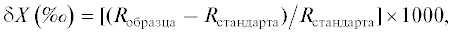Биология моря, 2022, T. 48, № 6, стр. 413-420
Состав стабильных изотопов углерода и азота у личинок роющих креветок инфраотрядов Gebiidea и Axiidea (Crustacea: Decapoda) из залива Восток Японского моря
Е. С. Корниенко 1, *, С. И. Кияшко 1
1 Национальный научный центр морской биологии им. А.В. Жирмунского (ННЦМБ) ДВО РАН
690041 Владивосток, Россия
* E-mail: kornielena@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 28.02.2022
После доработки 11.07.2022
Принята к публикации 02.09.2022
- EDN: MDMCMI
- DOI: 10.31857/S0134347522060080
Аннотация
Исследован изотопный состав углерода (δ13С) и азота (δ15N) у личинок восьми видов роющих креветок из зал. Восток Японского моря. Установлено, что у зоэа I этих видов состав изотопов углерода варьировал в диапазоне, характерном для планктотрофных организмов; средние значения δ13С у личинок упогебий были ниже, чем у личинок аксиид. Наибольшие значения δ15N, сопоставимые с данными для всеядного зоопланктона, показаны для личинок видов Leonardsaxius amurensis и Boasaxius princeps. На преобладание фитопланктона в рационе зоэа I Nihonotrypaea makarovi указывали низкие значения δ15N, близкие к соотношению изотопов азота взвешенного органического вещества. В соответствии с изотопным составом азота личинки трех видов Upogebia и двух видов Nihonotrypaea занимали промежуточное положение (δ15N от 6.2 до 6.4‰). Установлено, что рацион исследованных личинок роющих креветок не зависел от таксономического положения; пищевые предпочтения заметно различались даже у зоэа видов, принадлежавших к одному роду, что необходимо учитывать при культивировании личинок декапод в лабораторных условиях.
Десятиногие ракообразные – типичные обитатели морских экосистем, их свободно плавающие планктотрофные личинки (зоэа) – важный сезонный компонент прибрежного меропланктона. В трофических цепях личинки декапод являются потребителем более мелких планктонных организмов, а также служат пищей для хищного зоопланктона и рыб (Lindley et al., 1994). Однако их пищевые предпочтения все еще недостаточно изучены. Когда-то считали, что личинки декапод исключительно хищники (Thorson, 1946), однако к настоящему времени установлено, что они всеядны и в их рацион входят бактерии, фитопланктон от пико- до микроразмера, зоопланктон от нано- до мезоразмерных групп, детрит и фекальные гранулы (Anger, 2001; Schwamborn et al., 2006; Fileman et al., 2014; Umezawa et al., 2018, и др.). Потребляя широкий спектр пищевых частиц разного размера и разной подвижности, личинки декапод демонстрируют избирательность в отношении отдельных видов потенциальной добычи (Fileman et al., 2014). Известно также, что мелкие личинки (например, пенеидных креветок) в большей степени зависят от усвоения фитопланктона, тогда как крупные (например, личинки омаров) являются плотоядными; у личинок многих видов трофический уровень в ходе онтогенетического развития изменяется (Le Vay et al., 2001). Доступность и качество пищи влияют на выживаемость и рост личинок декапод (Anger, 2001; Zeng et al., 2020).
Выращивание личинок в лабораторной культуре – метод, широко применяемый при изучении биологии декапод. Описание морфологии личинок от самки, принадлежащей к определенному виду, позволяет идентифицировать их в планктоне, что вносит значительный вклад в изучение биоразнообразия десятиногих ракообразных, в первую очередь видов, ведущих скрытный образ жизни. Информация о рационах личинок декапод также получена в основном в результате лабораторных исследований. На лабораторной культуре происходит апробация оптимальных рационов и условий содержания при выращивании объектов марикультуры, например, палемонидных и пенеидных креветок. Показано, что у некоторых видов декапод в зависимости от условий питания может варьировать количество стадий зоэа (Hamasaki et al., 2020). При культивировании декапод подотряда Pleocyemata в качестве пищи для личинок обычно используют микрозоопланктон: науплиев Artemia sp. (см.: Rice, Williamson, 1970) или коловраток Brachionotus sp., иногда – личинок корнеголовых ракообразных (Корниенко, Корн, 2005; Корниенко и др., 2007) или зоэа других декапод, например, краба Uca spp. (McConaugha, 2002). Использование этих пищевых объектов позволило успешно выращивать в лабораторных условиях личинок десятиногих ракообразных многих видов до оседания или до первых ювенильных стадий. Высокая смертность зоэа, отмечавшаяся при культивировании некоторых видов, может быть связана с неподходящим рационом.
Роющие креветки инфраотрядов Axiidea и Gebiidea играют заметную роль в бентосных сообществах благодаря образу жизни. При рытье нор они биотурбируют осадок, изменяя его структуру и увеличивая скорость разложения органических веществ (Kinoshita et al., 2003; Webb, Eyre, 2004; Laverock et al., 2010; Das et al., 2017, и др.). Для многих из них характерна значительная плотность поселений, например, у каллианассид Nihonotrypaea harmandi и N. japonica у берегов Японии она достигала соответственно 1440 и 340 экз./м2 (Kubo et al., 2006), в российских водах для N. japonica отмечена плотность около 200 экз./м2 (Селин, 2015а). Это довольно крупные животные с высокой плодовитостью, например, длина тела Upogebia major может превышать 10 см, а плодовитость достигает более 4000 яиц (Селин, 2015б). Все это позволяет считать личинок роющих креветок значимым компонентом сезонного меропланктона. В зал. Восток (зал. Петра Великого, Японское море) известны 8 видов роющих креветок: Upogebia major (De Haan, 1841), U. issaeffi (Balss, 1913) и U. yokoyai Makarov, 1938 из инфраотряда Gebiidea, а также Leonardsaxius amurensis (Kobjakova, 1937), Boasaxius princeps (Boas, 1880), Nihonotrypaea japonica (Ortmann, 1891), N. makarovi Marin, 2013 и N. petalura (Stimpson, 1860) (см.: Marin, 2013, 2015; Марин и др., 2013; Марин, Корниенко, 2014) из инфраотряда Axiidea. В лабораторной культуре данные виды выращивали по общепринятой методике, используя науплиев артемии в качестве корма. В результате 7 видов были выращены до стадии мегалопы (Kornienko et al., 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2018; Корн и др., 2017), однако у N. makarovi описана только стадия зоэа I, так как высокая смертность личинок наблюдалась уже на ранних стадиях (Korn et al., 2016).
У личинок ракообразных основная роль в сортировке и физической переработке пищевого материала принадлежит, в первую очередь, мандибулам, а также максиллулам, максиллам и максиллипедам (Watling 2013). Мандибулы – это наиболее важная часть ротового аппарата, служащая для механической обработки пищи. Известно, что у взрослых ракообразных разных таксономических групп морфология мандибул позволяет получить представление о рационе и способе питания. Например, Буруковский (2022), рассматривая строение мандибул в связи с особенностями питания взрослых креветок, отмечает, что у хищников происходит редукция жевательного или режущего отростков, а у детритофагов перетирающие поверхности мандибул хорошо развиты. У личинок десятиногих ракообразных эта связь мало изучена, однако считают, что тупые размалывающие мандибулы характерны для травоядных личинок, присутствие на мандибулах острых зубцов указывает на плотоядность зоэа, а промежуточные формы мандибул встречаются у всеядных личинок (Anger, 2001). Исследование, проведенное нами ранее, показало, что морфология мандибул зоэа упогебий значительно отличается от таковой личинок каллианассид и аксиид (Корниенко, Голубинская, 2018, 2020). Было высказано предположение, что различия в морфологии мандибул у личинок Upogebia и Nihonotrypaea могут указывать на различия их рационов.
Метод стабильных изотопов углерода и азота все чаще используется в качестве инструмента для анализа трофической структуры наземных и водных экосистем. Содержание тяжелых природных изотопов 13C и 15N в тканях – это естественная метка, с помощью которой можно проследить обмен вещества и энергии между отдельными организмами и целыми сообществами. Соотношение изотопов углерода служит для идентификации источников пищи для животных, а изотопный состав азота позволяет определить позицию животных в трофических цепях (Тиунов, 2007; Le Vay, Gamboa-Delgado, 2011).
Цель настоящей работы – используя метод изотопного анализа, определить трофические позиции в планктонном сообществе у личинок восьми видов роющих креветок инфраотрядов Gebiidea и Axiidea; на основании этих данных выяснить, связаны ли морфологические особенности мандибул личинок гебиидей и аксиидей с различиями их рационов. Полученная информация о характеристиках питания личинок отдельных видов необходима при описании их трофического положения в экосистеме, а также при культивировании личинок декапод в лабораторных условиях.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДИКА
Планктонные пробы брали в районе биостанции “Восток” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН (зал. Восток, Японское море) в июне–июле 2019 г. В качестве образцов для изотопного анализа отбирали зоэа I роющих креветок видов Nihonotrypaea japonica, N. petalura и N. makarovi (семейство Callianassidae); Boasaxius princeps и Leonardsaxius amurensis (семейство Axiidae); Upogebia major, U. issaeffi и U. yokoyai (семейство Upogebiidae). Личинок идентифицировали до вида на основе морфологических признаков с помощью определительного ключа (Корн и др., 2017). Из этих же проб были отобраны основные компоненты планктонного сообщества: мизиды, копеподы и сагитты, а также взвешенное органическое вещество (ВОВ), представленное в основном фитопланктоном. Каждый образец для изотопного анализа состоял из нескольких целых особей (n = 7–25 экз. в зависимости от размера личинок); количество образцов (N) для отдельного вида личинок или компонента зоопланктона варьировало от 5 до 14 (табл. 1). Образцы сушили в сушильном шкафу при температуре 60°С и хранили в холодильнике при температуре −18°С.
Таблица 1.
Соотношения стабильных изотопов азота (δ15N) и углерода (δ13C) (среднее ± стандартная ошибка среднего) у личинок роющих креветок из зал. Восток Японского моря
| Вид | Индекс вида | N | δ15N, ‰ | δ13C, ‰ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boasaxius princeps | Bp | 6 | 8.0 ± 0.5a | −19.4 ± 1.3c, d |
| Leonardsaxius amurensis | La | 9 | 7.2 ± 0.3b | −20.6 ± 0.4b, c |
| Nihonotrypaea japonica | Nj | 8 | 6.4 ± 0.2c | −19.2 ± 0.5d |
| Nihonotrypaea makarovi | Nm | 5 | 5.3 ± 0.4d | −20.6 ± 0.4b, c, d |
| Nihonotrypaea petalura | Np | 5 | 6.2 ± 0.1c | −19.3 ± 0.1c, d |
| Upogebia issaeffi | Ui | 8 | 6.2 ± 0.2c | −21.0 ± 0.3b |
| Upogebia major | Um | 14 | 6.3 ± 0.2c | −21.6 ± 0.9a, b |
| Upogebia yokoyai | Uy | 10 | 6.2 ± 0.2c | −22.4 ± 1.5a |
Изотопный анализ выполнен в Лаборатории стабильных изотопов Дальневосточного геологического института ДВО РАН с помощью элементного анализатора FlashEA-1112, соединенного через интерфейс ConFlo-IV с изотопным масс-спектрометром МАТ-253 (Thermo Finnigan, Германия). Относительное содержание тяжелых изотопов 13С и 15N в образцах выражали в виде величин δ в промилле от соответствующего стандарта изотопного состава:
где X – стабильные изотопы 13C или 15N, а R – отношения содержаний стабильных изотопов (13C/12C или 15N/14N). Все приведенные ниже значения δ13С и δ15N даны в отношении к общепринятым международным стандартам изотопного состава карбоната PDB и атмосферного азота.Для калибровки использовали стандарты IAEA CH-6, NBS-22, IAEA N-1 и IAEA N-2 (Международное агентство по атомной энергии, Вена). Точность определения величин δ13С и δ15N составила ±0.10‰. Данные изотопного анализа приведены в виде среднего значения для нескольких образцов (N) личинок одного вида ± стандартная ошибка среднего (SE). Стандартная ошибка среднего на рисунке показана линиями. Достоверность различий полученных значений проверяли при помощи дисперсионного анализа (ANOVA). Статистическую обработку данных проводили с использованием программ STATISTICA 8.0 и Microsoft Office Excel.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
По результатам анализа изотопного состава всех образцов личинок роющих креветок (N = 65) размах изотопных соотношений углерода составил 6.9‰. Вариации изотопного состава углерода личинок определялись видовой принадлежностью образцов (F = 16.649, p < 0.0001). Средние значения δ13C всех исследованных видов находились в диапазоне от −22.4 до −19.2‰. У личинок каллианассид Nihonotrypaea japonica и N. petalura зарегистрированы самые высокие средние значения δ13C (−19.2 и −19.3‰ соответственно).
Сопоставимые значения δ13C отмечены для зоэа I Boasaxius princeps. Личинки всех видов упогебий показали самые низкие средние значения δ13C: от −22.4‰ у Upogebia yokoyai до −21.0‰ у U. issaeffi (табл. 1). В образцах зоэа каллианассиды Nihonotrypaea makarovi и аксииды Leonardsaxius amurensis соотношение изотопов углерода было одинаковым и имело промежуточное значение −20.6‰.
Образцы личинок исследованных видов роющих креветок различались и по изотопному составу азота, средние значения δ15N варьировали от 5.3 до 8.0‰ (F = 35.952, p < 0.0001). Диапазон вариаций изотопных соотношений азота составил 3.9‰. Самые высокие значения δ15N отмечены у личинок аксиид B. princeps и L. amurensis − 8 и 7.2‰ соответственно; самые низкие – у каллианассиды N. makarovi. Промежуточные значения δ15N показали зоэа I каллианассид N. japonica и N. petalura (6.4 ± 0.2 и 6.2 ± 0.1‰ соответственно), которые по изотопному составу азота мало отличались от личинок упогебий Upogebia major, U. issaeffi и U. yokoyai (рис. 1, табл. 1).
Рис. 1.
Соотношения стабильных изотопов углерода и азота (среднее ± стандартная ошибка среднего) у зоэа I восьми видов роющих креветок инфраотрядов Gebiidea и Axiidea, а также у основных компонентов планктонного сообщества в зал. Восток (Японское море). Индексы видов, как в табл. 1; ВОВ – взвешенное органическое вещество.
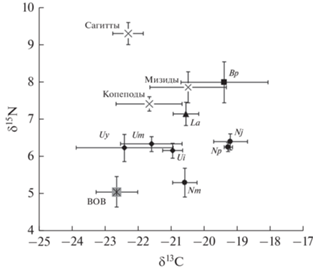
Изотопный состав углерода в образцах основных компонентов планктонного сообщества варьировал от −22.7 до −20.6‰. Заметно различался в образцах и изотопный состав азота, что, по-видимому, отражало положение исследованных объектов в трофической иерархии. В образцах ВОВ, представлявших смесь первичных продуцентов, средние значения δ15N составили 5.1 ± 0.4‰; у сагитт − хищного компонента зоопланктона, достигали 9.2 ± 0.3‰, а для всеядного зоопланктона (мелкие копеподы и мизиды) получены промежуточные значения δ15N − соответственно 7.4 ± 0.1 и 7.6 ± 0.1‰ (рис. 1).
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Информация о факторах окружающей среды, влияющих на продолжительность развития и рост личинок морских беспозвоночных, важна для понимания процессов выживания и распространения личинок, а также взаимосвязи популяций и динамики их пополнения. Доступность и качество пищи – это один из важнейших факторов, определяющих успех развития личинок (Anger, 2001; Schwamborn et al., 2006; Hamasaki et al., 2020; Zeng et al., 2020). Большая часть информации о рационах личинок декапод основана на лабораторных исследованиях, в ходе которых личинкам предлагали рацион (зачастую избыточный), состоявший из отдельных видов культивируемого фито- или зоопланктона или их смеси. Очевидно, что в естественной среде, где доступность подходящих пищевых организмов значительно варьирует из-за временнóй и пространственной пятнистости распределения планктона, для удовлетворения энергетических потребностей личинки десятиногих ракообразных используют более широкий спектр питания: растворенное органическое вещество, детрит, бактерии, микроводоросли, простейшие и зоопланктон. Это существенно расширяет возможности оптимального выбора пищи разными формами и стадиями личинок (Anger, 2001).
О рационах и пищевой избирательности личинок роющих креветок инфраотрядов Gebiidea и Axiidea в естественных условиях известно немного (Fileman et al., 2014; Somiya et al., 2014; Umezawa et al., 2018). Согласно результатам молекулярного анализа содержимого кишечника зоэа Upogebia spp. из планктона, собранного в прол. Ла-Манш, личинки упогебий всеядны и потребляют широкий спектр добычи разного размера и разной степени подвижности (Fileman et al., 2014). В этом же исследовании в экспериментах, основанных на методе проточной цитометрии, показано, что культивируемые личинки упогебий, которых кормили разными микроводорослями, обладали избирательностью по отношению к некоторым из них; кроме того, они поглощали мелкие клетки, включая нано- и пикопланктон.
Изучение функциональной морфологии ротовых придатков и содержимого пищеварительного тракта личинок каллианассиды Nihonotrypaea harmandi подтвердило, что зоэа этого вида могут регулярно питаться фитопланктоном, особенно диатомовыми водорослями (Somiya et al., 2014). Следует отметить, что полное развитие N. harmandi впервые описано по результатам лабораторных экспериментов, в которых личинок кормили коловратками или науплиями артемии (Konishi et al., 1999; Tamaki et al., 2013). В более поздних экспериментах зоэа, питавшиеся микроводорослями Chaetoceros gracilis, также успешно достигли стадии мегалопы (Umezawa et al., 2018). Ранние стадии зоэа N. harmandi встречаются, как правило, ниже слоя максимума хлорофилла; по результатам изотопного анализа среднее значение δ13C для них составило −18.3‰, а δ15N – около 6.0‰, что соответствует рациону из фитопланктона и тонущего фитодетрита, на котором присутствуют гетеротрофные простейшие (Umezawa et al., 2018).
По нашим данным в образцах личинок трех исследованных видов упогебий из зал. Восток соотношение изотопов азота было одинаковым, причем ниже, чем у всеядного зоопланктона, но выше показателей для ВОВ. Следовательно, как и личинки упогебий в планктоне прол. Ла-Манш, они могут потреблять разнообразную пищу, в том числе фитопланктон разного размера и простейших.
Среди образцов личинок каллианассид, исследованных нами, у зоэа Nihonotrypaea japonica и N. petalura соотношение изотопов азота было на 0.1–0.2‰ выше значений, полученных для личинок N. harmandi (см.: Umezawa et al., 2018). Напротив, у зоэа Nihonotrypaea makarovi это соотношение было на 0.7‰ ниже и близко к значению δ15N, полученному нами для ВОВ (5.1 ± 0.4‰), что указывает на преобладание в рационе личинок N. makarovi растительного компонента. Как и у личинок N. harmandi (см.: Somiya et al., 2014), на мандибулах зоэа I N. makarovi отмечены остатки пеннатных диатомовых водорослей и следы истирания жевательной поверхности молярного отростка (Корниенко, Голубинская, 2018), что также указывает на растительноядность личинок этого вида.
Личинки аксиид Boasaxius princeps и Leonardsaxius amurensis имеющие самые высокие значения δ15N среди исследованных видов в планктонном сообществе занимали трофическую позицию, соответствовавшую организмам всеядного зоопланктона (копеподам и мизидам) (рис. 1). Оба вида были успешно выращены в условиях лаборатории, в том числе B. princeps, развитие которого включает 8 стадий зоэа (стадии мегалопы личинки достигали через 38 сут после вылупления) (Kornienko et al., 2014, 2018). Вероятно, этому способствовал рацион, близкий к естественному, так как в качестве корма использовали свежевылупившихся науплиев Artemia sp. Согласно результатам изотопного анализа, естественный рацион исследованных личинок упогебий, а также каллианассид N. japonica и N. petalura (значения δ15N в диапазоне 6.2–6.4‰) заметно отличался от рациона личинок B. princeps и L. amurensis. Однако при культивировании личинок этих видов успешно использовали и кормление науплиями артемии (Konishi, 1989; Konishi et al., 1990; Miyabe et al., 1998; Kornienko et al., 2012, 2013, 2015). Вероятно, в данном случае успеху способствовали избыточная концентрация пищи в культуре или то, что вместе с зоопланктоном в культуру личинок попадали микроорганизмы, которые на начальных этапах развития зоэа частично удовлетворяли потребность личинок в пище. Сложности, возникшие при выращивании личинок N. makarovi, обусловлены в том числе и тем, что для них такой рацион оказался неприемлемым, так как, согласно результатам изотопного анализа, личинки этого вида предпочитают растительную пищу.
Анализ изотопного состава углерода всех 65 образцов личинок роющих креветок показал, что изотопные соотношения углерода в них оставались в пределах, характерных для прибрежных планктонных организмов, хотя и демонстрировали довольно большой размах вариаций. Самыми низкими были значения δ13C у личинок упогебий U. major, U. issaeffi и U. yokoyai. Соотношения изотопов углерода у личинок всех исследованных аксиидей были выше, чем у личинок упогебий, и изменялись в диапазоне от −20.6‰ у N. makarovi и L. amurensis до −19.2‰ у N. japonica. Большие различия в изотопных соотношениях углерода могут указывать на разные источники пищи животных (Post, 2002), например, личинки декапод способны потреблять разные виды фитопланктона или мертвые клетки микроводорослей на разной степени деградации (Umezawa et al., 2018). Мы не подвергали образцы личинок предварительному обезжириванию, поэтому возможно, что отмеченные вариации значений δ13C в какой-то степени отражают различия в содержании липидов в тканях исследованных организмов (Post et al., 2007). Однако из литературных источников известно, что содержание липидов в личинках декапод невысоко, например, у зоэа краба-паука Maja brachydactyla на липиды приходится 1.72 ± 0.25% от сухой массы (Rotllant et al., 2014), а у личинок лобстера Jasus edwardsii – от 7.9 до 12.5% в зависимости от стадии развития (Ritara et al., 2003).
Структура пищевых сетей водоемов тесно связана с размером тела составляющих их организмов. Размер в значительной степени определяет трофический уровень консументов и их добычи (Wirtz, 2012). Размер личинок десятиногих ракообразных также часто определяет их трофическое положение в планктонных пищевых сетях; мелкие личинки обычно питаются фито-, а крупные зоопланктоном (Le Vay, Gamboa-Delgado, 2011). В соответствии с полученными ранее данными зоэа I исследованных нами роющих креветок образуют следующий размерный ряд: L. amurensis > > N. makarovi > B. princeps > U. major > N. japonica > > N. petalura > U. issaeffi > U. yokoyai (Kornienko et al., 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2018; Korn et al., 2016; Корн и др., 2017), что в целом отражает их положение в пищевой сети, за исключением личинок N. makarovi, в рационе которых, несмотря на их довольно крупные размеры, преобладает растительный компонент.
Предположение о том, что различия в морфологии мандибул личинок Upogebia и Nihonotrypaea указывают на различия их рационов, не получило подтверждения, так как по результатам изотопного анализа личинки трех видов упогебий и двух видов Nihonotrypaea образовали группу с очень близкими значениями δ15N. В то же время у личинок аксиид и калианассид, имеющих общий план строения мандибул, эти значения заметно различались. У принадлежащих к одному роду N. makarovi и N. japonica различия в морфологии мандибул зоэа I отсутствуют (Корниенко, Голубинская, 2018), однако значения δ15N составили соответственно 5.3 ± 0.4 и 6.4 ± 0.2‰. Следовательно, строение мандибул у личинок исследованных видов роющих креветок не отражает специфику их рациона. Ранее было высказано мнение (Geiselbrecht, Melzer, 2010), что в строении мандибул личинок декапод имеются таксон-специфические наборы признаков, которые могут быть использованы для уточнения филогении видов. Наши исследования подтвердили, что особенности питания не скрывают филогенетически значимые морфологические характеристики мандибул личинок декапод.
Таким образом, согласно полученным данным, изотопный состав углерода зоэа исследованных видов декапод изменялся в диапазоне, характерном для планктотрофных организмов, однако у исследованных видов аксиидей значения δ13C были выше, чем у упогебий. Наибольшие значения δ15N, сопоставимые с данными для всеядного зоопланктона, показаны для личинок L. amurensis и B. princeps; низкие значения δ15N отмечены для зоэа N. makarovi, они близки к соотношению изотопов азота ВОВ и указывают на преобладание в рационе фитопланктона; промежуточное положение (δ15N от 6.2 до 6.4 ‰) занимали личинки трех видов Upogebia и двух видов Nihonotrypaea. Из этого следует, что рационы исследованных личинок роющих креветок не зависят от таксономического положения вида; строение ротового аппарата личинок, в частности мандибул, не всегда отражает их пищевые предпочтения, так как даже у зоэа декапод одного рода рационы могут заметно различаться, что необходимо учитывать при их культивировании в лабораторных условиях.
Список литературы
Буруковский Р.Н. Креветки: состав пищи и пищевые взаимоотношения. СПб.: Проспект науки. 2022. 568 с.
Корн О.М., Голубинская Д.Д., Корниенко Е.С. Ключ для определения зоэа роющих креветок инфраотрядов Gebiidea и Axiidea из зал. Петра Великого Японского моря // Биол. моря. 2017. Т. 43. № 5. С. 341–348.
Корниенко Е.С., Корн О.М. Культивирование в лабораторных условиях и особенности морфологии личинок японского мохнаторукого краба Eriocheir japonicus (De Haan) // Изв. ТИНРО. 2005. Т. 143. С. 35–51.
Корниенко Е.С., Корн О.М., Кашенко С.Д. Сравнительная морфология личинок прибрежных крабов семейства Varunidae (Crustacea: Decapoda) // Биол. моря. 2007. Т. 33. № 2. С. 83–101.
Корниенко Е.С., Голубинская Д.Д. Морфология мандибул зоэа I роющих креветок родов Upogebia (Gebiidea) и Nihonotrypaea (Axiidea) // Биол. моря. 2018. Т. 44. № 4. С. 243–254.
Корниенко Е.С., Голубинская Д.Д. Морфология мандибул личинок и взрослых роющих креветок Boasa-xius princeps и Leonardsaxius amurensis (Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae) // Биол. моря. 2020. Т. 46. № 4. С. 247–260. https://doi.org/10.31857/S013434752004004X
Марин И.Н., Корниенко Е.С. Десятиногие ракообразные (Decapoda) залива Восток Японского моря // Биота и среда заповедников Дальнего Востока. 2014. № 2. С. 49–71.
Марин И.Н., Корн О.М., Корниенко Е.С. Upogebia yokoyai Makarov, 1938 (Decapoda: Upogebiidae) – новый для фауны Японского моря вид креветок-гебиид // Биол. моря. 2013. Т. 39. № 3. С. 221–226.
Селин Н.И. Распределение и некоторые черты биологии креветки-привидения Nihonotrypaea japonica (Ortmann, 1891) (Decapoda: Callianassidae) из эстуария реки Волчанка (залив Восток Японского моря) // Биол. моря. 2015а. Т. 41. № 1. С. 13–19.
Селин Н.И. Некоторые особенности биологии рака-крота Upogebia major (De Haan, 1841) (Crustacea: Decapoda) из залива Петра Великого Японского моря // Зоол. журнал. 2015б. Т. 94. № 8. С. 989–992.
Тиунов А.В. Стабильные изотопы углерода и азота в почвенно-экологических исследованиях // Изв. РАН. Сер. биологическая. 2007. № 4. С. 475–489.
Anger K. The biology of decapod crustacean larvae. Crustacean issues. V. 14. Rotterdam, the Netherlands: Balkema. 2001. 419 p.
Das S., Tseng L.-C., Wang L., Hwang J.-S. Burrow characteristics of the mud shrimp Austinogebia edulis, an ecological engineer causing sediment modification of a ti-dal flat // PLoS One. 2017. V. 12. Art. ID e0187647. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187647
Fileman E.S., Lindeque P.K., Harmer R.A. et al. Feeding rates and prey selectivity of planktonic decapod larvae in the Western English Channel // Mar. Biol. 2014. V. 161. P. 2479−2494.
Geiselbrecht H., Melzer R.R. Mandibles of zoea I larvae of nine decapod species: a scanning EM analysis (Crustacea, Decapoda) // Spixiana. 2010. V. 33. P. 27–47.
Hamasaki K., Nishimoto S., Okada M. et al. Dietary effects of phytoplankton and zooplankton on larval survival, duration and growth of four Caridina species (Decapoda: Caridea: Atyidae) under laboratory conditions // Crustacean Res. 2020. V. 49. P. 225–236.
Kinoshita K., Wada M., Kogure K., Furota T. Mud shrimp burrows as dynamic traps and processors of tidal-flat materials // Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser. 2003. V. 247. P. 159–164.
Konishi K. Larval development of the mud shrimp Upogebia (Upogebia) major (De Haan) (Crustacea: Thalassinidea: Upogebiidae) under laboratory conditions, with comments on larval characters of thalassinid families // Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Aquacult. 1989. V. 15. P. 1–17.
Konishi K., Fukuda Y., Quintana R.R. The larval development of the mud-burrowing shrimp Callianassa sp. under laboratory conditions (Decapoda, Thalassinidea, Callianassidae) // Crustaceans and the biodiversity crisis. Proc. 4th Int. Crustacean Congr. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, July 20−24, 1998. V. 1. Leiden, the Netherlands: Brill. 1999. P. 781−804.
Konishi K., Quintana R.R., Fukuda Y. A complete description of larval stages of the ghost shrimp Callianassa petalura Stimpson (Crustacea: Thalassinidea: Callianassidae) under laboratory conditions // Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Aquacult. 1990. V. 17. P. 27–49.
Korn O.M., Kornienko E.S., Golubinskaya D.D. First stage larva of the mud shrimp Nihonotrypaea makarovi Marin, 2013 (Decapoda: Axiidea: Callianassidae) obtained in the laboratory // Zootaxa. 2016. V. 4083. № 2. P. 251–256.
Kornienko E.S., Korn O.M., Demchuk D.D. The larval development of the mud shrimp Upogebia issaeffi (Balss, 1913) (Decapoda: Gebiidea: Upogebiidae) reared under laboratory conditions // Zootaxa. 2012. V. 3269. P. 31–46.
Kornienko E.S., Korn O.M., Demchuk D.D. The larval development of the mud shrimp Upogebia yokoyai Makarov, 1938 (Decapoda: Gebiidea: Upogebiidae) reared under laboratory conditions // J. Nat. Hist. 2013. V. 47. № 29–30. P. 1933–1952.
Kornienko E.S., Korn O.M., Golubinskaya D.D. The complete larval development of the lobster shrimp Boasaxius princeps Boas, 1880 (Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae) obtained in the laboratory // J. Nat. Hist. 2014. V. 48. P. 1737–1769.
Kornienko E.S., Korn O.M., Golubinskaya D.D. The number of zoeal stages in larval development of Nihonotrypaea petalura (Stimpson, 1860) (Decapoda: Axiidea: Callianassidae) from Russian waters of the Sea of Japan // Zootaxa. 2015. V. 3919. № 2. P. 343–361.
Kornienko E.S., Golubinskaya D.D., Korn O.M., Sharina S.N. The complete description of larval stages of the lobster shrimp Leonardsaxius amurensis (Kobjakova, 1937) (Decapoda: Axiidea: Axiidae) identified by DNA barcoding // J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2018. V. 98. P. 1435–1453.
Kubo K., Shimoda K., Tamaki A. Egg size and clutch size in three species of Nihonotrypaea (Decapoda: Thalassinidea: Callianassidae) from western Kyushu, Japan // J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2006. V. 86. P. 103–111.
Laverock B., Smith C.J., Tait K. et al. Bioturbating shrimp alter the structure and diversity of bacterial communities in coastal marine sediments // ISME J. 2010. V. 4. P. 1531–1544.
Le Vay L., Jones D.A., Puello-Cruz A.C. et al. Digestion in relation to feeding strategies exhibited by crustacean larvae // Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001. V. 128. P. 621–628.
Le Vay L., Gamboa-Delgado J. Naturally-occurring stable isotopes as direct measures of larval feeding efficiency, nutrient incorporation and turnover // Aquaculture. 2011. V. 315. P. 95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.03.033
Lindley J.A., Williams R., Conway D.V.R. Variability in dry weight and vertical distributions of decapod larvae in the Irish Sea and North Sea during the spring // Mar. Biol. 1994. V. 120. P. 385–395.
Marin I.N. A new species of callianassid ghost shrimp of the genus Nihonotrypaea Manning & Tamaki, 1998 (Crustacea, Decapoda, Axiidea, Callianassidae) from sou-thern part of the Russian coast of the Sea of Japan // Zootaxa. 2013. V. 3694. № 5. P. 434–444.
Marin I.N. Complete morphological re-description of mud-dwelling axiid Leonardsaxius amurensis (Kobjakova, 1937) with remarks on Axiidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidea) from the Russian coast of the Sea of Japan // Zootaxa. 2015. V. 3937. № 3. P. 549–563.
McConaugha J. Alternative feeding mechanisms in megalopae of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus // Mar. Biol. 2002. V. 140. P. 1227–1233.
Miyabe S., Konishi K., Fukuda Y., Tamaki A. The complete larval development of the ghost shrimp, Callianassa japonica Ortmann, 1891 (Decapoda: Thalassinidea: Callianassidae), reared in the laboratory // Crustacean Res. 1998. V. 27. P. 101–121.
Post D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions // Ecology. 2002. V. 83. № 3. P. 703–718.
Post D.M., Layman C.A., Arrington D.A. et al. Getting to the fat of the matter: models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses // Oecologia. 2007. V. 152. P. 179–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0630-x
Rice A.L., Williamson D.I. Methods for rearing larval decapod Crustacea // Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1970. V. 20. P. 417–434.
Ritara A.J., Dunstan G.A., Crear B.J., Brown M.R. Biochemical composition during growth and starvation of early larval stages of cultured spiny lobster (Jasus edwardsii) phyllosoma // Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2003. V. 136. P. 353–370.
Rotllant G., Simeó C.G., Guerao G. et al. Interannual variability in the biochemical composition of newly hatched larvae of the spider crab Maja brachydactyla (Decapoda, Majidae) // Mar. Ecol. 2014. V. 35. № 3. P. 298–307.
Schwamborn R., Ekau W., Silva A.P. et al. Ingestion of large centric diatoms, mangrove detritus, and zooplankton by zoeae of Aratus pisonii (Crustacea: Brachyura: Grapsidae) // Hydrobiologia. 2006. V. 560. P. 1−13.
Somiya R., Suzuki T., Tamaki A. Mouthpart morphology and wild diet of zoeae of the ghost shrimp, Nihonotrypaea harmandi (Decapoda: Axiidea: Callianassidae) // J. Crustacean Biol. 2014. V. 34. P. 300−308.
Tamaki A., Saitoh Y., Itoh J. et al. Morphological character changes through decapodid-stage larva and juveniles in the ghost shrimp Nihonotrypaea harmandi from western Kyushu, Japan: Clues for inferring pre- and post-settlement states and processes // J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013. V. 443. P. 90−113.
Thorson G. Reproduction and larval development of Danish marine bottom invertebrates, with special reference to the planktonic larvae in the Sound (Øresund) // Medd. Komm. Dan. Fisk.- Havunders., Ser. Plankton. 1946. V. 4. P. 1–523.
Umezawa Y., Tamaki A., Suzuki T. et al. Phytoplankton as a principal diet for callianassid shrimp larvae in coastal waters, estimated from laboratory rearing and stable isotope analysis // Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser. 2018. V. 592. P. 141–158.
Watling L. Feeding and digestive system // Functional morphology and diversity. The natural history of the Crustacea. V. 1. New York: Oxford University Press. 2013. P. 237–260.
Webb A.P., Eyre B.D. Effect of natural populations of burro-wing thalassinidean shrimp on sediment irrigation, benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes and denitrification // Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser. 2004. V. 268. P. 205–220.
Wirtz K.W. Who is eating whom? Morphology and feeding type determine the size relation between planktonic predators and their ideal prey // Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser. 2012. V. 445. P. 1–12.
Zeng C., Rotllant G., Giménez L., Romano N. Effects of environmental conditions on larval growth and development // Developmental Biology and Larval Ecology, The Natural History of the Crustacea. V. 7. New York: Oxford University Press. 2020. P. 195–222.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.