Биология внутренних вод, 2022, № 3, стр. 290-299
Влияние биогенных элементов на рост нитчатых цианобактерий – возбудителей “цветения” воды – и синтез ими метаболитов
Т. Б. Зайцева a, *, Н. Г. Медведева a, **
a Санкт-Петербургский научно-исследовательский центр экологической безопасности Российской академии наук
Санкт-Петербург, Россия
* E-mail: zaytseva.62@list.ru
** E-mail: ngmedvedeva@gmail.com
Поступила в редакцию 13.04.2021
После доработки 26.10.2021
Принята к публикации 02.11.2021
- EDN: UVZFXM
- DOI: 10.31857/S0320965222030196
Аннотация
Повышение содержания в среде биогенных элементов приводило к интенсификации роста нитчатых цианобактерий Aphanizomenon flos-aquae и Planktothrix agardhii – возбудителей “цветения” воды – и снижению содержания в среде водорастворимых экзополисахаридов. При увеличении содержания азота и фосфора отмечено значительное повышение в среде содержания микроцистина dm-RR и одорирующего вещества бензотиазола, синтезируемых цианобактерией P. agardhii.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Массовое развитие цианобактерий в водоемах и водотоках вызывает серьезные негативные воздействия на экосистемы. Оно может вызвать ухудшение качества воды и снижение содержания растворенного кислорода, приводящие к подавлению роста эукариотических водорослей, к гибели беспозвоночных и рыб, снижению биоразнообразия, разрушению пищевых цепей и динамики экосистем. В целом, массовое развитие цианобактерий представляет угрозу для экологической и экономической устойчивости пресноводных экосистем (Facey et al., 2019).
Одна из причин “цветения” водоемов в последние десятилетия – глобальное изменение климата и эвтрофикация (Корнева, Глущенко, 2020; Gobler, 2020). Роль биогенных элементов – азота и фосфора – в процессах массового развития цианобактерий подтверждена результатами ряда исследований (Loza et al., 2014; Chaffin et al., 2018; Jankowiak et al., 2019; Fernández-Juárez et al., 2020). Относительно высокое содержание в воде фосфора, низкое отношение азота к фосфору, высокая температура воды и другие факторы могут вызывать массовое развитие цианобактерий и их конкурентное преимущество. Однако до сих пор невозможно точно спрогнозировать возникновение “цветения” воды при наличии отдельных факторов или их совокупности. Отмечено, что в водохранилищах, созданных на крупных реках и не испытывающих биогенного дефицита, не всегда прослеживается непосредственная связь между развитием фитопланктона и содержанием биогенных элементов, что свидетельствует о сложном и многокомпонентном характере их влияния на фитопланктон (Минеева, 2021).
Содержание азота и фосфора в водных объектах варьирует в широком диапазоне. Так, общий азот в водоемах фиксируется в концентрациях от <0.1 до сотен мг/л. Общий фосфор присутствует в водоемах в диапазоне концентраций <0.1 … >1 мг/л (Shaw et al., 2009). Зафиксированные уровни содержания фосфатов во внутренних водоемах достигали 1.87–6.79 мг/л, что соответствовало 0.61–2.2 мг P/л, нитратов – в концентрациях 100–1650 мг/л, что соответствовало 22.6–372.6 мг N/л (Prasad, Prasad, 2019).
Массовое развитие цианобактерий способствует ухудшению качества воды вследствие образования вторичных метаболитов, в том числе токсинов, одорантов и ЭПС.
После периода массового развития цианобактерий накопленная биомасса отмирает, и в воду выделяются внутриклеточные метаболиты, в частности, альготоксины, опасные для здоровья и жизни людей и животных (Facey et al., 2019).
Токсичные “цветения” воды, вызванные массовым развитием цианобактерий, продуцирующих токсины, зарегистрированы во всем мире. К развитию токсичных “цветений” воды может приводить повышение содержания питательных веществ в водоемах, а именно азота и фосфора (Srivastava et al., 2016). Аддитивное воздействие на увеличение темпов роста токсичных видов цианобактерий выявлено при совместном влиянии биогенных веществ и температуры. Так, например в эвтрофированном водохранилище Волго-Камско-Донского каскада – Чебоксарском вдхр. в период жаркого лета 2010 г. при доминировании в сообществе фитопланктона “токсичных” видов цианобактерий концентрация микроцистинов была 25.7 мкг/г сырой биомассы, а содержание наиболее токсичного из микроцистинов МС-LR достигало 14.0 мкг/г сырой биомассы (Корнева и др., 2014).
На формирование качества воды значительное влияние оказывают и другие метаболиты цианобактерий – ЭПС и одоранты. Будучи субстратом для развития других микроорганизмов, ЭПС усиливают биологическое загрязнение воды клетками микроорганизмов и их метаболитами (Сиренко, Козицкая, 1988). Эвтрофикация и загрязнение поверхностных вод вызывают увеличение числа случаев появления неприятных запахов, связанных с массовым развитием водных микроорганизмов, в частности, цианобактерий. Появление неприятного запаха в водной среде считается проблемой во всем мире, особенно в эвтрофных озeрах и водохранилищах, что приводит к большим экономическим потерям для аквакультуры, негативно влияет на эстетику и качество многих туристических объектов, вызывает повышение стоимости очистки воды. Появление запахов связано с присутствием в воде особых органических веществ биогенного происхождения ‒ одорантов (терпеноидов, производных каротиноидов, соединений серы и других летучих соединений), образующихся вследствие массового развития цианобактерий (Lee et al., 2017).
Цель работы – оценить влияние биогенных элементов азота и фосфора на рост нитчатых цианобактерий Aphanizomenon flos-aquae и Planktothrix agardhii и синтез ими метаболитов, влияющих на качество воды – альготоксинов, одорантов и экзополисахаридов.
МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Объекты исследования. Объектами исследования стали Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (L.) Ralfs CALU 1033, выделенные из Красноярского вдхр., и Planktothrix agardhii CALU 1113, выделенные из Невской губы Финского залива. Культуры цианобактерий получены из Ресурсного центра “Культивирование микроорганизмов” Научного парка Санкт-Петербургского гос. ун-та (Россия).
Культивирование цианобактерий. Цианобактерии выращивали на среде BG11 (Rippka et al., 1979) в статических условиях в колбах Эрленмейера объемом 250 мл, объем среды был 100 мл. Культивирование проводили в течение 10 сут при освещенности 1000 лк, световом режиме свет/темнота – 12 ч/12 ч и температуре 25 ± 1°С.
Азот в составе NaNO3 вносили в безазотистую среду BG11, создавая его концентрации в среде 0.05, 0.4, 20, 247 мг N/л. Фосфор в виде K2HPO4 вносили в среду BG11, не содержащую фосфора, в концентрациях 0.02, 0.2, 1.0, 5.4 мг/л. В среду вносили расчетные концентрации KCl таким образом, чтобы концентрация калия во всех вариантах соответствовала его содержанию в среде BG11.
В экспериментах по изучению влияния азота для получения посевного материала клетки, выращенные на среде BG11, трижды промывали дистиллированной водой и ресуспендировали в безазотистой среде BG11. В экспериментах по изучению влияния фосфора посевной материал получали при культивировании клеток на среде BG11, не содержащей ортофосфата калия. Посевной материал выращивали в течение 7 сут и вносили в среду из расчета 20 ± 2 мг с.в/л. Биомассу цианобактерий определяли весовым методом и выражали в г/л.
Определение водорастворимых экзополисахаридов. При определении содержания водорастворимых ЭПС клетки отделяли от среды центрифугированием при 8000 об./мин в течение 10 мин. Содержание ЭПС определяли в супернатанте антроновым методом (Herbert et al., 1971).
Определение микроцистинов. Концентрации внутри- и внеклеточных микроцистинов определяли методом высокоэффективной жидкостной хроматографии (ВЭЖХ) на хроматографе HP1090 (“Hewlett-Packard”, США) с диодно-матричным детектором (длина волны 238 нм, разрешение 1.2 нм) по методике, представленной ранее (Зайцева, Медведева, 2019). В работе использовали стандартный раствор микроцистина dm-RR (“Sigma-Aldrich”, США).
Определение одорирующих веществ. Наличие и содержание в среде одорирующих веществ, образуемых цианобактериями P. agardhii, определяли после 21 сут культивирования с помощью хромато-масс-спектрометрического анализа на хромато-масс-спектрометре единичного разрешения GC-MS QP-2010 (Shimadzu, Япония) методом равновесной паровой фазы в режиме полного сканирования по методике, представленной ранее (Zaytseva et al., 2015). Количественное определение проводили по внешней калибровке с использованием внутреннего стандарта – 2-фторнафталина. Стандартные растворы геосмина, бензотиазола, 2-фторнафталина получены от Supelco (США).
Статистическая обработка данных. Статистическая обработка результатов проводилась с помощью программного обеспечения PAST 4.x software (http://folk.vio.no/ohammer/past). Статистическую значимость различий между вариантами при определении влияния биогенных элементов на выход биомассы, содержание ЭПС и токсинообразование определяли посредством непараметрического дисперсионного анализа Краскела–Уоллеса с применением критерия Данна для попарных сравнений выборок, а на содержание одорирующих веществ – посредством U-критерия Манна–Уитни. Различия считали статистически значимыми при р < 0.05. В таблицах и на графиках полученные данные представлены в виде средней арифметической величины со стандартным отклонением (M ± SD) трех независимых повторов (n = 3).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Проведенные исследования показали, что рост нитчатых цианобактерий Aphanizomenon flos-aquae и Planktothrix agardhii зависит от содержания биогенных элементов в среде культивирования.
При увеличении концентрации азота в среде от 0.05 до 247 мг/л при постоянном содержании фосфора (5.4 мг/л) выявлено статистически значимое (р < 0.05) увеличение биомассы цианобактерий Р. agardhii в 6.3 раза, биомасса азотфиксирующих цианобактерий A. flos-aquae возрастала в 1.8 раза (рис. 1а).
Рис. 1.
Влияние азота (а) и фосфора (б) на выход биомассы цианобактерий: Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (I); Planktothrix agardhii (II) (M ± SD, n = 3).
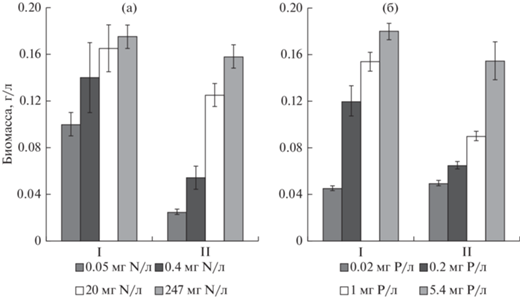
При повышении содержания фосфора (концентрация азота в среде была 247 мг/л) отмечена дозозависимая стимуляция роста исследованных цианобактерий (рис. 1б). Наименьшие уровни биомассы цианобактерий зафиксированы при самой низкой из исследованных концентраций фосфора в среде – 0.02 мг Р/л. При повышении содержания фосфора от 0.02 до 5.4 мг/л биомасса A. flos-aquae и Р. agardhii статистически значимо (р < 0.05) возрастала в 4 и 3.1 раза соответственно (рис. 1б).
Азот и фосфор оказывали влияние не только на рост нитчатых цианобактерий, но и на синтез и выделение в окружающую среду ряда метаболитов: полисахаридов, цианотоксинов и одорирующих веществ.
Выявлена зависимость содержания водорастворимых ЭПС в среде от концентраций азота и фосфора при культивировании цианобактерий A. flos-aquae и P. agardhii (рис. 2).
Рис. 2.
Влияние азота на содержание водорастворимых ЭПС в среде (a) и на удельную продуктивность биомассы по ЭПС (б) цианобактерий Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (I) и Planktothrix agardhii (II) (M ± SD, n = 3).
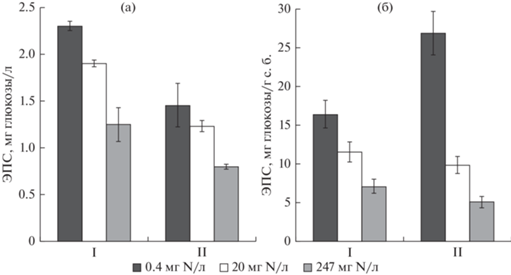
Исследование влияния азота в концентрациях 0.4–247 мг/л при постоянной фосфорной нагрузке (5.4 мг Р/л) на содержание ЭПС в среде выращивания цианобактерий показало, что в наиболее высокой концентрации ЭПС присутствуют в среде при наименьшей из исследованных концентраций азота – 0.4 мг/л. При увеличении концентраций азота в среде культивирования A. flos-aquae и P. agardhii от 0.4 до 247 мг/л выявлено статистически значимое (р < 0.05) снижение содержания ЭПС в среде в 1.8 раза для обеих культур (рис. 2а). Следует отметить, что удельная продуктивность по ЭПС биомассы цианобактерий A. flos-aquae и P. agardhii при этом снижалась в большей степени – в 2.3 и 5.3 раза соответственно (рис. 2б).
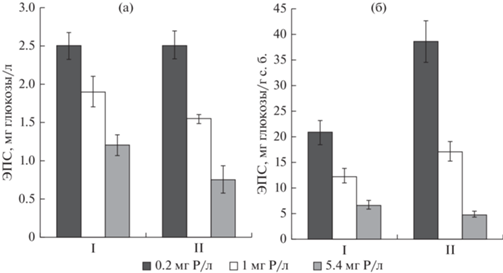
Повышение концентрации фосфора в интервале от 0.2 до 5.4 мг/л также приводило к снижению содержания ЭПС в среде культивирования A. flos-aquae и P. agardhii в 2.1 и 3.3 раза соответственно (рис. 3а). Выявлено большее уменьшение удельной продуктивности биомассы цианобактерий по ЭПС – в 3.1 и 8 раз соответственно (рис. 3б).
Рис. 3.
Влияние фосфора на содержание водорастворимых ЭПС в среде (a) и на удельную продуктивность биомассы по ЭПС (б) цианобактерий Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (I) и Planktothrix agardhii (II) (M ± SD, n = 3).
Влияния азота и фосфора на содержание цианотоксинов в среде изучали с использованием токсичного штамма цианобактерий P. agardhii CALU 1113, образующего несколько микроцистинов, основной из которых – микроцистин dm-RR (MC-dm-RR) (Зайцева и др., 2015).
Увеличение содержания азота в среде от 0.4 до 247 мг/л приводило к статистически значимому (р < 0.05) повышению концентраций внутриклеточного и суммарного (концентрация внутриклеточного МС + концентрация внеклеточного МС) микроцистина dm-RR в среде в 3.8 раза, при этом статистически значимых изменений в концентрации внеклеточного dm-RR не выявлено (H = 5.489, p = 0.06282). В удельной продуктивности биомассы по микроцистину (мг МС/г с. б.) при варьировании концентраций азота в диапазоне 0.4–247 мг/л также не зафиксировано статистически значимых изменений (H = 3.822, p = 0.1479) (табл. 1).
Таблица 1.
Влияние азота и фосфора на содержание MC-dm-RR в среде и удельную продуктивность биомассы цианобактерии P. agardhii по микроцистину
| Биогенный элемент |
Концентрация, мг/л | Концентрация MC-dm-RR в среде, мг/л | Удельная продуктивность биомассы по MC-dm-RR, мг МС/г с. б. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| внутрикле-точный MC | внеклеточный MC | суммарный МС | |||
| Азот (при Р = 5.4 мг/л) |
0.4 | 0.352 ± 0.004а | 0.031 ± 0.001а | 0.383 ± 0.004а | 7.093 ± 0.768a |
| 20 | 0.459 ± 0.004ab | 0.032 ± 0.003а | 0.491 ± 0.003ab | 3.928 ± 1.562a | |
| 247 | 1.343 ± 0.092b | 0.095 ± 0.005a | 1.438 ± 0.091b | 9.101 ± 2.094a | |
| Фосфор (при N = 247 мг/л) |
0.2 | 1.117 ± 0.011а | 0.081 ± 0.001а | 1.198 ± 0.008a | 18.431 ± 4.213a |
| 1.0 | 1.303 ± 0.016ab | 0.093 ± 0.001аb | 1.396 ± 0.012ab | 15.511 ± 2.764a | |
| 5.4 | 1.546 ± 0.049b | 0.111 ± 0.003b | 1.657 ± 0.006b | 10.69 ± 2.12a | |
Примечание. Здесь и в табл. 2 одинаковыми латинскими буквами обозначены величины, различия между которыми статистически не значимы (p ≥ 0.05), M ± SD, n = 3.
При повышении концентрации фосфора от 0.2 до 5.4 мг/л наблюдалось статистически значимое (р < 0.05) увеличение содержания в среде как внутриклеточного, так и внеклеточного и суммарного токсина в 1.4 раза при статистически незначимых различиях в удельной продуктивности биомассы P. agardhii по MC-dm-RR (мг МС/г с. б.) (H = 4.356, p = 0.1133) (табл. 1).
В результате анализа состава одорирующих веществ в среде культивирования P. agardhii были обнаружены соединения, обладающие сильным неприятным запахом: бензотиазол и геосмин (табл. 2).
Таблица 2.
Влияние азотно-фосфорной нагрузки на удельную продуктивность биомассы цианобактерии P. agardhii по одорантам и их концентрацию в среде
| Вариант | Биомасса, г/л | Удельная продуктивность, мкг/г с. б. | Концентрация в среде, мкг/л | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| бензотиазол | геосмин | бензотиазол | геосмин | ||
| Фосфор – 0.2 мг/л (азот – 0.4 мг/л) |
0.039 ± 0.005a | 533.3 ± 58.2a | 161.5 ± 22.3a | 20.8 ± 3.1a | 6.3 ± 0.7a |
| Фосфор – 1 мг/л (азот – 20 мг/л) |
0.085 ± 0.012b | 1058.8 ± 76.2b | 83.5 ± 9.6b | 90 ± 8b | 7.1 ± 0.9a |
Повышение уровня азотно-фосфорной нагрузки в 5 раз вызвало увеличение биомассы P. agardhii в 2.2 раза. Концентрация бензотиазола в среде возросла в 4.3 раза при увеличении удельной продуктивности биомассы (мкг/г с. б.) в 2 раза. Статистически значимых различий в содержании геосмина в среде при пятикратном повышении концентраций азота и фосфора не выявлено (p > 0.5), при этом продуктивность клеток P. agardhii по геосмину снизилась в 1.9 раза (табл. 2).
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТОВ
Биогенные элементы азот и фосфор имеют решающее значение для жизненного цикла цианобактерий, рост цианобактерий может быть ограничен в условиях их лимитирования. Фосфор необходим для клеточного синтеза нуклеиновых кислот и мембранных фосфолипидов, для переноса энергии через три- и бифосфорилированные нуклеотиды. В водной среде растворенный неорганический фосфор биологически доступен в виде ортофосфата. В условиях ограниченной доступности фосфор оказывает влияние на фотосинтез, дыхание и активность АТФ-зависимых ферментов. Наиболее распространенными формами азота в водной среде считаются неорганические – аммонийный и нитратный. Азот необходим цианобактериям для синтеза белков и аминокислот. Недостаток азота может привести к снижению скорости роста цианобактерий и способствовать возникновению хлороза, вызывающего деградацию фикобилипротеинов и, как следствие, подавление фотосинтеза (Fernández-Juárez et al., 2020).
Биогенные элементы оказывают существенное влияние на рост цианобактерий и структуру их сообществ. Так, при оценке сдвигов в сообществе цианобактерий оз. Эри (США) в ответ на изменения содержания биогенных элементов было выявлено, что азот значительно увеличивает относительное обилие недиазотрофных цианобактерий, в частности относящихся к роду Planktothrix, в то время как при повышении содержания фосфора в большей степени возрастает количество азотфиксирующих цианобактерий, в частности относящихся к родам Dolichospermum и Aphanizomenon (Jankowiak et al., 2019).
Характер влияния биогенных элементов на рост цианобактерий (стимуляцию, ингибирование) во многом зависит от вида исследованной культуры и от концентрации азота и фосфора в среде. В большинстве исследований прослежена положительная корреляция роста цианобактерий Anabaena spp., Halothece sp., Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis viridis, Phormidium sp., Leptolyngbya boryana, Lyngbya kuetzingii с концентрацией азота в среде (Saadoun et al., 2001; Polyak et al., 2013; Loza et al., 2014; Oh et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2017; Fernández-Juárez et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2020). Однако имеются сообщения как об ингибировании роста цианобактерий Nostoc carneum, так и об отсутствии изменений в росте цианобактерий Tolypothrix tenuis при повышении содержания азота в среде от 0.2 до 100 мг N${\text{O}}_{3}^{ - }$/л (от 0.045 до 22.6 мг N/л) (Loza et al., 2014). Отсутствие различий в выходе биомассы зафиксировано у Anabaena spp. при увеличении концентрации азота в среде от 0 до 50 мг/л (Rapala et al., 1997).
Избыток фосфора также считается важным фактором, способствующим интенсивности развития цианобактерий (Jankowiak et al., 2019). Рост цианобактерий Anabaena spp., Dolichospermum flos-aquae, Lyngbya kuetzingii, Microcystis aeruginosa положительно коррелировал с содержанием фосфора в среде (Rapala et al., 1997; Saadoun et al., 2001; Polyak et al., 2013; Loza et al., 2014; Park et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2018). Показано, что численность клеток цианобактерий Dolichospermum flos-aquae возрастала с 2.45 × 108 до 9.79 × × 108 кл./л в условиях дефицита фосфора (0.05 мг P/л), а при повышении концентрации фосфора до 2 мг/л достигала 2.69 × 109 кл./л (Wang et al., 2018). Повышение содержания фосфора в среде от 0.05 до 5.5 мг/л приводило к росту биомассы Anabaena spp. в >4 раз (Rapala et al., 1997). Однако, отмечено и значительное уменьшение количества клеток цианобактерий Nostoc carneum, Phormidium sp., Tolypothrix tenuis и Leptolyngbya boryana при повышении концентраций фосфора в среде культивирования (Loza et al., 2014).
В результате проведенных нами исследований показано, что биогенные элементы оказывают существенное влияние на рост нитчатых цианобактерий A. flos-aquae и P. agardhii. При увеличении содержания в среде фосфора от 0.02 до 5.4 мг/л и азота от 0.05 до 247 мг/л выявлено статистически достоверное (р < 0.05) увеличение биомассы этих видов.
Следует отметить, что при низком содержании азота в среде (0.05 мг/л) выход биомассы диазотрофных цианобактерий A. flos-aquae был в 4 раза выше, чем у Р. аgardhii. Возможно, это объясняется требовательностью N2-нефиксирющих цианобактерий к высоким концентрациям азота, поскольку известно, что доступность N является важным фактором для их роста (Корнева и др., 2014; Jankowiak et al., 2019), а также, возможно, способностью диазотрофных цианобактерий фиксировать атмосферный азот в условиях недостатка неорганического азота в среде (Wang et al., 2018). В водных экосистемах с ограниченным содержанием азота использование атмосферного N2 дает конкурентное преимущество диазотрофным цианобактериям перед N2-нефиксирующими цианобактериями (Fernández-Juárez et al., 2020).
Биогенные элементы азот и фосфор оказывают влияние не только на рост цианобактерий, но и на синтез ими метаболитов. Уровни продуктивности биомассы цианобактерий по метаболитам и их концентраций в среде в значительной степени зависят от содержания в среде биогенных элементов и от вида культуры. Повышение концентраций биогенных веществ не только способствует массовому развитию цианобактерий, приводящему к “цветению” воды, но и влияет на токсичность среды в результате этого явления. В ряде исследований изучали влияние различных факторов окружающей среды, в том числе биогенных элементов азота и фосфора, на синтез цианобактериями вторичных метаболитов и их содержание в среде. Большинство этих исследований посвящено гепатотоксинам – микроцистинам и продуцирующим их цианобактериям, поскольку микроцистины считаются наиболее заметной группой метаболитов цианобактерий из-за их высокой токсичности для живых организмов, в том числе для человека (Sivonen, 1990; Srivastava et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2020).
В клетках цианобактерий микроцистины выполняют многообразные функции. Они участвуют в адаптации цианобактерий к изменяющимся условиям освещения и наличия азота и углерода в среде, могут выполнять функции сидерофоров, участвующих в процессах QS (quorum sensing) регуляции (Omidi et al., 2018). В условиях окислительного стресса микроцистины выполняют функции антиоксидантов (Hernando et al., 2018). Предполагается, что микроцистины могут действовать как аллелопатические соединения против эукариотических микроводорослей и макрофитов (Omidi et al., 2018). Однако в ряде исследований аллелопатическая роль микроцистинов ставится под сомнение (Bajpai et al., 2013; Pinheiro et al., 2013).
В настоящем исследовании выявлена однотипность влияния азота и фосфора на суммарное содержание в среде микроцистина MC-dm-RR, образуемого токсичным штаммом цианобактерий P. agardhii, – повышение содержания биогенных элементов приводило к увеличению концентрации микроцистина в среде, что, несомненно, относится к серьезным негативным последствиям загрязнения окружающей среды биогенными элементами.
Полученные результаты согласуются с выявленной ранее положительной корреляцией между концентрацией микроцистинов и содержанием азота и/или фосфора в среде при культивировании цианобактерий родов Anabaena, Microcystis, Oscillatoria (Sivonen, 1990; Rapala et al., 1997; Polyak et al., 2013; Srivastava et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2020).
Повышение содержания микроцистинов в среде может происходить как в результате прямого воздействия биогенных элементов, при увеличении скорости продуцирования микроцистинов в каждой клетке, так и косвенного – в результате увеличения численности и биомассы вида-продуцента.
Существует гипотеза, что наибольший синтез микроцистинов происходит в условиях, благоприятных для роста цианобактерий, т.е. существует прямая корреляция между продуктивностью клеток цианобактерий по микроцистинам и их биомассой (Sivonen, Jones, 1999). Эта гипотеза согласуется с данными о параллельном с ростом накоплении микроцистинов. Увеличение продукции микроцистинов при стимуляции роста различных штаммов цианобактерий Microcystis aeruginosa, Oscillatoria agardhii выявлено при повышенных концентрациях азота (Sivonen, 1990; Polyak et al., 2013; Srivastava et al., 2016). Положительная корреляция между содержанием фосфора в среде и продуктивностью биомассы по микроцистинам зафиксирована у цианобактерий Anabaena sp. и Oscillatoria agardhii (Sivonen, 1990; Rapala et al., 1997). Однако в литературе представлены результаты исследований, не согласующиеся с данной гипотезой. Так, наиболее высокий уровень микроцистинов, синтезируемых двумя токсичными штаммами цианобактерий рода Anabaena, зафиксирован при их культивировании в безазотистой среде (Rapala et al., 1997). При повышении концентраций фосфора в среде выявлено как отсутствие изменений в продуктивности клеток Microcystis aeruginosa по микроцистинам (Polyak et al., 2013), так и ее снижение (Srivastava et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2020). Кроме того, показано, что влияние биогенных элементов на продуктивность цианобактерий по микроцистинам в значительной степени зависит от структуры микроцистина. При увеличении содержания азота в среде продукция деметилированных микроцистинов [D-Asp3]MCYST-LR и [D-Asp3]MCYST-RR клетками Anabaena strain 90 возрастала, однако синтез метилированных микроцистинов MCYST-LR и MCYST-RR снижался (Rapala et al., 1997).
В настоящем исследовании не выявлены статистически значимые изменения в удельной продуктивности биомассы P. agardhii по MC-dm-RR (мг МС/г с. б.) при стимуляции роста цианобактерии с повышением концентраций азота (от 0.4 до 247 мг/л) и фосфора (от 0.2 до 5.4 мг/л). Полученные результаты позволяют высказать предположение о косвенном влиянии биогенных элементов азота и фосфора на увеличение содержания микроцистинов в среде, связанное с повышением биомассы P. agardhii.
Важнейшую роль в основных метаболических и энергетических процессах клеток водорослей и цианобактерий играют углеводы. Значительная часть углеводов представлена экзогенными водорастворимыми полисахаридами слизей, а также простыми углеводами, выделяемыми клетками в среду прижизненно и постлетально (Сиренко, Козицкая, 1988).
ЭПС выполняют множественные функции в жизненном цикле цианобактерий, в том числе осуществляют защиту клеток от стрессов различной природы, к числу которых относится и дефицит биогенных элементов (Shalaby, Dubey, 2018).
Изменения содержания биогенных элементов в среде могут вызывать значительные штамм-зависимые изменения в синтезе ЭПС у цианобактерий. Так, в условиях дефицита фосфора у цианобактерий Cyanothece 16 СОМ 2 возрастал уровень экскретируемых ЭПС, у Phormidium J-1 и Cyanospira capsulata значительных эффектов не наблюдали, у Anabaena cylindrica выход ЭПС снижался. Штамм-специфические ответы цианобактерий наблюдали и при снижении концентраций азота. В исследовании, проведенном с 15 штаммами цианобактерий рода Cyanothece, при дефиците азота только у 10 штаммов зафиксировано увеличение количества экзополисахаридов (Rossi, De Philippis, 2016). Уменьшение содержания водорастворимых ЭПС в среде с повышенной концентрацией азота и фосфора ранее было выявлено при культивировании Microcystis aeruginosa (Polyak et al., 2013).
В настоящем исследовании показано, что повышение концентраций и азота, и фосфора вызывало снижение концентраций водорастворимых ЭПС в среде культивирования и удельной продуктивности биомассы цианобактерий A. flos-aquae и P. agardhii по ЭПС.
Увеличение содержания ЭПС при низких концентрациях азота может быть связано с повышением соотношения C : N, поскольку фиксируемый в результате фотосинтетических реакций в этих условиях углерод, в первую очередь, используется клетками для синтеза ЭПС (Rossi, De Philippis, 2016; Shalaby, Dubey, 2018). Снижение продукции ЭПС цианобактериями при их росте в условиях повышенных концентраций нитратного азота также может указывать на то, что гены, участвующие во внеклеточном синтезе полисахаридов, могут находиться под контролем азота (Tiwari et al., 2015). Ранее отмечали, что стимуляция образования ЭПС при дефиците фосфора может быть связана с повышенной экспрессией ответственных за синтез ЭПС ферментов на уровне генов (Zhan et al., 1991).
Одно из последствий массового развития цианобактерий – возникновение в воде посторонних привкусов и запахов, которые значительно снижают качество и, как следствие, потребительские свойства воды. В низких концентрациях одоранты, содержащиеся в природных водах, нетоксичны, однако имеют крайне низкий порог обнаружения органами чувств – между 5 и 10 нг/л (Jakubowska, Szeląg-Wasielewska, 2015). К продуцентам этой группы веществ относятся грибы, водоросли и бактерии, в том числе цианобактерии (Lee et al., 2017; Churro et al., 2020). В природных поверхностных водах основной источник одорантов – цианобактерии (Churro et al., 2020), они образуют широкий ряд соединений с неприятным вкусом и запахом – геосмин, 2-метилизоборнеол, β-циклоцитрал, β-ионон, диметилированные моно-, ди-, трисульфиды, производные полиненасыщенных жирных кислот и др. (Lee et al., 2017).
Анализ состава одорирующих веществ, синтезируемых P. agardhii CALU 1113, показал наличие в среде культивирования бензотиазола и геосмина – соединений, обладающих сильным неприятным запахом. Способность к синтезу бензотиазола ранее выявлена у цианобактерии Oscillatoria perornata (Tellez et al., 2001).
Геосмин считается одним из наиболее изученных одорантов, образуемых цианобактериями. К продуцентам этого соединения относятся различные штаммы цианобактерий, относящиеся к родам Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Lyngbya, Nostoc, Oscillatoria, Planktothrix, Phormidium и др. (Lee et al., 2017). Синтез и выделение геосмина в среду изменяется под действием различных стрессорных факторов, в том числе концентраций биогенных элементов. Так, повышение концентрации азота приводило к увеличению биомассы цианобактерий рода Anabaena, концентрации геосмина в среде и продуктивности биомассы по геосмину (Saadoun et al., 2001; Oh et al., 2017). Однако, при изучении влияния азота (0–247 мг N/л) на рост и синтез геосмина цианобактерий Lyngbya kuetzingii UTEX 1547 показано, что максимальная продуктивность по геосмину зафиксирована в условиях дефицита азота (0–24.7 мг N/л) при минимальном росте цианобактерии (Zhang et al., 2017).
Содержание фосфора в среде также влияло на синтез геосмина цианобактериями. При культивировании продуцирующей геосмин цианобактерии Anabaena sp., выделенной из поверхностных вод оз. Ogletree (США), в среде, содержащей фосфор в концентрациях 118–941 мкг/л, выявлена положительная корреляция между концентрацией фосфора, биомассой и содержанием геосмина. При повышении концентрации фосфора до 941 мкг/л концентрация геосмина возрастала до 6.2 мкг/л при увеличении продуктивности биомассы цианобактерии по геосмину до 40 мкг/мг с. б. (Saadoun et al., 2001). Однако имеются и противоположные данные. Так, увеличение содержания фосфора вызывало снижение как концентрации геосмина в среде, так и его продукции клетками Lyngbya kuetzingii при стимуляции роста цианобактерии (Zhang et al., 2017).
Данные по влиянию биогенных элементов азота и фосфора на синтез бензотиазола цианобактериями в доступной литературе отсутствуют. Нами выявлено, что пятикратное повышение азотно-фосфорной нагрузки в среде стимулировало рост цианобактерии P. agardhii и приводило к увеличению концентрации бензотиазола, образуемого P. agardhii, и удельной продуктивности биомассы цианобактерии по бензотиазолу (мкг/г с. б.). Повышение азотно-фосфорной нагрузки не приводило к статистически значимому изменению концентрации геосмина в среде, однако удельная продуктивность биомассы P. agardhii по геосмину снижалась при одновременном повышении концентраций азота и фосфора (в 5 раз) и их соотношения N : P (в 10 раз). Подавление синтеза геосмина при повышении отношения азота к фосфору ранее отмечено другими исследователями (Lee et al., 2017).
Выводы. Биогенные элементы азот и фосфор оказывали существенное влияние на рост нитчатых цианобактерий Aphanizomenon flos-aquae и Planktothrix agardhii и содержание в среде их вторичных метаболитов. Биогенные элементы стимулировали рост цианобактерий, сопровождавшийся снижением концентраций водорастворимых ЭПС в среде. Рост цианобактерий P. agardhii под влиянием азота и фосфора вызывал изменения содержания микроцистинов и одорирующих веществ в среде. Таким образом, антропогенное загрязнение водоемов азотом и фосфором стимулирует рост цианобактерий и увеличение содержания токсинов, одорирующих веществ, что может вызвать сукцессию цианобактерий, способствовать нарушению стабильности водных экосистем и привести к ухудшению качества воды.
Список литературы
Зайцева Т.Б., Медведева Н.Г. 2019. Молекулярные механизмы стрессового ответа цианобактерии Planktothrix agardhii на воздействие 4-трет-октилфенола // Микробиология. Т. 88. № 4. С. 417. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026365619040141
Зайцева Т.Б., Мильман Б.Л., Луговкина Н.В. и др. 2015. Влияние октил- и нонилфенолов на рост, фотосинтетическую активность и токсинообразование цианобактерии Planktothrix agardhii // Гидробиол. журн. Т. 51. № 4. С. 40. https://doi.org/10.1615/HydrobJ.v51.i6.40
Корнева Л.Г., Глущенко Г.Ю. 2020. Состав и сезонная сукцессия фитопланктона Таганрогского залива Азовского моря и нижнего течения р. Дон в условиях изменяющегося климата // Биология внутр. вод. № 1. С. 18. https://doi.org/10.31857/S032096522001009X
Корнева Л.Г., Соловьева В.В., Жаковская З.А. и др. 2014. Фитопланктон и содержание цианотоксинов в Рыбинском, Горьковском и Чебоксарском водохранилищах в период аномально жаркого лета 2010 г. // Вода: химия и экология. № 8. С. 24.
Минеева Н.М. 2021. Оценка связи содержания хлорофилла и биогенных элементов в водохранилищах Верхней Волги // Вестник Томского государственного университета. Биология. № 53. С. 151. https://doi.org/10.17223/19988591/53/8).
Сиренко Л.А., Козицкая В.Н. 1988. Биологически активные вещества водорослей и качество воды. Киев: Наукова думка.
Bajpai R., Sharma N.K., Rai F.R. 2013. Physiological evidence indicates microcystin-LR to be a part of quantitative chemical defense system // J. Appl. Phycol. V. 25(5). P. 1575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-9981-y
Chaffin J.D., Davis T.W., Smith D.J. et al. 2018. Interactions between nitrogen form, loading rate, and light intensity on Microcystis and Planktothrix growth and microcystin production // Harmful Algae. V. 73. P. 84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2018.02.001
Churro C., Semedo-Aguiar A.P., Silva A.D. et al. 2020. A novel cyanobacterial geosmin producer, revising GeoA distribution and dispersion patterns in Bacteria // Sci. Rep. V. 10. P. 8679. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64774-y
Facey J.A., Apte S.C., Simon M. et al. 2019. A Review of the Effect of Trace Metals on Freshwater Cyanobacterial Growth and Toxin Production // Toxins. V. 11. № 643. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110643
Fernández-Juárez V., Bennasar-Figueras A., Sureda-Gomila A. et al. 2020. Differential Effects of Varying Concentrations of Phosphorus, Iron, and Nitrogen in N2-Fixing Cyanobacteria // Front. Microbiol. V. 11. № 541 558. P. 19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.541558
Gobler C.J. 2020. Climate Change and Harmful Algal Blooms: Insights and perspective // Harmful Algae. V. 91. № 101731. P. 4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101731
Herbert D., Phipps P.J., Stange R.E. 1971. Chapter III Chemical Analysis of Microbial Cells // Methods in Microbiology. V. 5. Part B. P. 209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70641-X
Hernando M., Minaglia M.C.C., Malanga G. et al. 2018. Physiological responses and toxin production of Microcystis aeruginosa in short-term exposure to solar UV radiation // Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. V. 17. P. 69. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PP00265C
Jakubowska N., Szeląg-Wasielewska E. 2015. Toxic Picoplanktonic Cyanobacteria – Review // Marine Drugs. V. 13(3). P. 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13031497
Jankowiak J., Hattenrath-Lehmann T., Kramer B.J. et al. 2019. Deciphering the effects of nitrogen, phosphprous, and temperature on cyanobacterial bloom intensification, diversity, and toxicity in western Lake Erie // Limnol., Oceanogr. V. 9999. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11120
Lee J., Kumar Rai P.K., Jeon Y.J. et al. 2017. The role of algae and cyanobacteria in the production and release of odorants in water // Environ. Pollut. V. 227. P. 252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.058
Lee J.H., Lee K.L., Lee J.Y, Kim H.S. 2020. Effect of nitrate, ammonium and phosphate on the growth and microcystin production of Korean Microcystis species // J. Environ. Biol. V. 41. P. 812. https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/41/4/MRN-1294
Loza V., Perona E., Mateo P. 2014. Specific responses to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment in cyanobacteria: Factors influencing changes in species dominance along eutrophic gradients // Water Res. V. 48. P. 622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.014
Oh H., Lee C.S., Srivastava A. et al. 2017. Effects of Environmental Factors on Cyanobacterial Production of Odorous Compounds: Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol // J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. V. 27 (7). P. 1316. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1702.02069
Omidi A., Esterhuizen-Londt M., Pflugmacher S. 2018. Still challenging: the ecological function of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin – What we know so far // Toxin Rev. V. 37(2). P. 87. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2017.1326059
Park H.-J., Park M.-H., Sim Y.-B. et al. 2017. Geosmin Production Potential of a Cyanobacterium, Anabaena circinalis Isolated from Lake Paldang, Korea // Korean J. Ecol. Environ. V. 50(4). P. 363. https://doi.org/10.11614/KSL.2017.50.4.363
Pinheiro C., Azevedo J., Campos A. et al. 2013. Absence of negative allelopathic effects of cylindrospermopsin and microcystin-LR on selected marine and freshwater phytoplankton species // Hydrobiologia. V. 705 (1). P. 27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1372-x
Polyak Yu., Zaytseva T., Medvedeva N. 2013. Response of Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginos to Environmental Pollution // Water, Air, Soil Pollut. V. 224. № 1494. P. 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1494-4
Prasad R., Prasad S. 2019. Algal Blooms and Phosphate Eutrophication of Inland Water Ecosystems with Special Reference to India // Int. J. Plant Environ. V. 5. № 1. P. 1. https://doi.org/10.18811/ijpen.v5i01.1
Rapala J., Sivonen K., Lyra C., Niemelä S.I. 1997. Variation of Microcystins, Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins, in Anabaena spp. as a Function of Growth Stimuli // Appl. Environ. Microbiol. V. 63. № 6. P. 2206. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.63.6.2206-2212.1997
Rippka R., Deruelles J., Waterbury J.B. et al. 1979. Genetic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria // J. Gen. Microbiol. V. 111. P. 1.
Rossi F., De Philippis R. 2016. Exocellular Polysaccharides in Microalgae and Cyanobacteria: Chemical Features, Role and Enzymes and Genes Involved in Their Biosynthesis // The Physiology of Microalgae. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. P. 565. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24945-2_21
Saadoun I.M., Schrader K.K., Blevins W.T. 2001. Environmental and nutritional factors affecting geosmin synthesis by Anabaena sp. // Water Res. V. 35. № 5. P. 1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00381-X
Shalaby E.A., Dubey N.K. 2018. Polysaccharides from cyanobacteria: respons to biotic and abiotic stress and their antiviral activity // Indian J. Marin. Sci. V. 47. № 1. P. 21.
Shaw G., Moore D., Garnett C. 2009. Eutrophication and algal blooms // Encyclopedia of life support system. V. II. Environmental and ecological chemistry. Oxford: Eolss Publishing. P. 298.
Sivonen K. 1990. Effects of Light, Temperature, Nitrate, Orthophosphate, and Bacteria on Growth of and Hepatotoxin Production by Oscillatoria agardhii Strains // Appl. Environ. Microbiol. V. 56. № 9. P. 2658.
Sivonen K., Jones G. 1999. Cyanobacterial toxins // Toxic cyanobacteria in water – a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. London: E&FN Spon. P. 41.
Srivastava A., Ko S.-R., Ahn C.-Y. et al. 2016. Microcystin Biosynthesis and mcyA Expression in Geographically Distinct Microcystis Strains under Different Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Boron Regimes // BioMed Research International. V. 2016. Article ID 5985987. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5985987
Tellez M.R., Schrader K.K., Kobaisy M. 2001. Volatile Components of the Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria perornata (Skuja) // J. Agric. Food Chem. V. 49. № 12. P. 5989. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010722p
Tiwari O.N., Khangembam R., Shamjetshabam M. et al. 2015. Characterization and Optimization of Bioflocculant Exopolysaccharide Production by Cyanobacteria Nostoc sp. BTA97 and Anabaena sp. BTA990 in Culture Conditions // Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. V. 176. № 7. P. 1950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1691-2
Wang S., Xiao J., Wan L. et al. 2018. Mutual dependence of nitrogen and phosphorus as key nutrient elements: one facilitates Dolichospermum flos-aquae to overcome the limitations of the other // Environ. Sci. Technol. V. 52. № 10. P. 5653. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b04992
Zaytseva T.B., Medvedeva N.G., Mamontova V.N. 2015. Peculiarities of the Effect of Octyl- and Nonylphenols on the Growth and Development of Microalgae // Inland Water Biology. V. 8. № 4. P. 406. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082915040161
Zhan H.J., Lee C.C., Leigh J.A. 1991. Induction of the second exopolysaccharide (EPSb) in Rhizobium meliloti SU47 by low phosphate concentrations // Journal of Bacteriology. V. 173. № 22. P. 7391. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.22.7391-7394.1991
Zhang T., Li L., Zheng L., Song L. 2017. Effects of nutritional factors on the geosmin production of Lyngbya kuetzingii UTEX 1547 (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria) // Phycologia. V. 56. № 2. P. 221. https://doi.org/10.2216/16-98.1
Дополнительные материалы отсутствуют.
Инструменты
Биология внутренних вод


