Биология моря, 2023, T. 49, № 3, стр. 166-174
Биохимические и ультраструктурные изменения микроводоросли Tisochrysis lutea El M. Bendif & I. Probert, 2013 (Haptophyta) на разных стадиях роста в накопительной культуре
Т. Ю. Орлова 1, *, Ж. В. Маркина 1, А. А. Карпенко 1, В. И. Харламенко 1, А. А. Зинов 1
1 Национальный научный центр морской биологии им. А.В. Жирмунского (ННЦМБ) ДВО РАН
690041 Владивосток, Россия
* E-mail: torlova06@mail.ru
Поступила в редакцию 28.06.2022
После доработки 12.12.2022
Принята к публикации 26.01.2023
- EDN: SBMQTT
- DOI: 10.31857/S0134347523030099
Аннотация
Исследованы рост, биохимический состав и ультраструктура микроводоросли Tisochrysis lutea в накопительной культуре в течение 30-суточного эксперимента. Численность клеток T. lutea возрастала на протяжении всего опыта. В экспоненциальной и стационарной фазах роста отмечено увеличение размеров и количества липидных капель, содержащих жирные кислоты и каротиноиды, в том числе фукоксантин. Установлено, что суммарное содержание каротиноидов достигает максимума на стационарной фазе и снижается на фазе отмирания. В период стационарной фазы в клетках наблюдается экзоцитоз с выделением липидных капель. Настоящее исследование демонстрирует потенциал клона T. lutea MBRU_Tiso-08 из Биоресурсной коллекции “Морской биобанк” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН в качестве сырья для отечественной биотехнологии, направленной на совместное извлечение каротиноидов (включая фукоксантин) и липидов (включая докозагексаеновую и эйкозапентаеновую жирные кислоты).
В последние два десятилетия микроводоросли стали рассматривать как реальные “клеточные фабрики” для получения биологически активных веществ (De Vera et al., 2018). Микроводоросли производят ценные соединения, в том числе антиоксиданты, ферменты, полимеры, липиды, полиненасыщенные жирные кислоты, пептиды, витамины, токсины и стеролы, которые широко используются в фармакологии и косметологии, производстве продуктов питания и кормов, а также в других биотехнологических производствах (Vignesh, Barik, 2019). Они содержат такие пигменты, как хлорофиллы, каротиноиды, кето-каротиноиды и фикобилипротеины (Zullaikah et al., 2019). Микроводоросли характеризуются активным ростом и коротким временем генерации, что позволяет им почти ежесуточно удваивать биомассу клеток. Это также увеличивает их привлекательность для биотехнологического производства.
Фукоксантин остается одним из наиболее востребованных каротиноидов благодаря своим антиоксидантным, противоопухолевым и противовоспалительным свойствам (Mohibbullah et al., 2022). Микроводоросли рассматривают как перспективный источник фукоксантина не только из-за высокого содержания в них этого соединения (до 15–40 мг в одном грамме сухого веса микроводорослей), но и благодаря возможности их массового культивирования с помощью биореакторов и в открытых прудах (Zarekarizi et al., 2019).
Микроводоросли продуцируют полиненасыщенные жирные кислоты (ω-3 LC-PUFAs), такие как эйкозапентаеновая (ЭПК) и докозагексаеновая (ДГК) (Koller et al., 2014). Ценность этих кислот заключается в их способности снижать риск сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, диабета и артрита, улучшать состояние пациентов с деменцией, депрессивными состояниями и астмой. Эти кислоты важны для нормального эмбрионального развития организма (Hu et al., 2018). Микроводоросли продуцируют и нейтральные липиды, например триацилглицериды (ТАГ) (Соловченко, 2012), широко используемые для получения биотоплива (Custodio et al., 2014).
Среди морских микроводорослей наиболее высоким содержанием ДГК и ЭПК характеризуются представители семейства Isochrysidaceae (Bendif et al., 2013). Их выращивают в марикультуре, используя затем в качестве корма для личинок морских беспозвоночных и сырья для фармацевтической и косметической промышленностей (Perez-Garcia et al., 2011). Вид Tisochrysis lutea, ранее известный как Isochrysis aff. galbana клон T-ISO (см. Bendif et al., 2013), – один из самых широко используемых объектов биотехнологического производства (Araújo et al., 2021). В клетках этой водоросли в высоких концентрациях содержатся омега-3 жирные кислоты, в том числе ДГК и ЭПК (до 14% от общего содержания жирных кислот), а также омега-6 жирные кислоты (Del Pilar Sánchez-Saavedra et al., 2016). Установлено, что T. lutea может накапливать каротиноиды в рекордно высоких концентрациях (Alkhamis, Qin, 2016) и обладает способностью одновременно синтезировать фукоксантин и ДГК (Premaratne et al., 2021).
Цель настоящей работы – исследовать состав жирных кислот и фотосинтетические пигменты у T. lutea из Биоресурсной коллекции “Морской биобанк” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН, а также оценить изменения липидных капель на разных фазах роста микроводоросли.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДИКА
Объектом исследования служила культура одноклеточной водоросли T. lutea El M. Bendif & I. Probert, 2013 из отдела Haptophyta – штамм MBRU_Tiso-08 из Биоресурсной коллекции “Морской биобанк” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН (http://marbank.dvo.ru). Культура выделена из прибрежных вод зал. Петра Великого (Японское море) в 2012 г., ее идентификация подтверждена с помощью молекулярно-генетических методов (Ефимова и др., 2016). Культуру выращивали на среде f, приготовленной на основе стерилизованной морской воды в 250 мл колбах Эрленмейера с объемом культуральной среды 100 мл, при температуре 20°С, интенсивности освещения 70 мкмоль/с/м2 в области видимого света и свето-темновым периодом 14 ч свет : 10 ч темнота (Guillard, Ryther, 1962). В качестве инокулята использовали культуру на экспоненциальной стадии роста. Показатели pH культуральной среды измеряли pH-метром HI 8314F (Hanna Instruments, США).
Размер клеток и флуоресценцию хлорофилла а измеряли на проточном цитометре CytoFLEX (Beckman Coulter, США). Для анализа записывали данные 10 000 клеток водоросли в течение каждого измерения. Гейтирование для выбора клеток из общего числа событий проводили по флуоресценции хлорофилла а. Флуоресценцию хлорофилла а возбуждали лазером с длиной волны 488 нм и регистрировали при 690 ± 25 нм (Маркина, 2019). Размер клеток водоросли определяли с помощью калибровочных бусин (Molecular Probes, США) по показателю прямого светорассеяния. Получение данных и их первичный анализ проводили в программе CytExpert 2.0 (Beckman Coulter, США).
Для анализа содержания фотосинтетических пигментов (хлорофилла а и суммарного содержания каротиноидов) использовали образцы, собранные на мембранный фильтр. Пигменты экстрагировали 90%-ным ацетоном, затем центрифугировали для удаления взвеси в течение 15 мин при 7000 об/мин. Супернатант сливали и определяли на следующих длинах волн: 480, 630, 647, 664 и 750 нм с помощью спектрофотометра Shimadzu UV-2550 (Япония). Расчет концентраций пигментов проводили по стандартным формулам (Jeffrey, Humphrey, 1975).
Липиды экстрагировали с помощью метода Блая и Дайера (Bligh, Dyer, 1959) и разделяли одномерной тонкослойной хроматографией на силикагеле. В качестве системы растворителей использовали смесь гексана, диэтилового эфира и уксусной кислоты (80 : 20 : 1). Зоны силикагеля, содержащие ТАГ, сразу же собирали шпателем и затем элюировали липиды смесью хлороформа и метанола (1 : 1). Метиловые эфиры жирных кислот получали переэтерификацией липидов по известной методике (Carreau, Dubacq, 1978) и очищали тонкослойной хроматографией в бензоле. Метиловые эфиры жирных кислот анализировали на хроматографе Shimadzu GC-14A (Япония) с пламенно-ионизационным детектором с использованием капиллярной кварцевой колонки, при температуре 210°С; газ-носитель – гелий.
Спектры комбинационного рассеяния получали с помощью рамановского микроскопа-спектрометра inVia Reflex (Renishaw, Великобритания), объединенного с микроскопом падающего света Leica DM2500 M (Leica Microsystems, Германия). Для возбуждения использовали диодный лазер 532 нм при 1.0 мВт мощности на уровне объекта и времени экспозиции 0.1 с в 100 повторах. Лазерное пятно диаметром около 1.6 мкм на образце формировалось объективом ×20, NA = 0.6 (Leica). Измерили 20 спектров в диапазоне от 100 до 1800 см–1, в том числе 10 из центральной области клетки и 10 из периферийной (цитоплазма и мембрана). Для обработки спектров использовали функции сглаживания, вычитания базовой линии и подгонки пиков (Tschirner et al., 2008). Качественную оценку содержания каротиноидов в клетках проводили с учетом особенностей амплитуд рамановского спектра.
Для трансмиссионной электронной микроскопии клетки водорослей фиксировали в течение 2 ч в 2.5%-ном глутаральдегиде, приготовленном на фосфатном буфере (pH 7.4), а затем в 1%-ной четырехокиси осмия на том же буфере в течение 1 ч. Для повышения контрастности клетки окрашивали 0.15%-ным раствором рутения красного в течение 15 мин. Материал обезвоживали в серии спиртов возрастающей концентрации и ацетона и заливали в смесь эпона и аралдита (Fluka, Швейцария) по стандартной методике (Luft, 1961). Срезы толщиной 70 нм изготавливали с помощью алмазного ножа (Diatome, Швейцария) на ультрамикротоме Ultracut-R (Leica Microsystems, Германия) и контрастировали 2%-ным раствором уранилацетата и цитратом свинца по стандартной методике (Reynolds, 1963). Исследование срезов проводили на трансмиссионном электронном микроскопе Libra 120 (Carl Zeiss, Германия), ускоряющее напряжение 120 кВ.
Эксперименты проведены в трех биологических повторностях. На графиках и в таблицах представлены средние значения и стандартные отклонения.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Численность клеток в культуре T. lutea увеличивалась в течение 30 суток. На протяжении первых трех недель культивирования соотношение клеток размером 2–4 и 5–6 мкм было одинаковым, с 21-х суток и до конца эксперимента преобладали клетки меньшего размера (рис. 1).
Рис. 1.
Динамика численности популяции Tisochrysis lutea и ее размерная структура в течение культивирования.
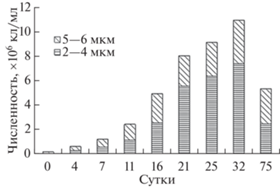
Содержание хлорофилла а и каротиноидов соответствовало динамике численности клеток (табл. 1). К началу стационарной фазы роста содержание хлорофилла а и каротиноидов увеличилось соответственно в 4 и 5 раз по сравнению с таковым на экспоненциальной фазе роста. На стадии отмирания содержание фотосинтетических пигментов снизилось.
Таблица 1.
Показатель pH культуральной среды и содержание фотосинтетических пигментов Tisochrysis lutea в зависимости от фазы роста
| Фаза роста культуры | Показатель | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Хлорофилл а, мкг/л | Каротиноиды, мкг/л | Хлорофилл а, г/1013 на клетку | Каротиноиды, г/1013 на клетку | |
| Экспоненциальная | 8.61 | 381 ± 43 | 482 ± 84 | 1.73 ± 0.08 | 2.17 ± 0.41 |
| Стационарная | 8.66 | 1505 ± 280 | 2572 ± 562 | 1.65 ± 0.32 | 2.79 ± 0.67 |
| Фаза отмирания | 8.36 | 561 ± 116 | 1314 ± 271 | 2.31 ± 0.24 | 5.54 ± 0.52 |
В течение всего периода наблюдений в клетках T. lutea отмечали липидные капли (рис. 2а, 2б), которые экстрагировались между органическими чешуйками, покрывающими клетку микроводоросли (рис. 2г, 2д). На стационарной фазе роста культуры липидные капли были обнаружены и у бактерий, ассоциированных с T. lutea (рис. 2в), и в культуральной среде (рис. 2е). Через 30 сут культивирования выделение липидных капель у T. lutea (рис. 3) хорошо заметно на световом уровне.
Рис. 2.
Изменения липидных телец внутри клеток Tisochrysis lutea и их экскреция в среду: а, б – общий вид клетки, содержащей липидные капли (трансмиссионная электронная микроскопия), lb – липидная капля; в – бактерии, содержащие липидные капли, в культуре микроводоросли; г, д – выделение липидных капель в среду; е – липидные капли в культуральной среде.
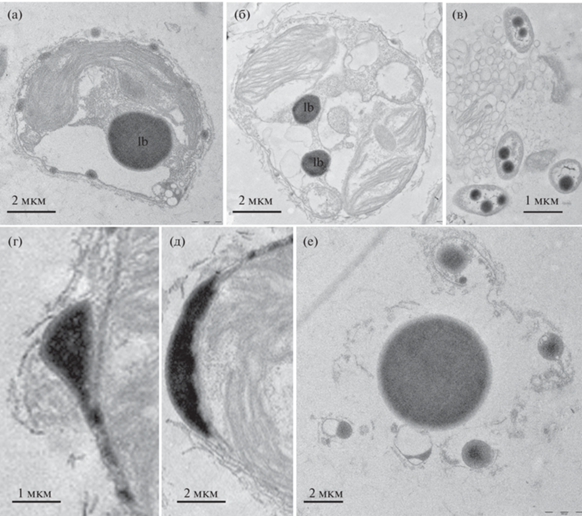
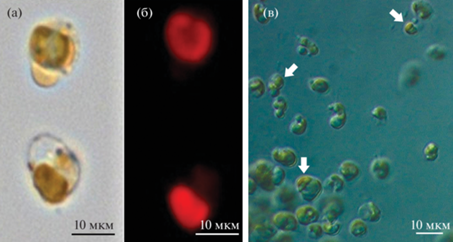
Рис. 3.
Клетки Tisochrysis lutea (световая микроскопия): а – клетки в проходящем свете; б – автофлуоресценция хлоропласта; в – клетки с DIC-контрастированием, стрелками обозначены липидные капли.
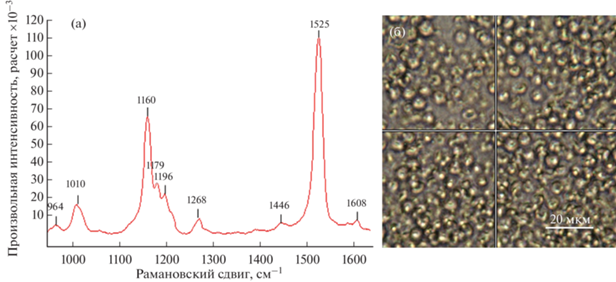
На рамановских спектрах липидных капель отмечено увеличение значений пиков β-каротина при 1157 и 1526 см–1 (рис. 4а, 4б). Это явление характерно как для экспоненциальной, так и стационарной фазы роста. Также при исследовании T. lutea получены моды 1525, 1160 и 1010 см–1, соответствующие изомерам каротиноида фукоксантина (рис. 5а, 5б).
Рис. 4.
Рамановский спектр Tisochrysis lutea на разных фазах роста культуры (а), черной линией обозначена экспоненциальная фаза роста, красной – стационарная; б – точка получения рамановского спектра (липидная капля).
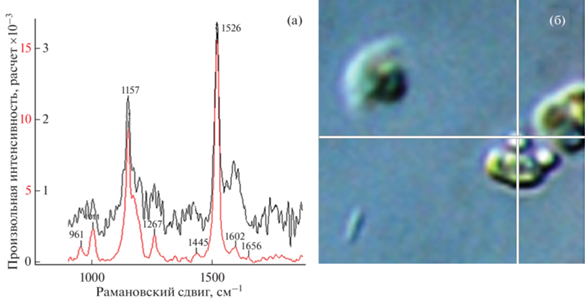
Рис. 5.
Рамановский спектр Tisochrysis lutea: а – моды фукоксантина (ν1 1525, ν2 1160, ν3 1010 см–1); б – точка получения рамановского спектра (клетка).
Содержание ТАГ на клетку T. lutea на экспоненциальной стадии роста составляло 0.61 пкг/103 клеток, на стационарной – 0.61 пкг/103 клеток и на стадии снижения численности – 0.67 пкг/103 клеток.
На стадии экспоненциального роста и в начале стадии стационарного роста (30 сут) в составе жирных кислот T. lutea (табл. 2) преобладали полиненасыщенные жирные кислоты (ПНЖК), содержание которых составляло 40.9%, содержание насыщенных и мононенасыщенных (МНЖК) жирных кислот было ниже. В конце стационарной фазы (60 сут) содержание ПНЖК было выше, чем содержание МНЖК. Среди ПНЖК наибольшая концентрация в клетке отмечена для жирных кислот 18:4n-3 (15.3–20.9%) и 22:6n-3 (7.7–11.3%). Концентрации 20:5n-3 и 20:4n-6 на всех стадиях были минимальными. Можно отметить заметные концентрации 22:5n-6, содержание которой со временем возрастало. Соотношение n-3/n-6 ПНЖК значительно уменьшалось в конце стационарной фазы. Концентрация докозагексаеновой кислоты, составлявшая на экспоненциальной фазе 0.82 мг/л, на стационарной достигала максимума (1.62 мг/л) и с началом отмирания культуры клеток снижалась до значений в экспоненциальной фазе.
Таблица 2.
Состав жирных кислот (% от суммы жирных кислот) на разных фазах роста культуры микроводорослей Tisochrysis lutea
| Жирные кислоты | Экспоненциальная | Стационарная | Фаза отмирания |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 3 | N = 4 | N = 4 | |
| 14:0 | 19.7 ± 1.2 | 14.6 ± 0.6 | 12.2 ± 0.8 |
| 15:0 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| 16:1n-7 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.1 |
| 16:0 | 14.1 ± 1.9 | 12.8 ± 0.3 | 12.6 ± 0.4 |
| 18:4n-3 | 20.9 ± 2.8 | 18.8 ± 0.6 | 15.3 ± 0.9 |
| 18:2n-6 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.0 | 2.8 ± 0.1 |
| 18:3n-3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.5 |
| 18:1n-9 | 17.1 ± 0.4 | 28.2 ± 0.9 | 23.8 ± 1.2 |
| 18:1n-7 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 0.7 |
| 18:0 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.5 |
| 19:1n-6 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 |
| 20:4n-6 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.2 |
| 20:5n-3 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 |
| 21:5n-3 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.0 |
| 22:5n-6 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 4.2 ± 0.1 |
| 22:6n-3 | 11.3 ± 1.4 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 7.7 ± 0.3 |
| НЖК | 35.7 | 28.6 | 28.5 |
| МНЖК | 23.4 | 33.0 | 35.8 |
| n-3 ПНЖК | 35.3 | 33.4 | 28.1 |
| n-6 ПНЖК | 5.6 | 5.0 | 7.6 |
| n-3/n-6 | 6.0 | 6.2 | 3.4 |
Среди МНЖК преобладала жирная кислота 18:1n-9 (17.1–28.2%), в поздней стационарной фазе значительно увеличивалось содержание 18:1n-7. Среди НЖК преобладали 14:0 и 16:0 кислоты, содержание 18:0 было невелико. Концентрация 22:6n-3, которая была максимальной в начале стационарной фазы, составляя 1.544 мг/л культуры, к концу опыта заметно уменьшалась.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Микроводоросль T. lutea продуцирует ряд каротиноидов, в том числе β-каротин и фукоксантин, содержание которых варьирует на разных этапах роста культуры и определяется параметрами культивирования (Pajot et al., 2022). Согласно полученным нами данным, содержание липидов и каротиноидов увеличивалось на стационарной фазе роста культуры (табл. 1, 2; рис. 4а). Максимальное содержание липидов в накопительной культуре на стадии стационарного роста показано для многих видов микроводорослей. При снижении количества питательных веществ в среде наступает так называемая липогенная фаза, которая характеризуется замедлением или остановкой клеточного деления и накоплением нейтральных липидов (Соловченко, 2012; Орлова и др., 2019).
Наибольшее содержание жирных кислот в культуре T. lutea также регистрировали на стационарной фазе. В разных штаммах Isochrysis galbana и T. lutea концентрация ПНЖК 22:6n-3 составила от 3.6 до 25.3% от общего содержания жирных кислот. Нами установлено, что содержание 18:4n-3 в клетках T. lutea значительно превышало таковое у большинства ранее исследованных штаммов (Liu et al., 2013).
Содержание ДГК и ЭПК свидетельствует о биотехнологическом потенциале культуры, поддерживаемой в Биоресурсной коллекции “Морской биобанк” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН (табл. 3).
Таблица 3.
Максимальное содержание докозагексаеновой (ДГК) и эйкозапентаеновой (ЭПК) кислот (% от суммы жирных кислот) в клетках разных клонов Tisochrysis lutea
| Клон, место содержания | ДГК | ЭПК | Литературный источник |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCAP 927/14 Т+ Institute for Exploitation of the Sea an oceanographic institution in Brest, France |
18.0 ± 0.5 | – | Da Costa et al., 2017 |
| T-ISO (LB 2307 Collection of Algae at the University of Texas (UTEX) at Austin, Texas, USA |
15.21 ± 0.00 | 3.43 ± 0.41 | Sancez-Saavedra et al., 2015 |
| CCMP 1324 National Center for Marine Algae and Microbiota (NCMA), East Boothbay, USA |
14.4 ± 0.7 | – | Lin et al., 2007 |
| ССМР 1324 National Center for Marine Algae and Microbiota (NCMA), East Boothbay, USA |
12.72 ± 0.17 | – | Hu et al., 2018 |
| Australian National Algae Culture Collection (ANACC) Hobart CSIRO, Australia | 10.1 ± 0.22 | 0.5 ± 0.01 | Alkhamis, Qin, 2016 |
| CS-177 Australian National Algae Culture Collection (ANACC) Hobart CSIRO, Australia |
11.1 ± 2.8 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | Mai et al., 2021 |
| Adelaide, Australia South Australian Research and Development Institute Aquatic Science Centre, Adelaide | 8.20 ± 0.10 | 0.57 ± 0.06 | Rasdi, Qin, 2015 |
| RCC1349 Roscoff Culture Collection of Marine Microalgae Roscoff, France |
4.8 ± 0.5 | – | Gnouma et al., 2017 |
| MBRU_Tiso-08 Биоресурсная коллекция “Морской биобанк” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН, Владивосток, Россия (The Resource Collection Marine Biobank on the basis of the National Scientific Center of Marine Biology (NSCMB), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences Vladivostok, Russia) |
11.3 ± 1.4 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | Настоящая работа |
В ходе нашего эксперимента обнаружено значительное увеличение размеров липидных капель в клетках, что является ответом на недостаток питательных веществ (Соловченко, 2012). Известно, что у представителей Isochrysidaceae липидные капли примыкают к хлоропласту и могут содержать каротиноиды (Pilát et al., 2012).
На стадии стационарного роста наблюдался экзоцитоз – выделение во внешнюю среду липидных капель, содержащих каротиноиды. На стадиях стационара и отмирания в культуре T. lutea отмечены бактерии, в клетках которых также содержались липидные капли. Их количество варьировало от 1 до 3. Подобное явление, отмеченное ранее на штаммах T. lutea CCAP 927/14 и CCAP 927/14 Т+, связывают с увеличением выделения вторичных метаболитов (Da Costa et al., 2017).
Таким образом, рост популяции T. lutea продолжается до 30-х суток. С увеличением времени экспозиции растет количество липидных капель, содержащих липиды и каротиноиды, в том числе фукоксантин. В период стационарной фазы у большинства клеток наблюдается явление экзоцитоза. Показано, что суммарное содержание каротиноидов увеличивается на стационарной фазе. Содержание докозагексаеновой и эйкозапентаеновой жирных кислот нарастает на экспоненциальной и стационарной фазах роста. Полученные нами данные свидетельствуют о высоком биотехнологическом потенциале штамма MBRU_Tiso-08 из Биоресурсной коллекции “Морской биобанк” ННЦМБ ДВО РАН.
Список литературы
Ефимова К.В., Орлова Т.Ю., Брыков Вл.А. Молекулярно-генетическая идентификация нового штамма Tisochrysis lutea (Bendif et Probert, 2013) из акватории российских прибрежных вод Японского моря // Микробиология. 2016. Т. 85. № 3. С. 309–316.
Маркина Ж.В. Проточная цитометрия как метод исследования морских одноклеточных водорослей: развитие, проблемы, перспективы // Биол. моря. 2019. Т. 45. № 5. С. 291–298.
Орлова Т.Ю., Сабуцкая М.А., Маркина Ж.В. Изменение ультраструктуры морских микроводорослей из разных отделов в накопительной культуре // Биол. моря. 2019. Т. 45. № 3. С. 188–196.
Соловченко А.Е. Физиологическая роль накопления нейтральных липидов эукариотическими микроводорослями при стрессах // Физиология растений. 2012. Т. 59. № 2. С. 192–192.
Alkhamis Y., Qin J.G. Comparison of pigment and proximate compositions of Tisochrysis lutea in phototrophic and mixotrophic cultures // J. Appl. Phycol. 2016. V. 28. P. 35–42.
Araújo R., Vázquez Calderón F., Sánchez López J. et al. Current status of the algae production industry in Europe: an emerging sector of the blue bioeconomy // Frontiers Mar. Sci. 2021. V. 7. № 626389.
Bendif E.M., Probert I., Schroeder D.C., Vargas C. On the description of Tisochrysis lutea gen. nov. sp. nov. and Isochrysis nuda sp. nov. in the Isochrysidales, and the transfer of Dicrateria to the Prymnesiales (Haptophyta) // J. Appl. Phycol. 2013. V. 25. P. 1763–1776.
Bligh E.G., Dyer W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification // Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959. V. 37. P. 911–917.
Carreau J.P., Dubacq J.P. Adaptation of macro-scale me-thod to the micro-scale for fatty acid methyl transesterification of biological lipid extracts // J. Chromatogr. 1978. V. 151. P. 384–390.
Custodio L., Soares F., Pereira H. et al. Fatty acid composition and biological activities of Isochrysis galbana T-ISO, Tetraselmis sp. and Scenedesmus sp.: possible application in the pharmaceutical and functional food industries // J. Appl. Phycol. 2014. V. 26 P. 151–161.
Da Costa F., Le G.F., Quéré C. Effects of growth phase and nitrogen limitation on biochemical composition of two strains of Tisochrysis lutea // Algal Res. 2017. V. 27. P. 177–189.
Del Pilar Sánchez-Saavedra M., Maeda-Martínez A.N., Acosta-Galindo S. Effect of different light spectra on the growth and biochemical composition of Tisochrysis lutea // J. Appl. Phycol. 2016. V. 28. P. 839–847.
De Vera C.R., Díaz Crespín G., Hernández Daranas A. et al. Marine microalgae: promising source for new bioactive compounds // Mar. Drugs. 2018. V. 16. № 9.
Gnouma A., Sadovskaya I., Souissi A. et al. Changes in fatty acids profile, monosaccharide profile and protein content during batch growth of Isochrysis galbana (T. iso) // Aquacult. Res. 2017. V. 48. P. 4982–4990.
Guillard R.R.L., Ryther J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. 1. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. // Can. J. Microbiol. 1962. V. 8. P. 229–239.
Hu H., Ma L.L., Shen X.F. et al. Effect of cultivation mode on the production of docosahexaenoic acid by Tisochrysis lutea // AMB Expr. 2018. V. 8. P. 1–12.
Jeffrey S.W., Humphrey G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophyll a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton // Biochem. Physiol. Planz. 1975. V. 167. P. 191–194.
Koller M., Muhr A., Braunegg G. Microalgae as versatile cellular factories for valued products // Algal Res. 2014. V. 6. P. 52–63.
Lin Y.-H., Chang F.-L., Tsao C.-Y., Leu J.-Y. Influence of growth phase and nutrient source on fatty acid composition of Isochrysis galbana CCMP 1324 in a batch photoreactor // Biochem. Engineer. 2007. V. 37 P. 166–176.
Liu J., Sommerfeld M., Hu Q. Screening and characterization of Isochrysis strains and optimization of culture conditions for docosahexaenoic acid production // Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013. V. 97. P. 4785–4798.
Luft J.H.J. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods // Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1961. V. 9. P. 409–414.
Mai T.D., Lee-Chang K.J., Jameson I.D. et al. Fatty Acid Profiles of Selected Microalgae Used as Live Feeds for Shrimp Postlarvae in Vietnam // Aquac. J. 2021. № 1. P. 26–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj1010004
Mohibbullah M., Haque M.N., Sohag et al. A systematic review on marine algae-derived fucoxanthin: an update of pharmacological insights // Mar. Drugs. 2022. V. 20. № 5.
Pajot A., Hao Huynh G., Picot L. et al. Fucoxanthin from algae to human, an extraordinary bioresource: insights and advances in up and downstream processes // Mar. Drugs. 2022. V. 20. P. 222.
Perez-Garcia O., Escalante F.M.E., de-Bashan L.E., Bashan Y. Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: metabolism and potential products // Water Res. 2011. V. 45. P. 11–36.
Pilát Z., Bernatová S., Ježek J. et al. Raman microspectroscopy of algal lipid bodies: β-carotene quantification // J. Appl. Phycol. 2012. V. 24 P. 541–546.
Premaratne M., Liyanaarachchi V.C., Nimarshana P.H.V. et al. Co-production of fucoxanthin, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and bioethanol from the marine microalga Tisochrysis lutea // Biochem. Engineer. J. 2021. V. 176. № 108160.
Rasdi N.W., Qin J.G. Effect of N:P ratio on growth and chemical composition of Nannochloropsis oculata and Tisochrysis lutea // J. Appl. Phycol. 2015. V. 27. P. 2221–2230.
Reynolds E. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaquestain in electron microscopy // J. Cell Biol. 1963. V. 17. P. 208–212.
Tschirner N., Schenderlein M., Brose K. et al. Raman excitation profiles of β-carotene—novel insights into the nature of the ν1-band // Phys. Stat. Sol. (B). 2008. V. 245. P. 2225–2228.
Vignesh G., Barik D. Energy From toxic organic waste for heat and power generation, chapter 6: Toxic waste from biodiesel production industries and its utilization. Sawston: Woodhead Publishing. 2019. P. 69–82.
Zarekarizi A., Hoffmann L., Burritt D. Approaches for the sustainable production of fucoxanthin, a xanthophyll with potential health benefits // J. Appl. Phycol. 2019. V. 31. P. 281–299.
Zullaikah S., Utomo A.T., Yasmin M. et al. Ecofuel conversion technology of inedible lipid feedstocks to renewable fuel // Advances in eco-fuels for a sustainable environment woodhead publishing series in energy. Amsterdam: Elsevier Ltd. 2019. P. 237–276.
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.


