727
Freeman D.J., Tham K., Brown E.A., Rumley A., Lowe G.D., Greer I.A. 2008. Fetal corticotrophin-releasing hormone mRNA, but not phosphatidylserine-exposing microparticles, in maternal plasma are associated with factor VII activity in pre-eclampsia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 6 (3), 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02882.x
Goswami D., Tannetta D.S., Magee L.A., Fuchisawa A., Redman C.W.G., Sargent I.L., von Dadelszen P. 2006. Excess syncytiotrophoblast microparticle shedding is a feature of early-onset pre-eclampsia, but not normotensive intrauterine growth restriction. Placenta. 27 (1), 56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2004.11.007
Knight M., Redman C.W.G., Linton E.A., Sargent I.L. 1998. Shedding of syncytiotrophoblast microvilli into the maternal circulation in pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 105 (6), 632–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb10178.x
Lok C.A.R, Van Der Post J.A.M, Sargent I.L., Hau C.M., Sturk A., Boer K., Nieuwland R. 2008. Changes in microparticle numbers and cellular origin during pregnancy and preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy. 27 (4), 344–360. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641950801955733
Huppertz B., Frank H.G., Kingdom J.C., Reister F., Kaufmann P. 1998. Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta. Histochem. Cell Biol. 110 (5), 495–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004180050311
Owens A.P. 3rd, Mackman N. 2012. Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. 108 (10), 1284–1297. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.233056
Fazel A., Vincenot A., Malassiné A., Soncin F., Gaus-sem P., Alsat E., Evain-Brion D. 1998. Increase in expression and activity of thrombomodulin in term human syncytiotrophoblast microvilli. Placenta. 19 (4), 261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0143-4004(98)90057-1
Lanir N., Aharon A., Brenner B. 2003. Haemostatic mechanisms in human placenta. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 16 (2), 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1521-6926(02)00098-1
Štok U., Čučnik S., Sodin-Šemrl S., Žigon P. 2021. Extracellular vesicles and antiphospholipid syndrome: State-of-the-art and future challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (9), 4689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094689
Goulopoulou S., Davidge S.T. 2015. Molecular mechanisms of maternal vascular dysfunction in preeclampsia. Trends Mol. Med. 21 (2), 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2014.11.009
Tannetta D.S., Dragovic R.A., Gardiner C., Redman C.W., Sargent I.L. 2013. Characterisation of syncytiotrophoblast vesicles in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia: Expression of Flt-1 and endoglin. PLoS One. 8 (2), e56754. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056754
Lok C.A.R., Böing A.N., Sargent I.L., Sooranna S.R., van der Post J.A.M., Nieuwland R., Sturk A. 2008. Circulating platelet-derived and placenta-derived microparticles expose Flt-1 in preeclampsia. Reprod. Sci. 15 (10), 1002–1010. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719108324133
Cronqvist T., Tannetta D., Mörgelin M., Belting M., Sargent I., Familari M., Hansson S.R. 2017. Syncytiotrophoblast derived extracellular vesicles transfer functional placental miRNAs to primary human endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 4558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04468-0
Tannetta D.S., Hunt K., Jones C.I., Davidson N., Coxon C.H., Ferguson D., Redman C.W., Gibbins J.M., Sargent I.L., Tucker K.L. 2015. Syncytiotrophoblast extracellular vesicles from pre-eclampsia placentas differentially affect platelet function. PLoS One. 10 (11), e0142538. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142538
Tannetta D., Masliukaite I., Vatish M., Redman C., Sargent I. 2017. Update of syncytiotrophoblast derived extracellular vesicles in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. J. Reprod. Immunol. 119, 98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jri.2016.08.008
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Биологические мембраны: Журнал мембранной и клеточной биологии


